
This issue is a compilation of five peer-reviewed articles on the combined application of UV-vis-NIR spectral data with advanced chemometrics.

This issue is a compilation of five peer-reviewed articles on the combined application of UV-vis-NIR spectral data with advanced chemometrics.

Classification and identification of different wood species are demonstrated using a portable near-infrared spectrometer, combined with four spectral pretreatment methods and three pattern recognition methods. Additional chemometric tools were used for comprehensive evaluation of classification model accuracy and complexity.

Given that grape seed oil has shown beneficial effects for consumers, there is a interest in measuring oil quality and potential adulteration. This study demonstrates an effective near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy method, using a series of machine learning approaches for wavelength variable selection, to rapidly discriminate grape seed oil adulteration.

Spectral reflectance is a non-destructive method that is applicable to remote sensing and may be used to measure the chlorophyll content in a crop, which indicates the photosynthetic capacity, growth cycles, and degrees of stress (such as disease, insect infestation, and heavy metal stress) on plant ecosystems. This vis-NIR spectral reflectance method measures leaf chlorophyll using a wavelet analysis algorithm approach.

Depletion of modern mineral resources due to continuous exploitation and utilization makes it economically necessary to quickly identify the locate sources of low-grade ore. Here, we propose a vis-NIR remote sensing method to determine copper content in mining areas as well as to measure the environmental impact of surface mining methods.

Regulations have been imposed to set legal limits of nitrate and nitrite in water worldwide. In this study, a highly accurate and optimized ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy method is proposed to simultaneously monitor nitrate and nitrite for rapid determination and continuous monitoring in environmental water applications.

A model has been developed to predict the “cold” or “hot” nature of Chinese medicines based on UV spectral data.
Peak shifts in infrared spectra may occur for many reasons other than structural changes on the molecular or unit cell level. Here, we discuss several examples.

Evaluation of the UV-vis spectra of the reaction product of ytterbium (III) with hematoxylin (HE) indicates the formation of a rare earth complex that further reacts with marine mammal DNA, indicating the potential that this complex may have anti-tumor properties.

Nitrite poses health risks. This study evaluates the results of using tannic acid- protected fluorescence copper nanoclusters (TA-CuNCs) to detect nitrite in food.

Measurements of the optical proper ties of a ceramic material, Z93, which is in current use on the International Space Station (ISS), reveal why this material is successful for thermal control in the ISS implementation, and also point to potential future material design improvements.
Spectroscopic ellipsometry, correlated with UV-vis-NIR spectroscopy, is used to determine the optical constants of thin films, such as in GexSb40-xSe60 chalcogenide glass.
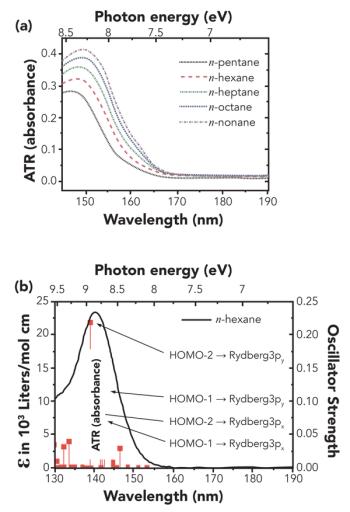
In celebration of Spectroscopy’s 35th Anniversary, leading experts discuss important issues and challenges in analytical spectroscopy.
Our annual review of products introduced at Pittcon or during the previous year
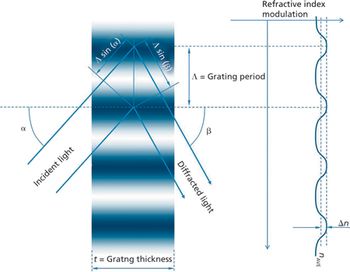
This article provides a basic overview of the capabilities of transmission gratings optimized for molecular spectroscopy.

Simulated leaf spectral data were generated to analyze scattering impact and then compared to experimental data to validate the conclusions of the simulation.
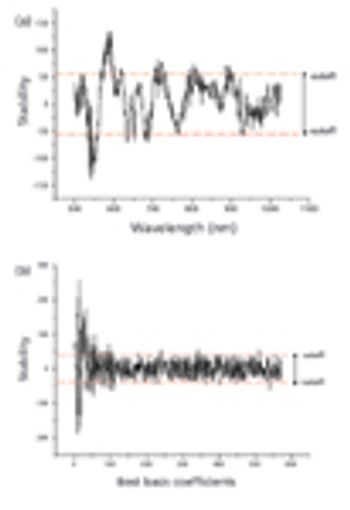
The wavelet packet transform (WPT) combined with the modified uninformative variable elimination (MUVE) method (WPT–MUVE) is proposed to select variables for multivariate calibration of spectral data.

The development of a method for the simultaneous determination of glycine, triglycine and fructose using UV–vis and evaporative light-scattering detection (ELSD) is described. This was necessary as part of a research project dealing with the recovery of functional peptides from aqueous streams on an industrial scale using adsorption or related technologies. Fructose is barely detectable by UV–vis as it lacks detectable functionalities, while glycine and triglycine are both UV–vis sensitive. An NH2 phase was chosen as a column and separation was obtained within seven minutes on a 250 X 4.6 mm column. Limits of detection are approximately 40 mg fructose/L, 4 mg glycine/L and 0.05 mg triglycine/L. Calibration functions are linear in a range of 40–1400 mg/L for fructose, 5–200 mg/L for glycine and 0.5–70 mg/L for triglycine.

In an upcoming spacewalk, shuttle astronauts will swap the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) device for the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS).

Some powders and rough surfaced solids change color as a function of temperature, a phenomenon known as thermochromism. Such phenomena can be effectively studied by UV-Visible spectroscopy in combination with a diffuse reflection accessory equipped with temperature-controlled reaction chamber, as demonstrated here with a thermal paint.

Data are presented for a pH-adjustable liquid UV-matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix for mass spectrometry analysis. The liquid matrix system possesses high analytical sensitivity within the same order of magnitude as that achievable by the commonly used solid UV-MALDI matrices but with improved spot homogeneity and reproducibility. The pH of the matrix has been adjusted, achieving an on-target pH range of 3.5?8.6, which has allowed for the performance of a tryptic digest within the diluted pH-optimized liquid matrix.

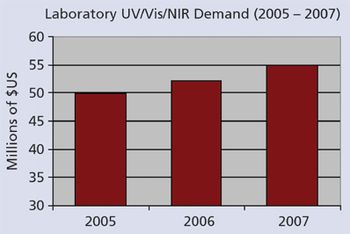
While the overall laboratory UV and Visible spectroscopy market was worth well over $700 million in 2007, the UV/Vis/NIR segment represented less than 10% of it. UV/Vis/NIR instruments utilize multiple detectors to cover a broader spectrum of analysis, and typically are among the highest-end systems in the UV-Vis market.


Data are presented for a pH-adjustable liquid UV-matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix for mass spectrometry analysis. The liquid matrix system possesses high analytical sensitivity within the same order of magnitude as that achievable by the commonly used solid UV-MALDI matrices but with improved spot homogeneity and reproducibility. The pH of the matrix has been adjusted, achieving an on-target pH range of 3.5?8.6, which has allowed for the performance of a tryptic digest within the diluted pH-optimized liquid matrix.