
Mississippi State University researchers show that mid-infrared (MIR), a.k.a. infrared (IR), portable spectrometers, combined with calibration transfer techniques, can match lab instruments for soil property analysis.

Using UV-vis Spectroscopy for Fast, Affordable Diagnosis of Post-Covid Conditions

New Study Reveals Optimal Storage Conditions for Preserving Health-Promoting Anthocyanins in Fruit Extracts

Mississippi State University researchers show that mid-infrared (MIR), a.k.a. infrared (IR), portable spectrometers, combined with calibration transfer techniques, can match lab instruments for soil property analysis.

This tutorial addresses the critical issue of analyte specificity in multivariate spectroscopy using the concept of Net Analyte Signal (NAS). NAS allows chemometricians to isolate the portion of the signal that is unique to the analyte of interest, thereby enhancing model interpretability and robustness in the presence of interfering species. While this tutorial introduces the foundational concepts for beginners, it also includes selected advanced topics to bridge toward expert-level applications and future research. The tutorial covers the mathematical foundation of NAS, its application in regression models like partial least squares (PLS), and emerging methods to optimize specificity and variable selection. Applications in pharmaceuticals, clinical diagnostics, and industrial process control are also discussed.

DOGE-related federal funding cuts have sharply reduced salaries, lab budgets, and graduate support in academia. Researchers view the politically driven shifts in priorities as part of recurring systemic issues in U.S. science funding during administrative transitions. The impact on Federal laboratories has varied, with some seeing immediate effects and others experiencing more gradual effects. In general, there is rising uncertainty over future appropriations. Sustainable recovery may require structural reforms, leaner administration, and stronger industry-academia collaboration. New commentary underscores similar challenges, noting scaled-back graduate admissions, spending freezes, and a pervasive sense of overwhelming stress among faculty, students, and staff. This article addresses these issues for the analytical chemistry community.

Researchers in Northeast China have demonstrated a new approach using drone-mounted multispectral imaging to monitor and predict soybean bacterial blight disease, offering a promising tool for early detection and yield protection.

A Virginia Tech study has combined drone-mounted NIR hyperspectral imaging (400 nm to 1100 nm) and AI to estimate soil moisture at root depths with remarkable accuracy, paving the way for smarter irrigation and resilient farming.

A recent study showcases a cost-effective, ecofriendly UV spectrophotometric method enhanced with dimension reduction algorithms to accurately quantify veterinary drugs dexamethasone and prednisolone, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional analysis techniques.

This tutorial examines the modeling of diffuse reflectance (DR) in complex particulate samples, such as powders and granular solids. Traditional theoretical frameworks like empirical absorbance, Kubelka-Munk, radiative transfer theory (RTT), and the Hapke model are presented in standard and matrix notation where applicable. Their advantages and limitations are highlighted, particularly for heterogeneous particle size distributions and real-world variations in the optical properties of particulate samples. Hybrid and emerging computational strategies, including Monte Carlo methods, full-wave numerical solvers, and machine learning (ML) models, are evaluated for their potential to produce more generalizable prediction models.

Researchers at Georgia College and Purdue University have developed a fast, low-cost method using Raman and UV–visible spectroscopy combined with chemometric modeling to accurately screen and quantify active ingredients in over-the-counter oral syrups, helping to fight counterfeit medications.

The recipient of the 2025 NYSAS Gold Medal Award is Geraldine L. Richmond, Presidential Chair in Science and Professor of Chemistry at the University of Oregon.

A new study reveals how changes in refractive index can skew transient absorption data in thin-film materials, leading to misinterpretations unless properly corrected.

Researchers in Brazil have developed new optical techniques—SLIM, IC-scan, and RICO-scan—to probe the complex nonlinear properties of scattering and disordered materials, expanding potential applications in photonics, biomedicine, and thermometry.
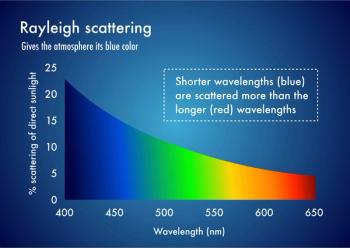
Researchers have introduced a simple yet powerful new rule based on Rayleigh scattering theory that accurately links the absorption behavior of composite media, like aerosols or colloids, to the properties of their nanoparticle constituents.

In this tutorial, Thomas G. Mayerhöfer and Jürgen Popp introduce complex-valued chemometrics as a more physically grounded alternative to traditional intensity-based spectroscopy measurement methods. By incorporating both the real and imaginary parts of the complex refractive index of a sample, this approach preserves phase information and improves linearity with sample analyte concentration. The result is more robust and interpretable multivariate models, especially in systems affected by nonlinear effects or strong solvent and analyte interactions.

Researchers at Sun Yat-sen University have applied visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy to reveal how iron oxide minerals, particularly hematite, define the iconic red hues of China's Danxia landforms.

Researchers from Northwestern University, University of Cádiz, and University of Arizona have developed new formulae for analyzing optical thin films that outperform traditional models by accounting for complex geometries and absorbing substrates. These advances offer more precise ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared (UV-vis-NIR) spectroscopic analysis of film materials used in critical modern technologies.

In this Icons of Spectroscopy article, Executive Editor Jerome Workman Jr. delves into the life and impact of Bruce Kowalski, an analytical chemist whose major contributions to chemometrics helped establish the field of applying advanced quantitative and qualitative mathematics to extract meaningful chemical information from complex datasets. Kowalski’s visionary approach to chemical data analysis, education, and software development has transformed the landscape of modern analytical chemistry for academia and industry.

Researchers in Rome used advanced spectroscopic techniques to probe the mineralogy of the CM2 carbonaceous chondrite NWA 12184. This revealed the effects of space weathering and provided insights into C-type asteroid evolution.

A newly published review in the journal Advanced Materials explores how intelligent wearable sensors, powered by smart materials and machine learning, are changing healthcare into a decentralized, personalized, and predictive modeling system. An international team of researchers highlights emerging technologies that promise earlier diagnosis, improved therapy, and continuous health monitoring—anytime, anywhere.

A study from Chinese researchers demonstrates how combining satellite imagery, land use data, and machine learning can improve pollution monitoring in fast-changing urban rivers. The study focuses on non-optically active pollutants in the Weihe River Basin and showcases promising results for remote, data-driven water quality assessments.

New research highlights how remote satellite sensing technologies are changing the way scientists monitor inland water quality, offering powerful tools for tracking pollutants, analyzing ecological health, and supporting environmental policies across the globe.

Modern remote sensing technologies have evolved from coarse-resolution multispectral sensors like MODIS and MERIS to high-resolution, multi-band systems such as Sentinel-2 MSI, Landsat OLI, and UAV-mounted spectrometers. These advancements provide greater spectral and spatial detail, enabling precise monitoring of environmental, agricultural, and land-use dynamics.

A global research team has detailed how smart sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are transforming the detection and management of environmental pollutants. Their comprehensive review highlights how spectroscopy and sensor networks are now key tools in real-time pollution tracking.

A new study published in Spectrochimica Acta Part A by Dominik Heger and colleagues at Masaryk University reveals that phenol's photophysical properties change significantly when frozen, potentially enabling its breakdown by sunlight in icy environments.

On April 9th, Marama Labs, a scientific instrument company with offices in Wellington, New Zealand, and Dublin, Ireland, announced in a press release the launch of its new CloudSpec instrument.