Microwave Digestion of Pharmaceutical Samples for USP Method
Application Notebook
Pharmaceutical samples spiked with several heavy metals were prepared for ICP-MS analysis using microwave digestion following the protocols in proposed USP chapters <232> and <233>. The results of the spike recovery study are discussed.
Pharmaceutical samples spiked with several heavy metals were prepared for ICP-MS analysis using microwave digestion following the protocols in proposed USP chapters <232> and <233>. The results of the spike recovery study are discussed.
The current United States Pharmacopeia (USP) chapter <231> Heavy Metals will be replaced in 2014 by USP chapter <232> Elemental Impurities – Limits and USP chapter <233> Elemental Impurities – Procedures. These new methods will provide a more accurate analysis by identifying specific elements of interest and will enable the detection of additional elements, such as chromium and catalyst metals, which may be introduced during the manufacturing process. Additionally, the new methods require closed vessel microwave digestion for samples that cannot be successfully dissolved in an aqueous solution or an organic solvent, preventing the loss of volatile analytes from the open flask heating technique used in Method <231>. The digested materials can then be analyzed by ICP-OES or ICP-MS, depending upon the detection limits required.
CEM's MARS 6 and Discover SP-D microwave sample preparation systems were used to prepare several finished pharmaceutical products. The MARS system has the ability to prepare up to 40 samples simultaneously, while the Discover SP-D with an autosampler can prepare a sample every 10 min completely unattended. The accuracy and precision of the spiked recovery results for each system are discussed.
Experimental
In our study, pharmaceutical finished products including a tablet with the active ingredient acetylsalicylic acid, a tablet with the active ingredient loratadine, and liquid gel capsule with the active ingredient diphenhydramine HCl were digested and analyzed with an ICP-MS. A tablet or liquid gel capsule was added to a MARS EasyPrep Plus vessel or a Discover SP-D 35-mL vessel along with 9 mL of concentrated nitric acid and 1 mL of spiked DI water containing 50 ppb of arsenic, mercury, and cadmium. The liquid gel capsule also required hydrogen peroxide in order to fully oxidize the sample – 1 mL in the EasyPrep Plus vessel and 0.5 mL in the 35-mL vessel. Each of the samples and blanks was prepared in triplicate using the digestion parameters shown in Table I.
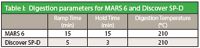
Table I: Digestion parameters for MARS 6 and Discover SP-D
The digested samples were then diluted with DI water to a volume of 50 mL and analyzed with an ICP-MS.
Results
The accuracy of proposed USP Method <233> is 70–150% with a relative standard deviation of not more than 20%. The results of the digestions performed with the MARS 6 and Discover SP-D are shown in Table II. The volatile elements, arsenic and mercury, achieved percent recoveries of 101–136% and an RSD of less than 15.1%. The non-volatile element, cadmium, showed percent recoveries from 94–111% and an RSD of less than 9.1%. The percent recovery and RSD for each element is within the proposed requirements of USP Method <233>.

Table II: Recovery results of 50 ppb spike of As, Hg, Cd in finished pharmaceutical products
Conclusions
The CEM MARS 6 and the Discover SP-D provide a fast, accurate means to prepare pharmaceutical ingredients and finished products to meet the requirements of the upcoming USP Method <233>.
CEM Corporation
P.O. Box 200, Matthews, NC 28106
tel. (800) 726-3331
Website: www.cem.com/usp

Single Cell and Microplastic Analysis by ICP-MS with Automated Micro-Flow Sample Introduction
April 25th 2024Single cell ICP-MS (scICP-MS) is increasingly seen as a powerful and fast tool for the measurement of elements in individual cells, mainly due to the high sensitivity and selectivity of ICP-MS. Analysis is performed in the same way as single nanoparticle (spICP-MS) analysis, which has become a well-established technique for the analysis of nanoparticles and particles.
Hot News on Agilent LDIR, New Developments, and Future Perspective
April 25th 2024Watch this video featuring Darren Robey and Dr. Wesam Alwan from Agilent Technologies to gain insights into the future trends shaping microplastics research and the challenges of their characterization. Discover the essential components necessary for accurate microplastics analysis and learn how the Agilent 8700 LDIR system addresses these challenges. Offering rapid and precise analysis capabilities, along with easy sample preparation methods that minimize contamination, the Agilent 8700 LDIR system is at the forefront of advancing microplastics research.
The World of Microplastics Up to Date – an Overview
April 23rd 2024Watch this 20-minute educational video by Andreas Kerstan, Agilent Product Specialist in molecular spectroscopy, to gain a comprehensive update on the microplastics landscape and the environmental concerns related to them. Discover the current challenges in microplastics characterization and how Agilent innovative solutions and techniques, including FTIR, LDIR, GC/MS, and ICP-MS, are addressing these issues head-on.