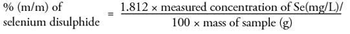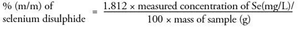Articles by Thermo Fisher Scientific
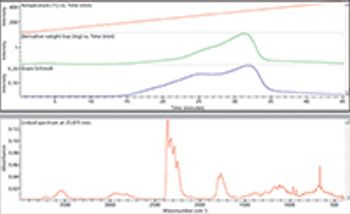
Thermal decomposition provides valuable information about the chemical composition of a material. Although thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) measures small weight losses during a heating ramp, it cannot identify the chemicals corresponding to the weight loss.
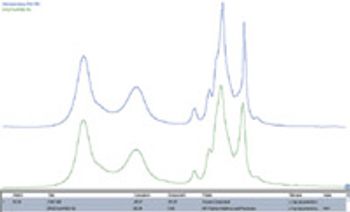
Identifying contaminants in materials is a common troubleshooting need for which FT-IR spectroscopy is ideally suited. Thermo Scientific OMNIC Specta software provides a unique and powerful tool to assist the analyst to quickly identify unexpected constituents. The OMNIC? Specta? Contaminant Search feature allows for rapid investigations that can save time and minimize the impact of product issues.
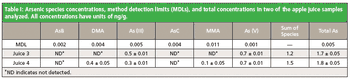
In this study, apple juice samples are analyzed by IC–ICP–MS to determine the concentration of six arsenic species: the two inorganic, and highly toxic, species (As (V) and As [III]) and four organic species (arsenobetaine [AsB], arsenocholine [AsC], monomethylarsonic acid [MMA], and dimethylarsinic acid [DMA]).
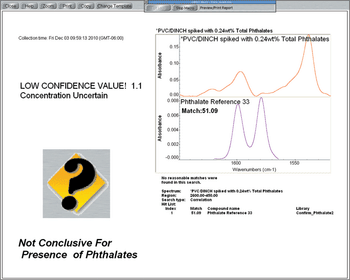
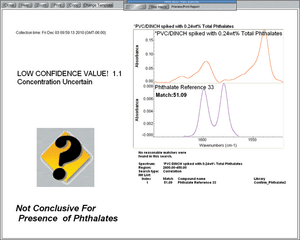
Recent evidence that the phthalate plasticizers may cause health problems, particularly in children, has resulted in many countries prohibiting the use of phthalates in toys and clothing. The United States Child Safety Law actually prohibits the presence of several phthalate compounds at levels exceeding 0.1 wt % even though the commercial levels are often greater than 10%. While ATR spectroscopy works well for identifying phthalates at commercial levels, a more sensitive technique is required to detect trace levels.
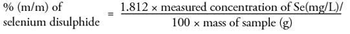
The formal European Union analytical method to measure and regulate the concentration of selenium disulphide is by the determination of selenium via flame atomic absorption spectrometry.

One of the most powerful aspects of Raman microscopy is the capability to do confocal analysis of features inside of a sample without having to prepare or damage the sample to get the important spectral information.