Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)
Latest News

Latest Videos
More News

A new study highlights terahertz (THz) metamaterials as a promising non-invasive, highly sensitive technology for improving food safety testing in agriculture.
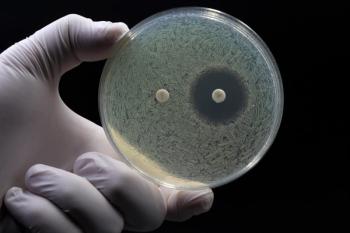
A research team from Putian University has developed a dual surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) approach to reveal detailed molecular changes in E. coli exposed to different antibiotics.


A new review published in Trends in Food Science & Technology highlights how advanced spectroscopy, multidimensional chromatography, artificial intelligence (AI), and novel sensors are improving food safety by enhancing sensitivity, speed, and sustainability in contaminant detection.

Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University are harnessing artificial intelligence to elevate surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) for highly sensitive, multiplexed biomedical analysis, enabling faster diagnostics, imaging, and personalized treatments.

A multinational research team explores Raman spectroscopy's expanding role in medicine and microbiology, revealing its powerful potential in diagnostics, drug analysis, and microbial classification.

In this tutorial article, Yukihiro Ozaki explores the recent advancements and broadening applications of tip-enhanced Raman scattering (TERS), a cutting-edge technique that integrates scanning probe microscopy (SPM) with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS).

Researchers use EC-SERS to reveal the first detailed structural study of hU-II peptide in aqueous solution, paving the way for new drug development.

A new review in TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry by Alfred Chin Yen Tay and Liang Wang highlights how machine learning (ML) is transforming surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) into a powerful, clinically viable tool for rapid and accurate medical diagnostics.

Researchers at Harbin Medical University recently developed a SERS-based diagnostic platform that uses DNA-driven “molecular hooks” and AI analysis to enable real-time detection of cardiovascular drugs in blood while eliminating interference from larger biomolecules.
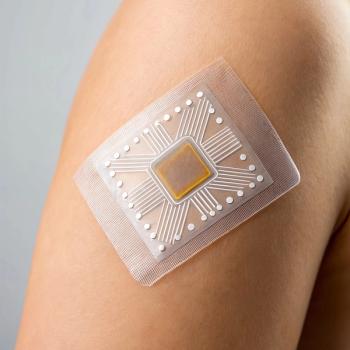
A new comprehensive review explores how wearable plasmonic sensors using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) are changing the landscape for non-invasive health monitoring. By combining nanotechnology, AI, and real-time spectroscopy analysis to detect critical biomarkers in human sweat, this integration of nanomaterials, flexible electronics, and AI is changing how we monitor health and disease in real-time.

A new deep learning-enhanced spectroscopic platform—SERSome—developed by researchers in China and Finland, identifies medicinal and edible homologs (MEHs) with 98% accuracy. This innovation could revolutionize safety and quality control in the growing MEH market.
Researchers are using AI-enabled Raman spectroscopy to enhance the development, administration, and response prediction of cancer immunotherapies. This innovative, label-free method provides detailed insights into tumor-immune microenvironments, aiming to optimize personalized immunotherapy and other treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes.

A recent study explored using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to detect β-agonists.
Scientists from China and Finland have developed an advanced method for detecting cardiovascular drugs in blood using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) and artificial intelligence (AI). This innovative approach, which employs "molecular hooks" to selectively capture drug molecules, enables rapid and precise analysis, offering a potential advance for real-time clinical diagnostics.

A recent study highlights how anisotropic nanostructures can improve surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) analysis of cultural artifacts, including artwork.

Top articles published this week include a Q&A interview that discussed using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to investigate microplastics released from chewing gum and an article about Agilent’s Solutions Innovation Research Award (SIRA) winners.
A combination of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) and machine learning on microfluidic chips has achieved an impressive 98.6% accuracy in classifying leukemia cell subtypes, offering a fast, highly sensitive tool for clinical diagnosis.
Researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed an optical detection strategy for circulating tumor cells (CTCs), combining machine learning (ML) and dual-modal surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). This approach offers high sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency, potentially advancing early cancer diagnosis.

A recent study used surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) combined with chemometrics to assess polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water.

Researchers from the University of Liege have demonstrated the potential of surface-enhanced transmission Raman spectroscopy (SETRS) for detecting impurities in pharmaceuticals. The study highlights SETRS’s superior sensitivity, precision, and efficiency in quantifying toxic impurities like 4-aminophenol (4-AP), offering a promising alternative to traditional methods.

Researchers have developed a rapid, reagent-free method to estimate the saponification value (SV) of edible oils using handheld Raman spectroscopy. This innovative approach simplifies oil quality testing, cutting time and costs while enhancing accuracy and portability.
Researchers from Stanford University have combined surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) with machine learning (ML) to enable rapid, precise single-cell analysis, offering potentially transformative applications in diagnostics and personalized medicine.
Researchers have developed a highly sensitive method using Raman and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) with gold nanoparticles to accurately quantify intracellular cholesterol.

Researchers at Henan Agricultural University have developed a multi-channel magnetic flow device combined with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) for the rapid and precise isolation, identification, and quantification of lactic acid bacteria and yeast, revolutionizing quality control in fermented food production.







