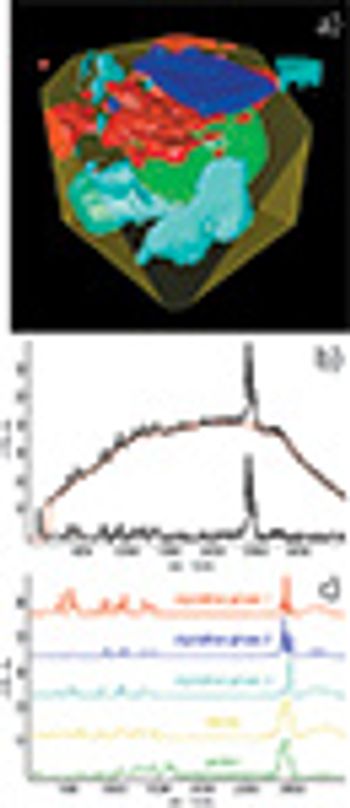
Newly developed software tools provide various functions for the acquisition, evaluation, and processing for high-resolution 3D Raman images.

Newly developed software tools provide various functions for the acquisition, evaluation, and processing for high-resolution 3D Raman images.

Bruker's IFS 125HR spectrometer is designed as an ultra-high resolution FT-IR spectrometer which provides outstanding performance for R&D laboratory application.
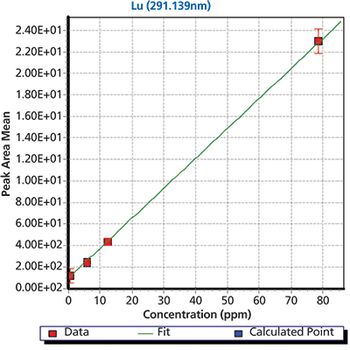
The lanthanide series is a series of metallic elements, with atomic numbers 58 through 71, which are - in order of increasing atomic number - cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and lutetium.
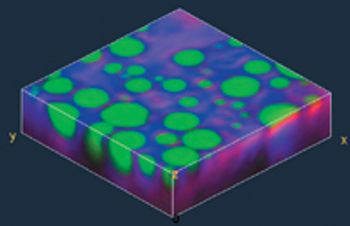
Raman microscopy is a high resolution imaging technique that has become widely used for the characterization of materials in terms of their chemical composition.

The new Savillex C400d PFA concentric nebulizer for ICP-MS combines the reliability of a low flow glass nebulizer with the chemical resistance and low elemental background of a PFA concentric nebulizer.
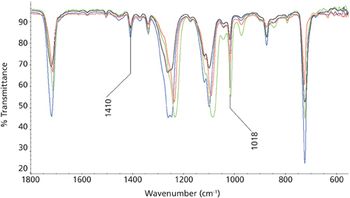
Polymer orientation of a blow-molded plastic was investigated using FTIR-ATR with polarization. By using a variable angle ATR accessory, changes in spectral features were observed at two different probing depths.
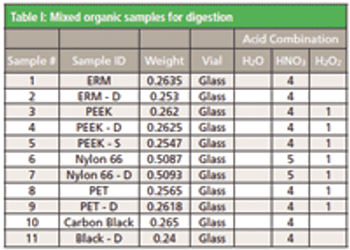
Sample matrices with high organic content have created a significant challenge for sample preparation methods.

This application note introduces an Application Package for quantitative analysis of additive elements in polymer.

Low concentration natural methanol exists in most alcoholic beverages and usually causes no immediate health threat.
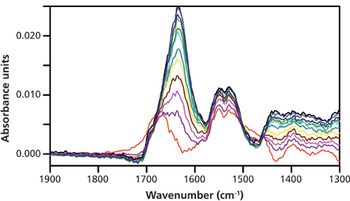
Infrared ATR spectroscopy has recently gained recognition as a viable technique for protein structural analysis due to its high information content, rapid sampling rate, and minimal sample preparation.

This application note describes the capability of the Teledyne Leeman Lab's Prodigy7 High-Dispersion ICP for performing analysis according to SW-846 Method 6010C.

Moxtek now has a full energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence detector solution with Moxtek's XPIN detectors and our new MXDPP-50 electronics.
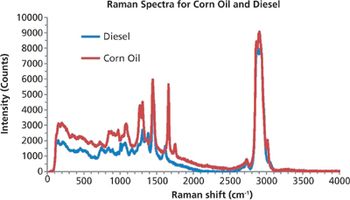
Raman spectroscopy is an excellent technique for the identification and characterization of fuels. With no requirement for sample preparation and the power to identify and quantify materials, Raman has many uses across a range of industries.
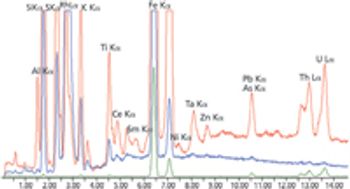
Demonstration of the advantages of using the Orbis micro-XRF elemental analyzer rather than other analysis techniques to perform elemental analysis through a plastic barrier and/or at atmospheric pressure.
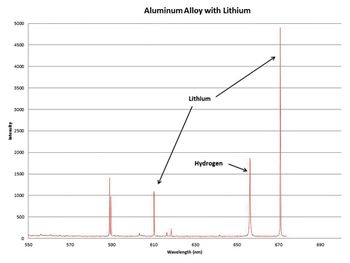
SciAps has developed a handheld analyzer based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS).

Raman microscopy has evolved into a common method for fast and nondestructive analysis of microscopic samples in forensic and R&D laboratories as well as for troubleshooting in the field of quality control.
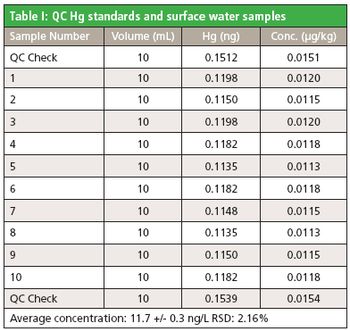
With over 1300 commercial testing labs in the United States, one out of every three samples is for water analysis. There has been an even stronger emphasis on mercury testing and its concentration in our water supplies.

Raster orbital scanning (ROS) is a technique that dramatically increases the signal-to-noise ratio of Raman measurements made from target materials dispersed on surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates.
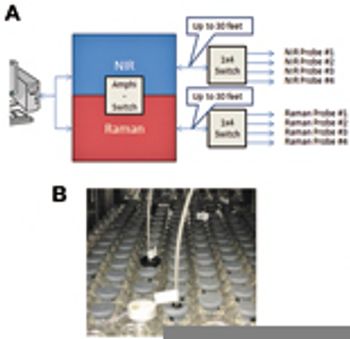
A new compact instrument (Amphi-Spec) combining dispersive Raman and NIR spectroscopy has been developed at BaySpec, Inc., to deliver maximum analytical power.
Moxtek makes ultra-thin polymer X-ray windows that are often used in SEM and TEM microanalysis detectors.
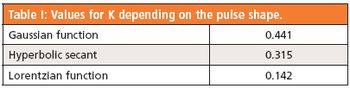
Even though no current electronics is fast enough to measure femtosecond lasers, an estimation of the pulse duration, peak wavelength, and relative intensity is possible.
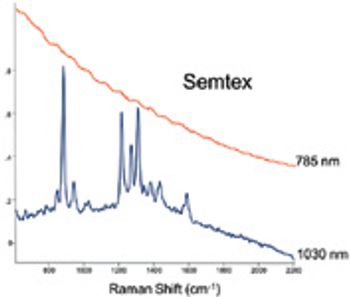
Handheld Raman analyzers have found widespread use in the pharmaceutical industry for excipients and raw materials verification, and in first responder/security applications. Most portable Raman units utilize lasers operating at 785 nm because of the relatively good signal strength at this wavelength.
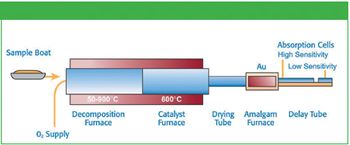
Mercury is a toxic, persistent pollutant found in many native ores rich in copper, silver and gold. As such ores are processed mercury can be released to the environment.
Single reaction chamber microwave digestion enables a chemist to digest up to 15 different specialty chemical samples simultaneously at temperatures as high as 300 ?C, greatly simplifying the workflow while maintaining superior quality digestions.
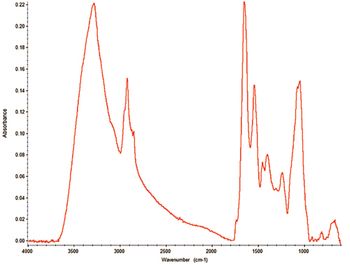
Yeast suspensions were dried and analyzed via FT-IR using an automated transmission sampling accessory. Up to six-fold sampling capacity increase may be realized through automation.
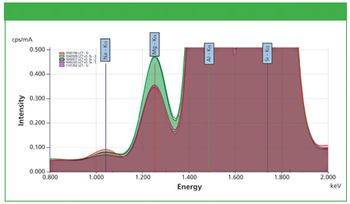
The analysis of coal is demonstrated, with specific emphasis on the measurement of Na2O, using a Cartesian geometry energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) spectrometer employing the Fundamental Parameters (FP) approach.
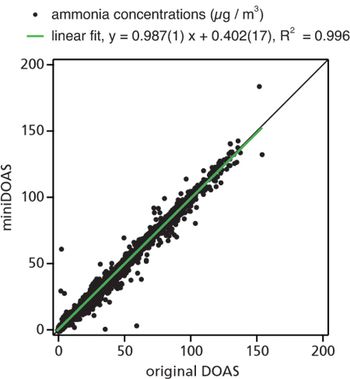
Knowledge of atmospheric ammonia concentrations is important, but ammonia is difficult to measure. We report here on the development of a low-cost ammonia measuring differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) instrument, based on a small sized and low priced spectrograph.
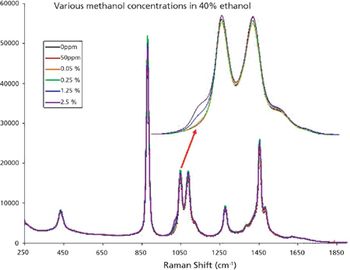
Low concentration natural methanol exists in most alcoholic beverages and usually causes no immediate health threat.
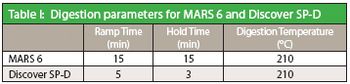
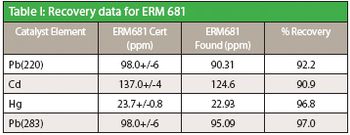
Pharmaceutical samples spiked with several heavy metals were prepared for ICP-MS analysis using microwave digestion following the protocols in proposed USP chapters <232> and <233>. The results of the spike recovery study are discussed.

Confocal Raman imaging opened the door for many applications in Raman spectroscopy and imaging that were previously unavailable for measurement with conventional (non-confocal) Raman methods.