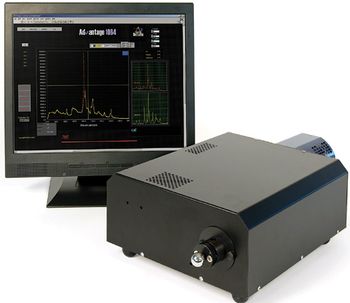
Spectroscopy
In part I of this series, columnist David Ball laid the groundwork for why the scientific understanding of nature in the late 19th century was found wanting: it could not explain a variety of phenomena that scientists were examining. (One of these phenomena was spectroscopy itself!) In this installment, he reviews the paradigm shifts in science that preceded the development of the currently accepted theories of the nature of matter. It all starts with the nature of light.