
Disinfection by-products (DBP) are an ever-present nuisance in the efforts to purify drinking water, wastewater, and municipal waters from various sources.

Disinfection by-products (DBP) are an ever-present nuisance in the efforts to purify drinking water, wastewater, and municipal waters from various sources.
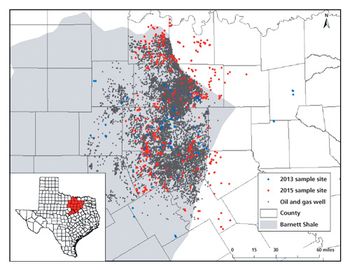
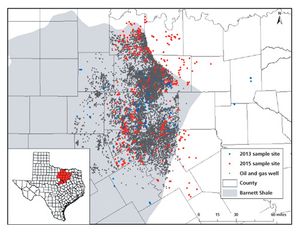
A mix of analytical methods is required to understand the impact, if any, that UOG activity is having on groundwater.
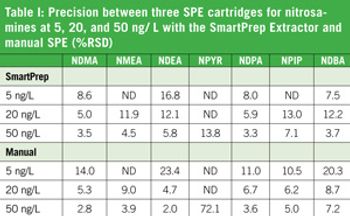
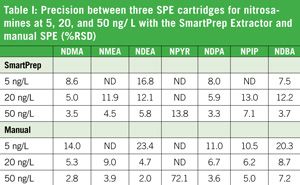
Disinfection by-products (DBP) are an ever-present nuisance in the efforts to purify drinking water, wastewater, and municipal waters from various sources. An emerging class of DBP compounds with health effects is nitrosamines which result from chloramination or chlorination if the water is nitrogen-rich. Five of these nitrosamines have been listed on the US EPA’s new Contaminant Candidate List (CCL-3). Of the nitrosamines, the most common and problematic is N-nitrosdimethylamine (NDMA). The maximum admissible levels set by the US EPA are 7 ng/L for NDMA and 2 ng/L for N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA).
Published: July 1st 2015 | Updated:
Published: October 2nd 2015 | Updated:

Published: May 1st 2016 | Updated: