UV-vis Spectroscopy
Latest News

Latest Videos
More News
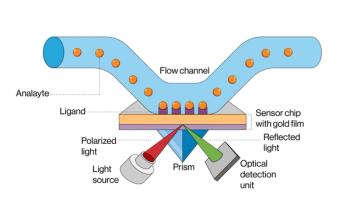
A research team has developed the first short synthetic peptide-based biosensor for real-time tracking of the disease-related protease matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), using multi-parametric surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy (MP-SPR).

This tutorial introduces spectroscopy professionals to the operational principles, practical workflows, and laboratory applications of biosensors. It covers core definitions, biosensor types, transduction methods, nanomaterials-enabled strategies, and optical/electrochemical approaches relevant to spectroscopic analysis. Readers will learn how biosensors integrate biological recognition with physicochemical detection, how to implement them in real-world measurement tasks, and how to avoid common technical pitfalls when translating biosensor theory into laboratory practice.
The miniaturization of spectroscopic instruments has reached a remarkable milestone: wearable vibrational spectroscopy. Techniques such as Raman, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), infrared (IR), and functional near-infrared (fNIRS) spectroscopy are no longer confined to the laboratory bench—they now fit on our bodies, into household devices, and onto industrial equipment. These wearable devices promise continuous, real-time monitoring, offering molecular-level insights for personal health, household management, clinical care, and industrial applications.

Using optical and near-infrared spectroscopy, researchers have identified crystalline water ice as the likely driver of explosive outbursts on comet 12P/Pons-Brooks. Their findings link this dramatic cometary activity to a process once observed in comets 17P/Holmes and 332P/Ikeya–Murakami.

A new international review highlights how hyperspectral imaging (HSI) is revolutionizing diverse fields—from counterfeit detection and agriculture to cancer diagnostics—by capturing unprecedented spectral detail invisible to traditional cameras. The study identifies major advances, challenges, and the growing role of artificial intelligence in real-time HSI applications.

Researchers have developed a new method combining unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) hyperspectral imaging with satellite data to monitor chlorophyll-a (Chla) and total nitrogen (TN) concentrations in coastal wetland waters. Their approach enhances the precision and scalability of water quality assessments, providing a model for managing eutrophication in fragile ecosystems.

This article provides a clear refresher on key spectroscopy techniques—IR/NIR, Raman, UV–Vis, XPS/XAS, NMR, ICP-MS, and LIBS—and their applications in the energy industry, from batteries and solar panels to fuel production and emissions monitoring.
Researchers at the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) have developed a new framework for onboard hyperspectral image processing that uses deep learning to analyze massive volumes of spectral data in real time. Their review highlights lightweight neural networks, generative models, and hardware accelerators as key technologies shaping the next generation of spaceborne Earth observation.

Here are ten main unsolved problems in vibrational and atomic spectroscopy, each accompanied by a tutorial-style synopsis suitable for advanced practitioners or graduate-level students. Each of these tutorials, spanning advanced spectroscopy modeling, chemometrics, machine learning (ML) interpretability, and standardization, consists of a descriptive article. Each piece is well-referenced (with detailed matrix equations, radiative transfer models, chemometric derivations, and so forth), and includes the following. • Special focus on each topic—including mathematical derivations in matrix notation. • Conservative, verifiable content anchored to established reference sources. • Appropriate tutorial article structure: Title, Summary, Abstract, Introduction, Theory with equations, Examples, Discussion & Future Research, and References.

A new study reveals that resveratrol binds to peanut protein arachin through hydrophobic and hydrogen-bond interactions, enhancing protein stability and offering valuable insights for developing functional peanut-based food products.

This tutorial explains how baseline drift and multiplicative scatter distort spectroscopic data, reviews correction techniques such as MSC, SNV, EMSC, wavelet-based detrending, and AsLS baseline estimation with matrix-based derivations, and explores emerging data-driven scatter modeling strategies and future research directions.

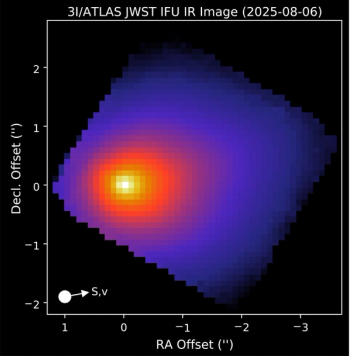
Astronomers have captured the first detailed optical spectrum of 3I/ATLAS, the third known interstellar object to visit our Solar System. Using the VLT’s MUSE instrument, the team finds a red, dust-dominated coma with no detectable gas emissions, offering a rare glimpse into the composition of alien comets.

This tutorial examines the development of universal spectral libraries, reviewing standardization efforts, mathematical frameworks, and practical examples across multiple spectroscopies, while emphasizing metadata harmonization, FAIR principles, and the emerging role of AI in building interoperable, machine-readable repositories. This remains an unsolved problem in spectroscopy.

New observations of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS, the third known interstellar object ever to visit our solar system, reveal unexpected activity and composition, challenging many previous assumptions about interstellar objects.

Newly captured spectroscopic data of the third-ever known interstellar object, 3I/ATLAS, reveals a red, organic-rich surface and an enigmatic early dust coma, providing unprecedented insight into materials from beyond our solar system.

Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS Shows Its Spectral Secrets Through Palomar and Apache Point Observations
Astronomers have conducted detailed spectrophotometric observations of the mysterious interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS using the Palomar 200-inch and Apache Point telescopes. The findings reveal unexpected activity and unique spectral features, enhancing our understanding of this cosmic visitor.
The interstellar object 3I/ATLAS, discovered in July, has captivated astronomers with its unusual characteristics. While some scientists attribute its behaviors to natural cometary processes, others propose more speculative theories, including the possibility of it being an artificial probe. This article examines both mainstream and speculative interpretations of 3I/ATLAS's anomalous features. Other news articles this week will look specifically at the spectroscopic results of telescopes recently analyzing this mysterious object.

This tutorial explores the motivation, mathematical underpinnings, and practical approaches to fusing spectral data, with emphasis on early, intermediate, and late fusion strategies.

This tutorial provides an in-depth discussion of methods to make machine learning (ML) models interpretable in the context of spectroscopic data analysis. As atomic and molecular spectroscopy increasingly incorporates advanced ML techniques, the black-box nature of these models can limit their utility in scientific research and practical applications. We present explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) approaches such as SHAP, LIME, and saliency maps, demonstrating how they can help identify chemically meaningful spectral features. This tutorial also explores the trade-off between model complexity and interpretability.

This tutorial contrasts classical analytical error propagation with modern Bayesian and resampling approaches, including bootstrapping and jackknifing. Uncertainty estimation in multivariate calibration remains an unsolved problem in spectroscopy, as traditional, Bayesian, and resampling approaches yield differing error bars for chemometric models like PLS and PCR, highlighting the need for deeper theoretical and practical solutions.

A recent study demonstrated that UV–visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy combined with machine learning (ML) can provide a fast, cost-effective, and automated method for detecting biological contamination in microalgae cultures.

This tutorial investigates the persistent issue of sample heterogeneity—chemical and physical—during spectroscopic analysis. Focus will be placed on understanding how spatial variation, surface texture, and particle interactions influence spectral features. Imaging spectroscopy, localized sampling strategies, and adaptive averaging algorithms will be reviewed as tools to manage this problem, as one of the remaining unsolved problems in spectroscopy.
Researchers at Santiago de Compostela University (Santiago, Spain) find ultraviolet–visible (UV–vis) spectroscopy can detect and quantify post-COVID condition with high accuracy, paving the way for real-time clinical use.

A new study reveals that anthocyanin-rich fruit extracts degrade rapidly under sunlight but remain most stable in cold, dark storage.

Inter-instrument variability is a major obstacle in multivariate spectroscopic analysis, affecting the reliability and portability of calibration models. This tutorial addresses the theoretical and practical challenges of model transfer across instruments. It covers spectral variability sources—such as wavelength shifts, resolution differences, and line shape variations—and presents key standardization techniques including direct standardization (DS), piecewise direct standardization (PDS), and external parameter orthogonalization (EPO). We discuss the underlying mathematics of these approaches using matrix notation and highlight limitations that must be considered for reliable universal calibration.