Survey of Key Descriptive References for Chemometric Methods Used for Spectroscopy: Part II
This article is the second in a series that lists four key explanatory or tutorial references for each of the 29 chemometric methods previously described. The references selected are particularly helpful to explain the use of each method for spectroscopic data. Also included are common computer software platforms used for chemometrics.
In the August 2020 and June 2021 “Chemometrics in Spectroscopy” columns, we described 29 key common chemometric methods used by spectroscopists, and selected corresponding literature reference numbers using a set of tables. The first article introduced the chemometric methods. The second article introduced a two-part series with expanded references, included the following: Part I includes Tables I and II with references, and Part II includes Tables III through V with corresponding selected literature references. The five tables mentioned and the chemometric methods they cover are listed below:
- Table I: Signal preprocessing comparison table (alphabetical order)
- Table II: Component analysis com- parison table (alphabetical order)
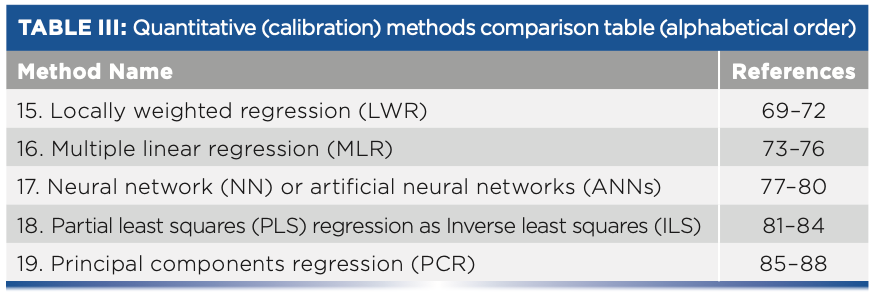
- Table III: Quantitative (calibration) methods comparison table (alphabetical order)
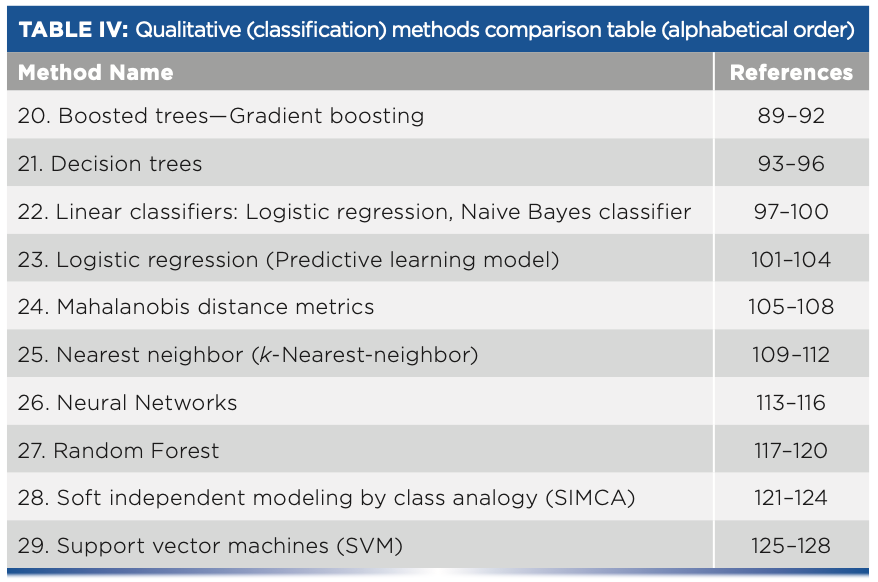
- Table IV: Qualitative (classification) methods comparison table (alphabetical order)
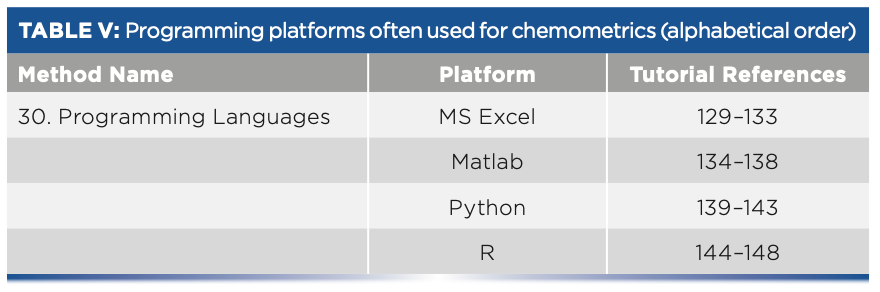
- Table V: Programming platforms often used for chemometrics (alphabetical order).
Description of References
In this article, a set of four references are given in Tables III and IV for each of 15 chemometric methods (numbers 15–29), and five references are given for each computer software platform introduced in Table V (method number 30). This article lists the corresponding references from 69 to 148. The method numbers and references for the two-part series are sequential from methods 1–30, which correspond to references 1–148, respectively. Thus, the two-part reference article series can be viewed as a single body of work.
Introduction to Tables
For Part II of the series, Table III shows the variety of references for quantitative (calibration) methods used to take raw or preprocessed data and compute predictive calibration models for quantitative determination of physical or chemical parameters in a data set. Table IV demonstrates the references for the qualitative (classification) methods used to take raw or preprocessed data and compute predictive calibration models for classification of different groups or types of samples or of physical or chemical parameters in a data set. Table V includes references for using the most common programming languages or platforms for general data interpretation using chemometrics or other statistical analysis methods.
References
Quantitative (Calibration) Methods
15. Locally Weighted Regression
69. T. Næs and T. Isaksson, Appl. Spectrosc. 46(1), 34–43 (1992).
70. B. Igne, J.B. Reeves, G. McCarty, W.D. Hively, E. Lund, and C.R. Hurburgh, J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 18(3), 167–176 (2010).
71. T. Naes, T. Isaksson, and B. Kowalski, Anal. Chem. 62(7), 664–673 (1990).
72. H. Nakagawa, T. Tajima, M. Kano, S. Kim, S. Hasebe, T. Suzuki, and H. Nakagami, Anal. Chem. 84(8), 3820–3826 (2012).
16. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR)
73. D. Broadhurst, R. Goodacre, A. Jones, J.J. Rowland, and D.B. Kell, Anal. Chim. Acta 348(1–3), 71–86 (1997).
74. M.J. Lerma-García, E.F. Simó-Alfonso, A. Bendini, and L. Cerretani, Food Chem. 124(2), 679–684 (2011).
75. A. O’Neil, R. Jee, and A. Moffat, Analyst 123(11), 2297–2302 (1998).
76. C. Schierle and M. Otto, J. Anal. Chem. 344(4–5), 190–194 (1992).
17. Neural Network (NN)
77. D. Svozil, V. Kvasnicka, and J. Pospichal, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 39(1), 43–62 (1997).
78. P. Bhandare, Y. Mendelson, R.A. Peura, G. Janatsch, J.D. Kruse-Jarres, R. Marbach, and H.M. Heise, Appl. Spectrosc. 47(8), 1214–1221 (1993).
79. R. Goodacre, E.M. Timmins, P.J. Rooney, J.J. Rowland, and D.B. Kell, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 140(2– 3), 233–239 (1996).
80. P.J. Gemperline, J.R. Long, and V.G. Gregoriou, Anal. Chem. 63(20), 2313–2323 (1991).
18. Partial Least Squares (PLS) Regression (Inverse Least Squares)
81. P. Geladi and B.R. Kowalski, Anal. Chim. Acta 185, 1–17 (1986).
82. M.P. Fuller, G.L. Ritter, and C.S. Draper, Appl. Spectrosc. 42(2), 217–227 (1988).
83. E. Vigneau, D. Bertrand, and E.M. Qannari, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 35(2), 231–238 (1996).
84. F. Lindgren, P. Geladi, and S. Wold, J. Chemom. 8(6), 377–389 (1994).
19. Principal Components Regression (PCR)
85. C.W. Chang, D.A. Laird, M.J. Mausbach, and C.R. Hurburgh, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 65(2), 480–490 (2001).
86. O. Faix and J.H. Böttcher, Holzforschung (HF) 47(1), 45–49 (1993).
87. S.K. Schreyer, M. Bidinosti, and P.D. Wentzell, Appl. Spectrosc. 56(6), 789–796 (2002).
88. P.J. Gemperline and A. Salt, J. Chemom. 3(2), 343–357 (1989).
Qualitative (Classification) Methods
20. Boosted Trees—Gradient Boosting
89. A. Natekin and A. Knoll, Neurorobot. 7, 21 (2013).
90. S. Nawar and A.M. Mouazen, Sensors 17(10), 2428 (2017).
91. D.J. Brown, K.D. Shepherd, M.G. Walsh, M.D. Mays, and T.G. Reinsch, Geoderma 132(3–4), 273–290 (2006).
92. K.D. Shepherd, C.A. Palm, C.N. Gachengo, and B. Vanlauwe, Agron. J. 95(5), 1314–1322 (2003).
21. Decision Trees
93. J.R. Quinlan, Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 27(3), 221–234 (1987).
94. A.J. Myles, R.N. Feudale, Y. Liu, N.A. Woody, and S.D. Brown, J. Chemom. 18(6), 275–285 (2004).
95. S. Kucheryavskiy, J. Anal. Test. 2(3), 274–289 (2018).
96. D. Fernandes Andrade, E.R. Pereira-Filho, and D. Amarasiriwardena, Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 56(2), 1–17 (2021).
22. Linear Classifiers: Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes Classifier
97. I. Rish, “An empirical study of the naive Bayes classifier,” in IJCAI 2001 Workshop on Empirical Methods in Artificial Intelligence 3(22), 41–46 (2001).
98. J.D. Rennie, L. Shih, J. Teevan, and D.R. Karger, “Tackling the poor assumptions of naive bayes text classifiers,” in Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03) 3, 616–623 (2003).
99. E. Tsolaki, P. Svolos, E. Kousi, E. Kapsalaki, K. Fountas, K. Theodorou, and I. Tsougos, Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 8(5), 751–761 (2013).
100. S. Sankaran and R. Ehsani, Trans. ASABE 55(1), 313–320 (2012).
23. Logistic Regression (Predictive Learning Model)
101. J. Merlo, B. Chaix, H. Ohlsson, A. Beckman, K. Johnell, P. Hjerpe, L. Råstam, and K. Larsen, J. Epidemiol. Community Health 60(4), 290–297 (2006).
102. Y. So, “A tutorial on logistic regression,” SAS White Papers (1995). https://support.sas.com/rnd/app/stat/papers/logistic.pdf
103. T.C.B. Schut, P.J. Caspers, G.J. Puppels, A. Nijssen, F. Heule, M.H. Neumann, and D.P. Hayes, J. Invest. Dermatol. 119(1), 64–69 (2002).
104. M.G. Sowa, L. Leonardi, J.R. Payette, K.M. Cross, M. Gomez, and J. Fish, J. Biomed. Opt. 11(5), 054002 (2006).
24. Mahalanobis Distance Metrics
105. H.L. Mark and D. Tunnell, Anal. Chem. 57(7), 1449–1456 (1985).
106. R.G. Whitfield, M.E. Gerger, and R.L. Sharp, Appl. Spectrosc. 41(7), 1204–1213 (1987).
107. R. De Maesschalck, D. Jouan-Rimbaud, and D.L. Massart, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 50(1), 1–18 (2000).
108. G. Downey, Analyst 119(11), 2367–2375 (1994).
25. Nearest Neighbor
109. U. Von Luxburg, Stat Comput. 17(4), 395–416 (2007).
110. B. Li, Y. Wei, H. Duan, L. Xi, and X. Wu, Vib. Spectrosc. 62, 17–22 (2012).
111. R.M. Balabin, R.Z. Safieva, and E.I. Lomakina, Anal. Chim. Acta 671(1–2), 27–35 (2010).
112. V. Allen, J.H. Kalivas, and R.G. Rodriguez, Appl. Spectrosc. 53(6), 672–681 (1999).
26. Neural Network (for Classification)
113. G.P. Zhang, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part C Appl. Rev. 30(4), 451–462 (2000).
114. W. Wu, B. Walczak, D.L. Massart, S. Heuerding, F. Erni, I.R. Last, and K.A. Prebble, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 33(1), 35–46 (1996).
115. J.B. Sirven, B. Bousquet, L. Canioni, L. Sarger, S. Tellier, M. Potin-Gautier, and I. Le Hecho, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 385(2), 256–262 (2006).
116. J. Acquarelli, T. van Laarhoven, J. Gerretzen, T.N. Tran, L.M. Buydens, and E. Marchiori, Anal. Chim. Acta 954, 22–31 (2017).
27. Random Forest
117. N.L. Afanador, A. Smolinska, T.N. Tran, and L. Blanchet, J. Chemom. 30(5), 232–241 (2016).
118. L. Sheng, T. Zhang, G. Niu, K. Wang, H. Tang, Y. Duan, and H. Li, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 30(2), 453–458 (2015).
119. H. Chen, Z. Lin, H. Wu, L. Wang, T. Wu, and C. Tan, Spectrochim. Acta A 135, 185–191 (2015).
120. J. Bin, F.F. Ai, W. Fan, J.H. Zhou, Y.H. Yun, and Y.Z. Liang, RSC Advances 6(36), 30353–30361 (2016).
28. Soft Independent Modeling by Class Analogy (SIMCA)
121. O.G. Meza-Márquez, T. Gallardo-Velázquez, and G. Osorio-Revilla, Meat Sci. 86(2), 511–519 (2010).
122. T. Gallardo-Velázquez, G. Osorio-Revilla, M. Zuñiga-de Loa, and Y. Rivera-Espinoza, Food Res. Int. 42(3), 313–318 (2009).
123. A.L. Pomerantsev and O.Y. Rodionova, J. Chemom. 28(6), 518–522 (2014).
124. E. Smidt, K. Meissl, M. Schwanninger, and P. Lechner, Waste Manage 28(10), 1699–1710 (2008).
29. Support Vector Machines (SVM)
125. J. Luts, F. Ojeda, R. Van de Plas, B. De Moor, S. Van Huffel, and J.A. Suykens, Anal. Chim. Acta 665(2), 129–145 (2010).
126. O. Devos, C. Ruckebusch, A. Durand, L. Duponchel, and J.P. Huvenne, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 96(1), 27–33 (2009).
127. A. Borin, M.F. Ferrao, C. Mello, D.A. Maretto, and R.J. Poppi, Anal. Chim. Acta 579(1), 25–32 (2006).
128. R.M. Balabin, R.Z. Safieva, and E.I. Lomakina, Microchem. J. 98(1), 121–128 (2011).
Programming Platforms
30. Programming Languages Excel
129. A.L. Pomerantsev, Chemometrics in Excel (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2014).
130. J. Miller and J.C. Miller, Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry (Pearson Education, London, England, 2018).
131. H.J. Brightman, Data Analysis in Plain English: With Microsoft Excel (International Thomson Publishing, Boston, Massachusetts, 1998)
132. N.H. Spencer, Essentials of Multivariate Data Analysis (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2013).
133. D. Grapov and J.W. Newman, Bioinformatics 28(17), 2288–2290 (2012).
Matlab
134. T.C. O’Haver, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 6(2), 95–103 (1989).
135. S. Mitra and T. Bose, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 22(1), 3–16 (1994).
136. P. Geladi and H. Martens, J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 4(1), 225–242 (1996).
137. P. Geladi, H. Martens, L. Hadjiiski, and P. Hopke, J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 4(1), 243–255 (1996).
138. C.A. Andersson and R. Bro, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 52(1), 1–4 (2000).
Python
139. R.M. Jarvis, D. Broadhurst, H. Johnson, N.M. O’Boyle, and R. Goodacre, Bioinformatics 22(20), 2565–2566 (2006).
140. W. McKinney, Pandas (Python Data Analysis Library, 2015). http://pandas.pydata.org.
141. A. Hughes, Z. Liu, and M. Reeves, J. Open Res. Softw. 3(1) (2015).
142. B. Thompson, K. Sunden, D. Morrow, D. Kohler, and J. Wright, J. Open Source Softw. 4(33), 1141 (2019).
143. Y. Koush, J. Ashburner, E. Prilepin, R. Sladky, P. Zeidman, S. Bibikov, F. Scharnowski, A. Nikonorov, and D. Van De Ville, NeuroImage 156, 489–503 (2017).
R programming
144. U. Grömping, J. Stat. Softw. 17(1), 1–27 (2006).
145. S. Lê, J. Josse, and F. Husson, J. Stat. Softw. 25(1), 1–18 (2008).
146. R. Wehrens, Chemometrics with R: Multivariate Data Analysis in the Natural Sciences and Life Sciences (Springer Science & Business Media, New York, New York, 2011).
147. K.M. Mullen and I.H. Van Stokkum, J. Stat. Softw. 18(3), 1–46 (2007).
148. A. Stevens and L. Ramirez-Lopez, An introduction to the prospectr package. R Package Vignette, Report No.: R Package Version 0.1, 3. (2014). https://cran.r- project.org/web/packages/ prospectr/vignettes/prospectr.html and https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/prospectr/prospectr.pdf
Jerome Workman, Jr. serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Spectroscopy and is the Senior Technical Editor for LCGC and Spectroscopy. He is also a Certified Core Adjunct Professor at U.S. National University in La Jolla, California. He was formerly the Executive Vice President of Research and Engineering for Unity Scientific and Process Sensors Corporation.

Howard Mark serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Spectroscopy, and runs a consulting service, Mark Electronics, in Suffern, New York. Direct correspondence to: SpectroscopyEdit@mmhgroup.com ●


Newsletter
Get essential updates on the latest spectroscopy technologies, regulatory standards, and best practices—subscribe today to Spectroscopy.
Scientists Use Water and Light to Uncover Honey Adulteration
July 30th 2025In a 2025 study, Indian researchers demonstrated that combining near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy with aquaphotomics enables rapid, non-destructive detection of adulterants in honey by analyzing changes in water’s spectral behavior. Using chemometric models, they accurately identified and quantified six common adulterants, offering a powerful tool for food authenticity and quality control.
Scientists Use AI and Spectroscopy to Detect Fake Honey in Bangladesh
July 29th 2025Researchers in Bangladesh have developed a rapid, non-destructive method to detect honey adulteration using UV-Vis-NIR spectroscopy paired with machine learning. Their findings could protect consumers and support food quality enforcement.
Random Forest Algorithms Gain Ground in Biomedical Signal Analysis and Chemico-Biological Research
July 29th 2025A new review article highlights the growing use of random forest machine learning (ML) models in biomedical signal analysis, emphasizing their potential for detecting cell damage, assessing toxicity, and advancing diagnostic classification.
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Honey Authentication: A Practical Mini-Tutorial for Food Quality Labs
July 28th 2025This tutorial introduces how NIR spectroscopy works for honey analysis, explores practical workflows, discusses real-world applications, and outlines best practices for implementing this technique in food labs.