
Raman spectroscopy is a well-accepted, powerful tool for material identification, and the ability of a Raman spectrometer to acquire spectra through plastic and glass packaging materials protects sample integrity and greatly reduces analysis time.

Raman spectroscopy is a well-accepted, powerful tool for material identification, and the ability of a Raman spectrometer to acquire spectra through plastic and glass packaging materials protects sample integrity and greatly reduces analysis time.

Confirming the water content of pharmaceuticals and food during processing is critical for GmP results. The ability to measure water content until recently has been a difficult challenge until now. As a result of developments in the telecom industry, NIR spectrometers offer highly repeatable, cost effective solutions.

And as usual, Spectroscopy will not simply be a spectator at Pittcon, as we have a great many new products to offer as well.

The new technique of dynamic multi-mode spectroscopy (DMS) was used to study the stability of a monoclonal antibody biotherapeutic formulated in acetate and lactate buffers. The samples were measured several times over a period of weeks and it became apparent that the antibody behaved differently as it aged in the two formulations, with the lactate formulation imparting greater robustness than the acetate.

Some powders and rough surfaced solids change color as a function of temperature, a phenomenon known as thermochromism. Such phenomena can be effectively studied by UV-Visible spectroscopy in combination with a diffuse reflection accessory equipped with temperature-controlled reaction chamber, as demonstrated here with a thermal paint.

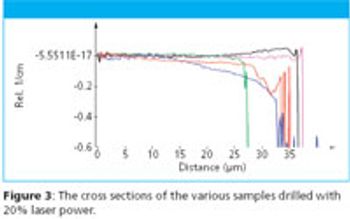
Energy generation using photovoltaic devices is regarded as an important component in overcoming future energy shortages. This is reflected in a dramatic increase in photovoltaic production and demand. In the research and development of photovoltaic devices, the primary goals are to increase the conversion efficiency of the solar cells or to improve the production process. The following study describes the application of Confocal Raman Imaging for the analysis of stress fields around laser-drilled holes on a Si solar cell using the large area scanning capabilities of the WITec alpha500 Confocal Raman Microscope.

Cardiovascular diseases are among the most important causes of death in The Netherlands. It is of great importance to be able to detect these diseases at an early stage. However, current methods that use classical risk factors such as cholesterol and blood pressure do not come up to the mark.
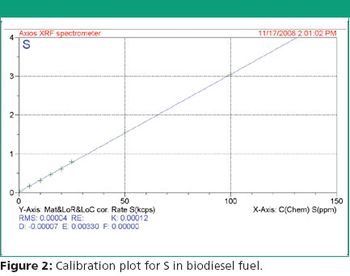
Global warming is seen as a growing problem across the world. One of the major contributing factors to global warming is greenhouse gas emissions and particulates emitted from automobiles. In an attempt to control the particulate emissions from motor vehicles, limits have been placed on the amount of elements such as Sulfur allowed in automotive fuels. Currently in the US, the EPA tier 2 regulations have set the limit for S in road fuels (Gasoline, Diesel and Biodiesel) at 150 ppm.
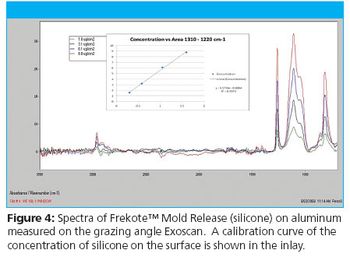
Infrared spectroscopy has long been recognized as a selective and sensitive technique for analysis and characterization of surfaces. From material identification to quantitative analysis, infrared analyses can establish if a surface is composed of the correct material, has the proper coating thickness, is free of contaminants, is properly cured, or has the correct properties for the next step in a manufacturing process.

A method for the determination of elemental impurities in solid silver samples was developed using a spark ablation accessory in combination with ICP-OES. Detection limits at the sub-ppm level were achieved along with good accuracy and precision.

It is shown that the Retsch CryoMill polymers are ground to a significantly smaller fineness compared to other methods. Especially for inhomogeneous materials, small particles are the key for a high reproducibility.

Building on more than 10 years of Micro-XRF experience, the Orbis spectrometer yields a system with excellent Micro-XRF capability while setting a new standard in analytical flexibility. The Orbis incorporates a unique motorized turret integrating video and X-ray optics allowing coaxial sample view and X-ray analysis. The turret can accommodate two additional collimators along with the X-ray optic for a total of three X-ray beam sizes to expand the Orbis analytical capabilities beyond traditional Micro-XRF analysis. Primary beam filters can be used with all spot sizes available on the turret to allow true XRF analytical capabilities in a micro-spot analysis. The working distance is increased to allow analysis over rougher sample topography without sacrificing signal intensity.


The form and frequency of the amide I band, assigned to the C=O stretching vibration within peptide bonds, is informative and predictive of peptide or protein secondary structure. Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy analysis of protein secondary (2°) structure is particularly useful in peptide, protein, or enzyme formulation, widespread in the pharmaceutical and biofuel production industries.

This September issue of The Application Notebook should be reaching our audience just as the busiest time of the year ramps up in the world of spectroscopy.

Carbon black rubbers often contain multiple components, but are strongly absorbing in the infrared. The combination of Ge ATR, Advanced ATR correction and multi-component searching permits the full analysis of these important materials.

The simplicity of Raman spectroscopy provides an ideal method for the quantitative determination of liquid mixtures.

With gas and diesel fuel prices rising, there is an increasing need to monitor online quality control and blending mixtures. The benefits include improved accuracy in blending mixtures, solid state reliability, lifetime calibration and fraud avoidance.
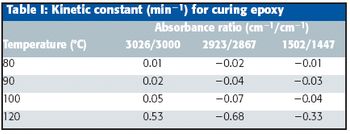
Some ATR / FTIR applications require a high performance, robust, and versatile accessory to accommodate difficult materials or high temperatures. As an example, the curing of a thermoset epoxy is evaluated and results are discussed.

Wavelength-Scanned Cavity Ring Down Spectroscopy combines the real-time speed and turnkey simplicity of optical spectroscopy with the precision (<0.1 δ18O [‰], < 0.5 δD [‰]) previously only available from complex IRMS systems.


In the Life Sciences, Materials Research, and Nanotechnology, obtaining as much information as possible about the chemical and structural composition of a sample is essential. Confocal Raman Microscopy can play an important role in the nondestructive characterization and imaging of chemical properties while requiring only minimal, if any sample preparation. Systematic and routine research tasks with repetitive experiments or a large number of measurement points, as well as high-level quality control can benefit from an automated instrument.

Spectral measurements down to 153 nm can be achieved easily and economically with the high-sensitivity Maya2000 Pro with Extra-Deep-UV Option. Nitrogen purging of the spectrometer helps to mitigate water and oxygen absorption in the vacuum ultraviolet.

Semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) can be used as nonclassical light sources with applications in next-generation quantum communication and computing. Electrically pumped QDs are all solid-state sources of single photons that are not limited by Poisson statistics (1). Recent work by the group of Dieter Bimberg at Technische Universität-Berlin has demonstrated the selective pumping of a single InAs QD with emission from a single exciton (1–3).

The factors that affect the long-term stability of ICP instruments are discussed and details of the performance of the Thermo Scientific iCAP 6000 Series for extended period analyses are given.

The availability of new silicon drift detectors (SDD) allows for more precise measurements in less acquisition time. SDDs are often praised for their excellent energy resolution, but it is their increased throughput that make them ideal for many industrial applications. Due to the detector's smaller capacitance, a much shorter peaking time is used in the shaping amplifier without sacrificing resolution. This dramatically increases the throughput of the system. Compared with a conventional Si-PIN detector where the peaking time is as long as 25 ms, the drift detector operates at 1.6 ms, thereby increasing throughput from 10,000 counts per second to over 100,000. This advantage can be used in two primary ways.


