
Spectroscopy
Click the title above to open the Spectroscopy June regular issue, Volume 34, Issue 6, in an interactive PDF format.

Spectroscopy
Click the title above to open the Spectroscopy June regular issue, Volume 34, Issue 6, in an interactive PDF format.

Spectroscopy
The spectral behavior of water is studied using Raman with an NIR spectrograph and dual wavelength lasers for measurements of both the fingerprint and the OH stretching regions. Raman spectra are recorded between 5 ⁰C and 80 ⁰C, and treated with both band-fitting and the 2D-COS algorithm revealing improved insights into the spectral behavior of water.

Spectroscopy
A newly discovered effect can introduce large errors in many multivariate spectroscopic calibration results. The CLS algorithm can be used to explain this effect. Having found this new effect that can introduce large errors in calibration results, an investigation of the effects of this phenomenon to calibrations using principal component regression (PCR) and partial least squares (PLS) is examined.
Spectroscopy
The platinum-group metals platinum, palladium, and rhodium are essential and valuable elements in catalytic converters, and thus must be recycled. Handheld X-ray fluorescence (XRF) can be extremely beneficial for analysis of these metals in finely ground materials extracted from used catalytic converters.
Spectroscopy
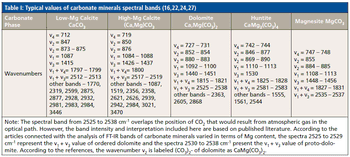
In this study, FT-IR spectroscopy was used for identification of carbonate minerals in limestone with variable contents of magnesium. Associated spectral bands were identified and assigned. Results of studies of Triassic limestone samples taken from the area of the Polish part of the Germanic Basin using FT-IR are presented. The results of research show that substitution of Ca2+ by Mg2+ in the carbonate phase lattices leads to a continuous wavenumber increase in the assigned band locations.