
The application of data mining combined with data fusion of Raman and mid- infrared spectra was studied to improve discrimination ability for modeling the geographical origins of rice.


The application of data mining combined with data fusion of Raman and mid- infrared spectra was studied to improve discrimination ability for modeling the geographical origins of rice.

This work shows that the combination of THz-TDS and DFT can provide an effective method to investigate the connection mode of hydrogen bonds and thus aid in characterizing compounds such as this potential drug candidate.

Raman measurements of chromite minerals demonstrated that chromium content could be accurately determined, supporting a possible application of portable Raman devices on Earth or in space for mineral analysis of asteroids and planets.

Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) is combined with an extreme learning machine (ELM) model, tailored by genetic algorithm (GA) parameter searching, to produce a more robust analytical method for trace gas analysis of ethylene.

We investigate the effect of an applied electric field on the laser-induced titanium plasma for laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for the purpose of assessing electron density with respect to laser energy.

A rapid vis-NIR spectroscopy method for determining soil particle size and quality.

The advantages of machine-learning methods have been widely explored in Raman spectroscopy analysis. In this study, a lightweight network model for mineral analysis based on Raman spectral feature visualization is proposed. The model, called the fire module convolutional neural network (FMCNN), was based on a convolutional neural network, and a fire-module was introduced to increase the width of the network, while also ensuring fewer trainable parameters in the network and reducing the model’s computational complexity. The visualization process is based on a deconvolution network, which maps the features of the middle layer back to the feature space. While fully exploring the features of the Raman spectral data, it also transparently displays the neural network feature extraction results. Experiments show that the classification accuracy of the model reaches 0.988. This method can accurately classify Raman spectra of minerals with less reliance on human participation. Combined with the analysis of the results of feature visualization, our method has high reliability and good application prospects in mineral classification.

Test firing a firearm is frequently used for forensic firearms and bullet identification. Airborne lead-containing particles are emitted when a firearm is tested, leading to lead building up on surfaces, exposing employees to potential lead-related health risks. Prior to cleaning, lead surface concentrations in the firing range at the National Forensic Laboratory Services in Ottawa were found to be higher than the Environmental Abatement Council of Ontario (EACO) post-abatement limit, with the highest level 56 times the limit. Inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), along with internal standardization, revealed that wiping surfaces with either a commercial decontamination product containing ethylene glycol butyl ether (EGBE) or alcohol cleaning pads satisfied the EACO standard by removing over 90% of lead from test surfaces whereas an external cleaning company only removed 36% of lead from the same surfaces. Fortunately, lead cross-contamination was minimal outside the firearms section and well below the residential EACO limit.

Fungal infections and mycotoxin contamination in food products pose a major threat to the world population. Mycotoxins contaminate approximately 25% of the world’s food products and cause severe health problems through the utilization of affected food products. The major mycotoxins in different foods are aflatoxins, ochratoxins, fumonisins, zearalenone, trichothecenes, and deoxynivalenol. Today, various conventional and nondestructive techniques are available for the detection of mycotoxins across multiple food products. Conventional methods are time-consuming, require chemical reagents, and include many laborious steps. Therefore, nondestructive techniques like near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, hyperspectral imaging, and the electronic nose are a priority for online detection of fungal and mycotoxin problems in different food products. In this article, we discuss recent improvements and utilization of different nondestructive techniques for the early detection of fungal and mycotoxin infections in various food products.

With this cooling system, which maintains the chemical composition and temperature of the frozen sample, a higher S/N was achieved for LIBS analysis of a NaCl solution.

We compare the advantages and disadvantages of each laser wavelength.

Raman spectroscopy is a powerful, label-free spectral imaging technique for biomedical sample measurements. The chemometric approaches described here increase the speed of data acquisition and improve the resolution of Raman images.
A Raman study of vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is conducted at high pressure to determine phase changes and crystal symmetry through spectral interpretation.
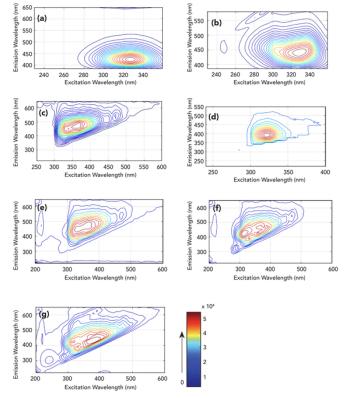
Many foods containing potentially harmful additives are labeled as additive-free. Detecting these additives can be challenging. A rapid method for additive detection is demonstrated using 3D fluorescence spectroscopy combined with an independent component analysis algorithm.

By applying vis-NIR spectroscopy, combined with an integrating sphere technique, a method for nondestructive testing of internal lesions in apples has been developed. This work provides a theoretical basis for the nondestructive testing of apples using tissue optical parameters.

High-precision statistics on desertification of grassland features are an important part of ecosystem research. In this study, a vis-NIR hyperspectral remote sensing system for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) was used to analyze the type and presence of vegetation and soil of typical desertified grassland in Inner Mongolia using a deep belief network and 2D and 3D convolutional neural networks.
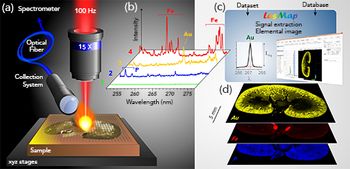
LIBS-based imaging has a broad range of applications. Here, we demonstrate those capabilities with examples from paleoclimate research and toxicology studies.
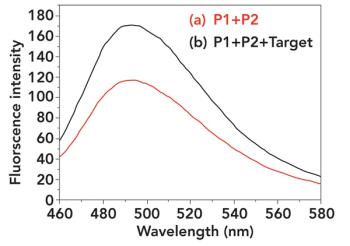
A novel method was developed for detecting Hg2+ in tobacco, with potential application to mercury detection in environmental water samples.
This study shows, for the first time, that limits of detection (LOD) can be improved for P, S and Ca nanoparticles by the addition of N2 to the plasma flow for single-particle inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (spICP-MS). The work also examined the relative LOD differences using Ar-N2 and Ar-N2-H2 mixed-gas plasmas.
In this study, WDXRF and FT-IR are used to analyze a tooth sample of a renal patient, and to compare the results to healthy patients. The quantities of multiple elements are reported using the XRF technique, and FT-IR spectroscopy is used to extract relevant information about the molecular contents of the sample with the important absorption bands identified.

Well-diffracting crystals are essential for X-ray diffraction of crystallized protein for structural determination. A quantum cascade laser (QCL) infrared microscope is used to determine protein aggregation, distinct from self-association, for the success of the crystallization effort.

The morphology and gap spacing of nano-island film SERS substrates are key factors defining the properties of analyte‒substrate interactions. These results of the study described here have implications for understanding signal variation in SERS and in designing future SERS assays.

A Raman spectroscopy method was used to assess the binding of dyes to different samples of carbon-bearing shungite rock with the same carbon content, but different mineral composition.
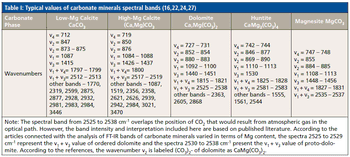
In this study, FT-IR spectroscopy was used for identification of carbonate minerals in limestone with variable contents of magnesium. Associated spectral bands were identified and assigned. Results of studies of Triassic limestone samples taken from the area of the Polish part of the Germanic Basin using FT-IR are presented. The results of research show that substitution of Ca2+ by Mg2+ in the carbonate phase lattices leads to a continuous wavenumber increase in the assigned band locations.
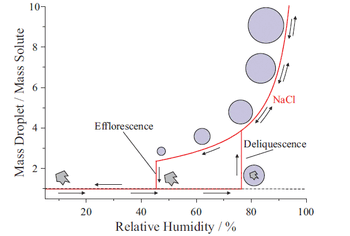
Raman spectroscopy, using optical tweezers, is capable of measuring the size, refractive index, and chemical composition of single aerosol droplets, at picoliter volumes. This information improves our understanding of molecular-level chemical processes within droplets.