Spectroscopy
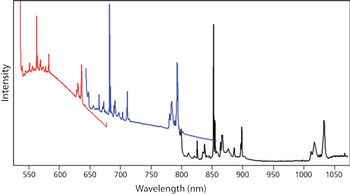
Were it not for the problem of photoluminescence, only one laser excitation wavelength would be necessary to perform Raman spectroscopy. Here, we examine the problem of photoluminescence from the material being analyzed and the substrate on which it is supported. Selecting an excitation wavelength that does not generate photoluminescence reduces the noise level and yields a Raman spectrum with a superior signal-to-noise ratio. Furthermore, we discuss the phenomenon of resonance Raman spectroscopy and the effect that laser excitation wavelength has on the Raman spectrum.