
Confocal Raman imaging opened the door for many applications in Raman spectroscopy and imaging that were previously unavailable for measurement with conventional (non-confocal) Raman methods.

Confocal Raman imaging opened the door for many applications in Raman spectroscopy and imaging that were previously unavailable for measurement with conventional (non-confocal) Raman methods.
Owing to technological improvements spurred on by the telecommunications boom of the last decade, Raman spectroscopy has become much more accessible to users in all application areas, including agricultural, forensic, pharmaceutical, biomedical, and others.
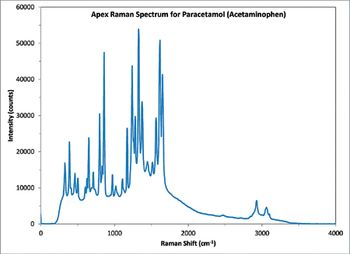
Although Raman spectroscopy is an excellent analytical tool, Raman signals are often weak and traditional slit spectrometers typically have poor optical throughput, limiting their effectiveness in low light level setups.
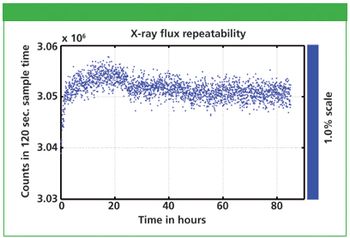
Moxtek's ULTRA-LITE X-ray source is a very small self contained X-ray source (X-ray tube and high voltage power supply) for use in portable X-ray applications, such as the handheld X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometers. This note demonstrates that this X-ray source has a stable and repeatable X-ray flux output over time, which is vital for the precision of the calibrated XRF measurements.
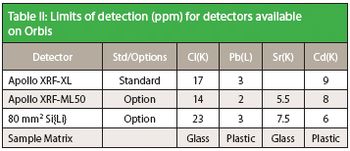
The measurement of trace elements is important across a wide variety of materials characterization problems. When measuring small glass fragments collected from crime and accident scenes, forensics experts analyze trace strontium (Sr) and zirconium (Zr) typically unintentionally incorporated into the glass during manufacturing as one point of identification or comparison.

Multiple reflection ATR is ideal for detecting miniscule levels of components in solutions. If one component is volatile, trace analysis can be simplified by allowing the volatile liquids to evaporate.
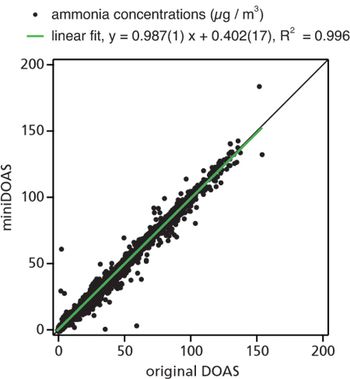
The miniDOAS: Low Cost, High Performance Contactless Ammonia Measurements
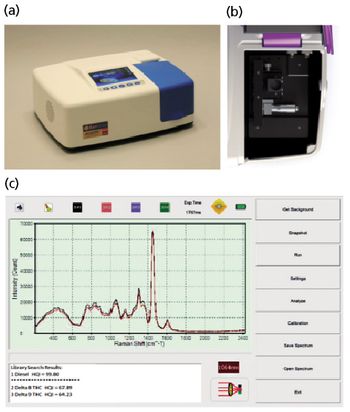
Transportable Dual-Band Raman System for Fuel Analysis
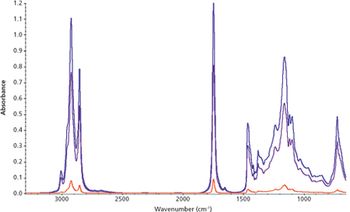
Probing the Detection Limits of Concentrated Multiple Reflection ATR Spectroscopy
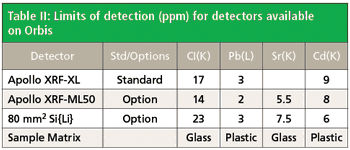
Improved Sensitivity with the New Apollow XRF ML-50 Detector on the Orbis Micro-XRF Analyzer
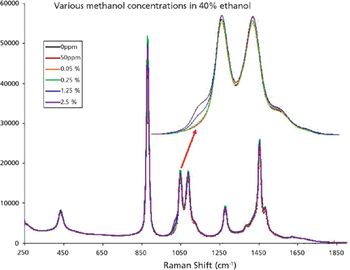
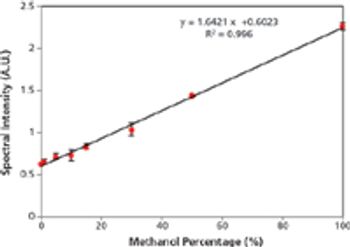
Determination of Low Concentration Methanol in Alcohol by an Affordable High Sensitivity Raman Instrument
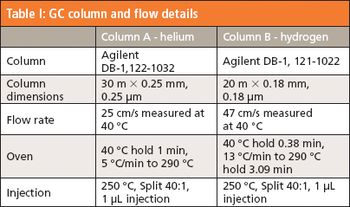
Experimental data show the crystal dimensions of an ATR-FT-IR sampling accessory influence the usable spectral range. An expanded range germanium crystal is introduced for the measurement of high refractive index samples.
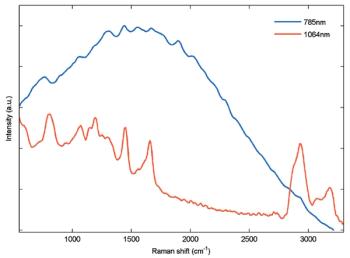
Biological tissues and other materials often autofluoresce at near-infrared wavelengths, prohibiting Raman acquisition. New, dispersive Raman systems at 1064 nm allow fluorescence-free measurement in similar integration times.
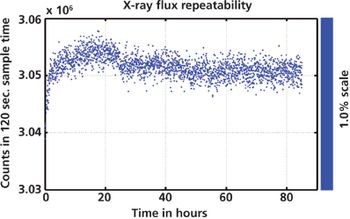
Moxtek's ULTRA-LITE X-ray source is a very small self contained X-ray source (X-ray tube and high voltage power supply) for use in portable X-ray applications, such as the handheld X-ray florescence (XRF) spectrometers. This note demonstrates that this X-ray source has a stable and repeatable X-ray flux output over time, which is vital for the precision of the calibrated XRF measurements.
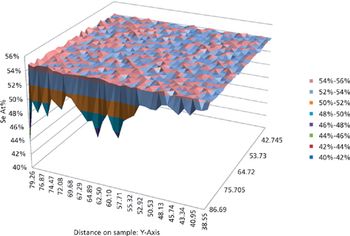
Building on more than 10 years of Micro-XRF experience, the Orbis spectrometer yields a system with excellent Micro-XRF capability while setting a new standard in analytical flexibility. The Orbis incorporates a unique motorized turret integrating video and X-ray optics allowing coaxial sample view and X-ray analysis. The turret can accommodate two additional collimators along with the X-ray optic for a total of three X-ray beam sizes to expand the Orbis analytical capabilities beyond traditional Micro-XRF analysis.
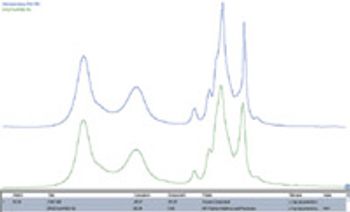
Identifying contaminants in materials is a common troubleshooting need for which FT-IR spectroscopy is ideally suited. Thermo Scientific OMNIC Specta software provides a unique and powerful tool to assist the analyst to quickly identify unexpected constituents. The OMNIC? Specta? Contaminant Search feature allows for rapid investigations that can save time and minimize the impact of product issues.

Clays, like kaolinite and smectite, are hygroscopic and it is well known that the adsorbed water can be driven off at elevated temperatures. At very low temperatures, in addition to the typical band narrowing and shifting, changes in the O-H bond vibrational modes of clays have also been observed.

Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) is a powerful technique for rapid and non-destructive material analysis. Scientific breakthroughs over the past several decades have made NIR one of the most powerful tools for research, especially in industries such as food and drug, chemical, oil and gas, and plastics. This technique has mainly been limited to non-portable applications due to instrument size, fragility, and cost. Additionally, Database Search Software or Multivariate Prediction Software must also be employed to extract results; however, user-friendly and cost effective solutions have not been widely available.
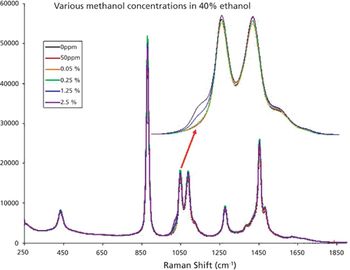
Low concentration natural methanol exists in most alcoholic beverages and usually causes no immediate health threat. Nevertheless, it is possible to have natural occurring methanol in beverages with concentration as high as 18 g/L of ethanol; or equivalent to 0.72% methanol in 40% ethanol, in alcohol (1). Current EU regulation limits naturally occurring methanol to below 10 g/L of ethanol; or equivalent to 0.4% methanol in 40% ethanol.
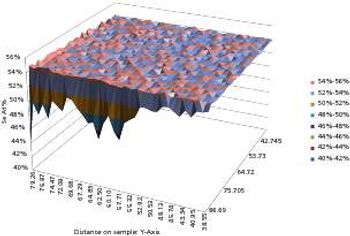
Building on more than 10 years of Micro-XRF experience, the Orbis spectrometer yields a system with excellent Micro-XRF capability while setting a new standard in analytical flexibility. The Orbis incorporates a unique motorized turret integrating video and X-ray optics allowing coaxial sample view and X-ray analysis. The turret can accommodate two additional collimators along with the X-ray optic for a total of three X-ray beam sizes to expand the Orbis analytical capabilities beyond traditional Micro-XRF analysis. Primary beam filters can be used with all spot sizes available on the turret to allow true XRF analytical capabilities in a micro-spot analysis. The working distance is increased to allow analysis over rougher sample topography without sacrificing signal intensity.
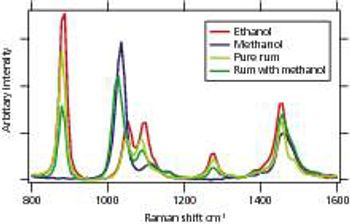
Increased capability for identifying genuine versus counterfeit materials is achieved by using dispersive 1064 nm Raman analyzers.
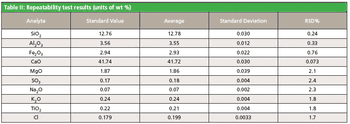
Cement is one of the most important materials in the construction industry. Traditionally, WDXRF spectrometers used in cement plants have been large, floor-standing models with substantial installation requirements and ownership expenses. This application note demonstrates the capabilities of the Rigaku Supermini - a new low-cost, benchtop wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WDXRF) spectrometer - for the rapid quantitative elemental analysis of cement raw meal.

Infrared (IR) sampling techniques of attenuated total reflectance (ATR) and transmission for polymer analysis are compared and contrasted. Using a real-world application, IR analysis of silane-grafted linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) pellets is presented to illustrate the benefit of IR film transmission sampling.
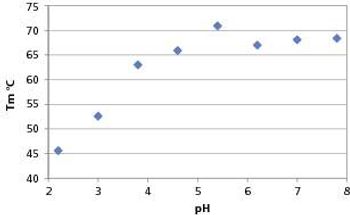
The polyclonal IgG in this study is more thermally stable at neutral pH, (4.8 to 7.8) than it is at lower pH. The loss of thermal stability at lower pH is concomitant with a change in the pre-transition folded structure of the protein.
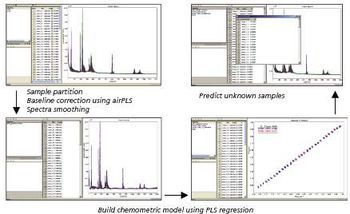
Raman is a well-developed and implemented qualitative spectroscopic tool for molecular identification, but in recent years with the development of high resolution portable Raman spectrometers and cutting edge chemometric modeling, software has now enabled the use of Raman for highly precise quantitative measurements of mixtures and reactions.
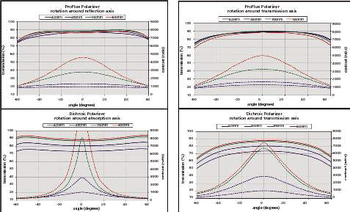
This technical brief compares imaging needs and how Moxtek is improving its products. It explains how competing technologies in LCoS projectors compare in terms of brightness, performance, durability and reliability.
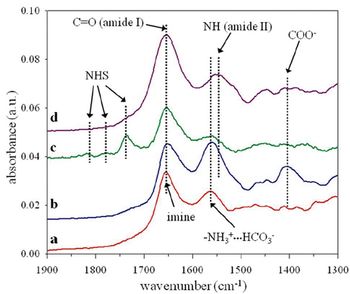
The formation of organic silane-based thin films on silicon substrates provides a simple opportunity to introduce chemically well-defined thin films at the molecular scale (1).
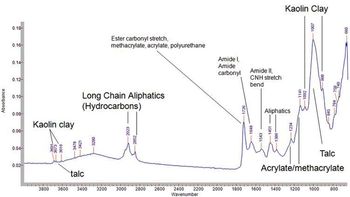
FTIR spectroscopy has long been used for the analysis of art and historical objects in support of efforts to conserve, restore, and validate authenticity of these rare objects. The value of the technique for this application lies in its inherent sensitivity, specificity, and non-destructive capabilities.