
A new article reviews methods for determining trace elements in germanium and germanium dioxide, highlighting the advantages and limitations of methods with and without matrix separation procedures.

An Examination of Drinking Water in Pakistan: Using Atomic Absorption and Emission Spectroscopy to Detect Heavy Metals

A new article reviews methods for determining trace elements in germanium and germanium dioxide, highlighting the advantages and limitations of methods with and without matrix separation procedures.

Detecting inorganic chromium in water requires a more efficient approach than the current methods. In a recent study, researchers proposed a methodology for detecting inorganic chromium (Cr) in environmental water samples using direct immersion dual-drop microextraction (DIDDME) followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry detection.

Studying the experimental absorption spectra of different proportions co-crystallized mixtures and 1:1 physical mixture of L-thr and L-allo-thr, it was found that the characteristic peaks of the physical mixture include the characteristic peaks of the two diastereomers in the THz band, while amino acid co-crystallized mixtures formed their own characteristic peaks depending on the proportion.
The physics and chemistry of the phenomenon have been well known for many years, and this knowledge can tell us how self-absorption can be not only “corrected,” but also tuned to our advantage in analytical applications of LIBS.

The winner of Spectroscopy's inaugural Emerging Leader in Atomic Spectroscopy Award is highlighted.
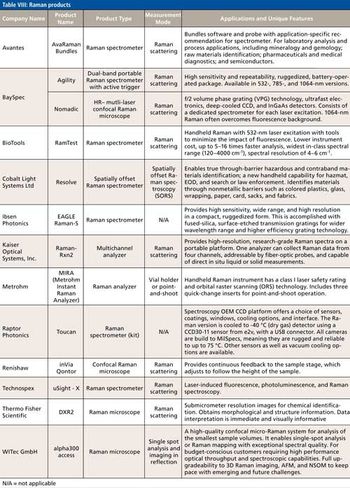
Our annual review of products introduced at Pittcon or during the previous year, broken down by the following categories: accessories, atomic spectroscopy, components, imaging, mass spectrometry, mid-IR, NIR, NMR, Raman, software, UV-vis, and X-ray.

In honor of Spectroscopy's celebration of 30 years covering the latest developments in materials analysis, we asked a panel of experts to assess the current state of the art of inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and to try to predict how the technology will develop in the future.
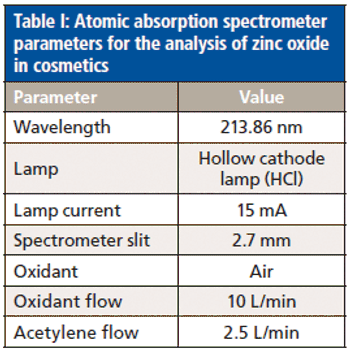
Zinc oxide levels in cosmetic formulations are commonly analyzed by atomic absorption (AA) spectroscopy using the fusion method for sample digestion, a labor-intensive and time-consuming process that causes lengthy delays in product manufacturing.
A look at ICP–MS, ICP–OES, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in the areas of research and development, marketing, application, and use of these techniques.

While viewed as a mature technology, atomic absorption is still an attractive choice, particularly in the area of food safety.