
Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy was used in this paper to rapidly analyze seven light alkanes (methane, ethane, propane, n-butane, i-butane, n-pentane, and i-pentane) in wellhead gases.
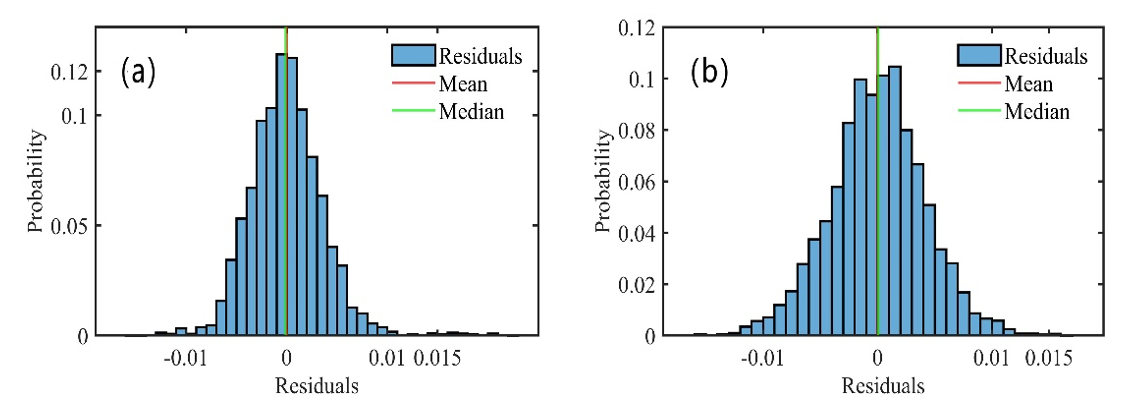

Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy was used in this paper to rapidly analyze seven light alkanes (methane, ethane, propane, n-butane, i-butane, n-pentane, and i-pentane) in wellhead gases.

In this study, a hyperspectral (400–1000 nm) system was utilized to acquire hyperspectral images of gardeniae fructus (GF) and construct a data set containing 3146 spectral data.

Raman spectroscopy emerges as a powerful tool for quantifying adenine in nucleic acid therapeutics, enhancing analytical efficiency and quality assessment.

A proposed solution is a coal species classification method that combines terahertz time-domain spectroscopy with machine learning - specifically, principal component analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis (CA). By using terahertz (THz) time-domain spectroscopy (TDS), the absorption coefficient, dielectric constant, and refractive index of each sample were obtained from lignite, bituminous coal, and anthracite samples.

This work shows the great potential of mushrooms as excellent raw materials in the development of multifunctional fluorescence carbon materials.

Surface hardness is one of the most important parameters which describes the degree of aging in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cables. In this work, the hardness of PVC sheathing material was studied using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS).

This research investigates the application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and machine learning (ML) for detecting elemental composition of food, using rice as an example.

In this study, the feasibility of the rapid discrimination of three different geographical origins of purple sweet potato with a hyperspectral imaging (HSI) system was examined.

The study developed an effective mid-infrared spectroscopic identification model, combining principal component analysis (PCA) and support vector machine (SVM), to accurately determine the geographical origin of five types of millet with a recognition accuracy of up to 99.2% for the training set and 98.3% for the prediction set.

To improve the robustness and accuracy of logistic regression identification method, a new Raman spectroscopy identification method was proposed that combines a distributionally robust optimization technique and fused lasso technique with logistic regression. Then, Raman spectroscopy was used to analyze two types of dairy products that were collected for anti-jamming identification testing to verify the effectiveness of the new method.

Vibrational spectra of six new hexafluorosilicate salts containing different amino acids (glycine (Gly), sarcosine (Sar), dimethylglycine (DMG), betaine (Bet), β-alanine (β-Ala) and l-proline (l-Pro)) are typically recorded and discussed on the basis of their structures. The presence of cations, dimeric cations with short hydrogen bonds, and hexafluorosilicate anions is reflected in the spectra.

In this article, it is explored whether THz-TDS combined with LS-SVM can be used to effectively identify the authenticity of Panax notoginseng, a traditional Chinese medicine.

In this article, the basic principles, advantages, and limitations of different optical techniques for obtaining seed vigor estimates are introduced and reviewed, and the key technology of non-destructive optical detection of single seeds will be discussed.

In this study, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) was applied in conjunction with principal component analysis (PCA) to identify and classify flower species.
This study uses Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy to analyze how the globular protein ovalbumin's secondary structures transition under varying pH conditions in the presence of the cosolvent xylitol, highlighting the role of noncovalent interactions in these conformational changes.

In this paper, a system based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and back propagation (BP) method was developed for the composition and traceability analysis of crop burning smoke.

A method combining inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) with inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) was developed for multielement determination of 50 species of major, minor, micro, and trace, rare earth, and rare elements in geological samples.
This study applied principal component regression (PCR) and partial least squares (PLS) algorithms for the spectrophotometric analysis of a drug containing antazoline hydrochloride (AN) and naphazoline hydrochloride (NP) without chemical separation. Both methods showed high accuracy and precision, with results closely matching those from a reference HPLC method, and were successfully validated for analyzing commercial pharmaceutical products.

This study uses hyperspectral imaging (HSI) technology, in synergy with machine learning and deep learning algorithms, to innovate a non-destructive method for the assessment of chicken freshness.

This study aimed to establish a fast, accurate method for quality evaluation of herbal medicine using NIR and chemometrics with ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-vis) as a standard method to determine the total flavonoids content.

In this work, a stable variable selection method based on variable stability correction (VSC) and modified iterative predictor weighting-partial least squares (mIPW-PLS) is proposed for the quantitative analysis of steel samples by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS).
Photodynamic therapy is widely used as an established biomedical optical modality for the conservative treatment of tumors. This work investigates laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy of the emerging photodynamic photosensitizer BODIPY-520 in turbid media.

To study the optical properties of mixed crude oil, the optical constants of samples consisting of two crude oils mixed in different proportions were obtained by the double-thickness transmittance method based on transmittance spectra.

In this article, tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) is used to measure ammonia leakage, where a new denoising method combining empirical mode decomposition with the Savitzky-Golay smoothing algorithm (EMD-SG) is proposed to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of absorbance signals.