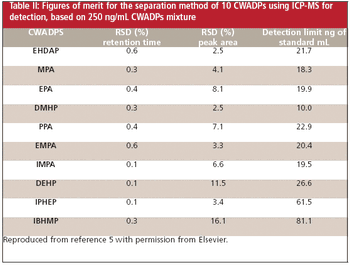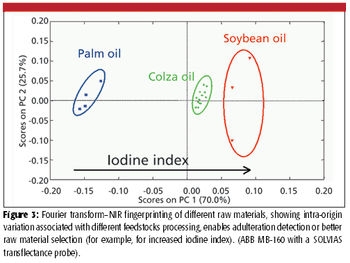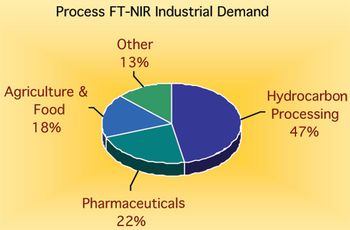
Spectroscopy
Fourier transform–near infrared spectroscopy, generally referred to as FT-NIR, is a rapidly growing process analytical technique. The technique has a number of inherent advantages over other spectroscopy techniques for online monitoring, and is now used widely across a number of contrasting industries.