Spectroscopy
Latest Content

Light-Metal Sorting and Rugged Engineering in Handheld XRF Instrumentation

Top 10 Most Influential Articles on FT-IR Spectroscopy in Biopharmaceutical Applications during 2024–2025

Previewing Pathways in Spectroscopy: Starting A Spectroscopy Business

How Should You Spend Your Free Time at Pittcon 2026?

Career Advice for Aspiring Forensic Scientists: An Interview with Kelly Elkins and Jaden Force

Shorts










Podcasts
Videos
All Content

Between 2023 and 2026, Raman spectroscopy transitioned from a supportive analytical technique to a central enabling technology in biopharmaceutical analysis and manufacturing. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), automation, and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) have expanded Raman’s role from nutrient monitoring to real-time prediction of critical quality attributes (CQAs), inline control of complex bioprocesses, and non-destructive analysis of finished drug products. This article reviews ten of the most influential publications from this period, highlighting how they collectively reshaped expectations for Raman spectroscopy as a process analytical technology (PAT) and a quality-by-design (QbD) tool in modern biopharmaceutical development.

This year’s Emerging Leader in Atomic Spectroscopy Award recipient is Sarah Theiner, whose research is focused on the application of atomic spectroscopy techniques—laser ablation inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and single-cell ICP-MS—to expand these analytical techniques as tools for biological and clinical imaging and drug-distribution studies.

A recent study investigated the use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) as a viable technique for detecting and quantifying trace technetium-99 (^99Tc) for future molten salt reactor applications, where long-lived fission products must be carefully monitored. Spectroscopy spoke to Hunter Andrews of Oak Ridge National Laboratory (Oak Ridge, Tennessee), corresponding author of the paper resulting from their research, about their findings.

A study from the İzmir Institute of Technology published in Food Chemistry shows that combining FT-IR spectroscopy with chemometric modeling enables rapid, non-invasive screening of iron supplements and protein–iron complexes for their ability to restore cellular iron status in iron deficiency anemia models.
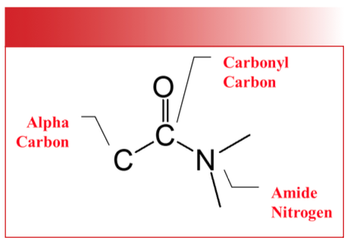
In our ongoing review of infrared spectra, we will study organic nitrogen containing compounds including amides and amines. Amides contain both nitrogen and a C=O group and are found in proteins and polymers. Amines contain carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen, and are ubiquitous in medicines. As always, concepts will be illustrated with reference spectra.
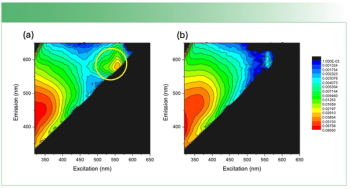
This column will show Raman results and ATEEM fluorescence whose correlations indicate that important information is available non-destructively.

Pittcon, one of the foremost laboratory science conferences, makes its Texas debut at San Antonio’s Henry B. González Event Center from March 7 to 11. The conference’s technical program of over 1100 sessions provides analytical scientists with direct access to the latest research and developments from an international assembly of top scientists and research pioneers.
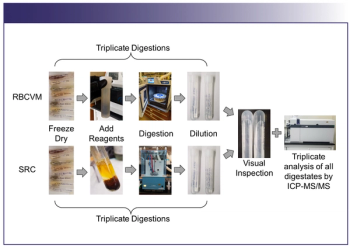
The primary goal of this study was to evaluate two microwave digestion systems for the acid decomposition of biological tissues: (1) a single reaction chamber (SRC) system and (2) a rotor-based, closed vessel microwave (RBCVM) system.

In a recent interview, we sat down with Kelly Elkins, a Professor of Chemistry at Towson University and Jaden Force, a Graduate Research Assistant at Towson University, to talk about the state of forensics and how they apply spectroscopic techniques in their research.

Top articles published this week include several interviews from our ongoing coverage of the Winter Conference on Plasma Spectrochemistry and the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS) Conference.

Tucson was a great host city for the 2026 Winter Conference on Plasma Spectrochemistry, but there are other cities that make sense to host future iterations of this conference. Here are our top five suggestions.

Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst demonstrated that X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy combined with chemometric modeling can provide a rapid, minimally destructive, and accurate alternative to traditional methods for routine arsenic quantification in rice and rice-based foods.

A new review article explores how integrating artificial intelligence (AI) with established analytical techniques such as spectroscopy, chromatography, mass spectrometry (MS), and sensors is significantly improving the efficiency, accuracy, and scope of food chemistry research and food quality assessment.

In this article, we look at the five major reasons why San Antonio is set to be a perfect host city for Pittcon this year.

Over the past two years, near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and related NIR techniques have seen rapid adoption in biomedical research. These developments span non invasive diagnostics, functional monitoring, machine learning integration, point of care probes, and applications in complex clinical settings such as liver fibrosis, viral detection, neonatal care, brain injury, and neurodegenerative disorders. This article synthesizes 10 key publications, highlighting trends, methodologies, and clinical potential.


















