
Members of Spectroscopy's readership have always been attuned to the science behind the headlines.

Members of Spectroscopy's readership have always been attuned to the science behind the headlines.
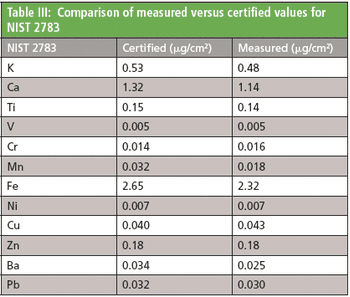
The measurement of the elemental composition of suspended particulate matter (SPM) in air is a key factor in understanding the health effects of pollution.

FT-NIR analyzer to perform in-line determination of tablet coating thickness during spray coating.
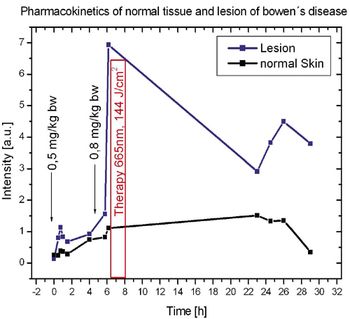
For the optimization of photodynamic therapy the spectroscopic detection of photosensitizer molecules, which are selectively enriched in tumour cells, can be useful.

For the characterization of the properties of a sample with Raman spectroscopy, an ultrasensitive confocal Raman microscope allows the acquisition of a Raman image stack revealing 3-D information on the distribution of the chemical compounds.

Low concentration natural methanol exists in most alcoholic beverages and usually causes no immediate health threat.

A2 Technologies' Exoscan hand-held FTIR (Figure 1) is increasingly being used by researchers involved in the geosciences for analysis of rocks, minerals, and soil for a broad variety of applications.

The amaZon series is the next step in Bruker Daltonics' family of ion trap mass spectrometers.
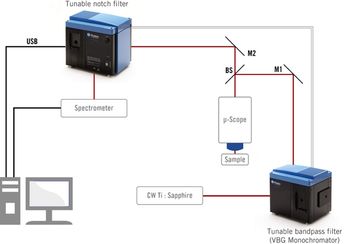
Photon etc. has designed two narrowband tunable filters for resonance Raman spectroscopy.
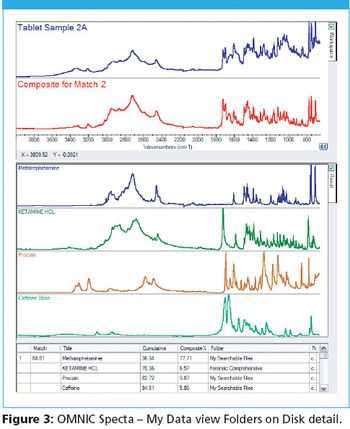
According to the Scientific Working Group for the Analysis of Seized Drugs (SWGDRUG), techniques with the highest discriminating power should preferentially be used for forensic identification of seized drugs.

In the life sciences and bio-medical research, in the food as well pharmaceutical industry, the development of characteristic emulsions and suspensions with distinctive features play an important role.

Grazing angle Ge ATR spectroscopy is extremely sensitive to monolayers and thin films on high refractive index substrates such as Si.
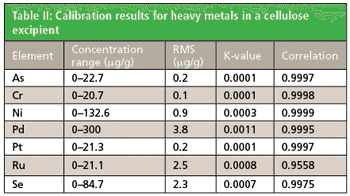
One of the most common product safety-related analytical tests in the pharmaceutical industry (often referred to as a Limit Test) is the quantification of heavy metals or inorganics in all materials within a pharmaceutical product.
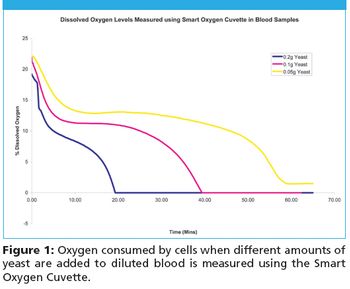
A "Smart" Oxygen Cuvette has been developed by coating the inner surface of a plastic (PMMA) cuvette with sol-gel based oxygen-sensitive indicator material.
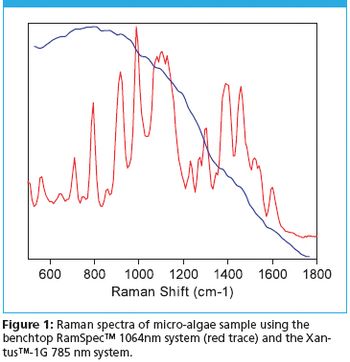
BaySpec, Inc. has developed a complete line of 1064 nm excitation, dispersive Raman systems that offer maximum reduction in fluorescence interference from biological samples and thus making them very useful tools for biofuel research.
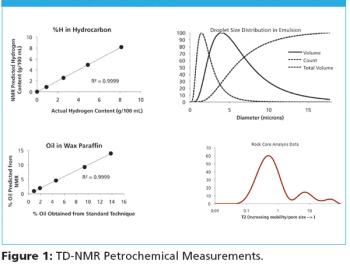
TD-NMR (Time-Domain Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) is a powerful tool for the petrochemical industry, from exploration to refining, that examines materials at the molecular level to quantify physicochemical properties.
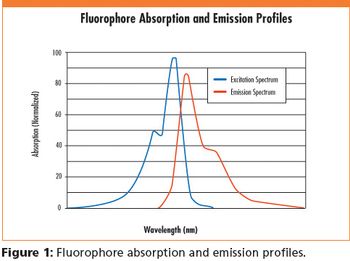
Diagnostic instruments such as blood analyzers and flow cytometers utilize induced fluorescence to detect bio-factors of interest in a heterogeneous sample.
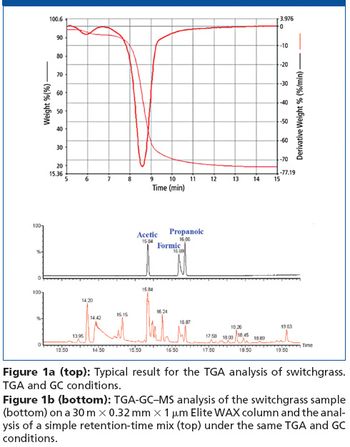
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) measures the change in the weight of a sample as a function of temperature.
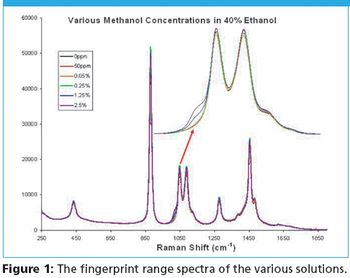
Low concentration natural methanol exists in most alcoholic beverages and usually causes no immediate health threat.

A prerequisite for a successful biotherapeutic formulation is one where the protein is stable and correctly folded.

Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) is a powerful technique for fast and non-destructive analysis of plastic films.

Fat and other nutritional values can easily be determined by NIR analysis. However a proper sample preparation beforehand is essential for a correct result.
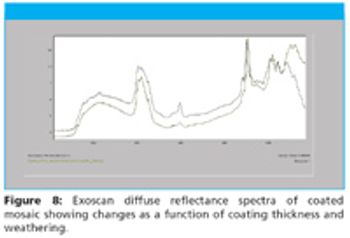
As has been previously discussed (1), FTIR spectroscopy is emerging as a technique that can be effectively used for applications and/or in locations that heretofore would be considered too demanding. The development of portable FTIRs, and more recently handheld FTIRs, is significant because it enables this powerful analytical technique to solve problems for a whole range of new applications, both in the laboratory, and out of the laboratory.
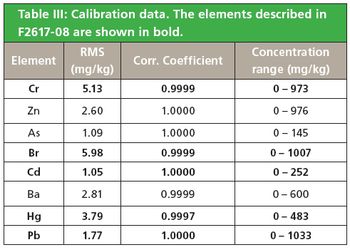
This application note demonstrates the analysis of lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium, and bromine in polymers, compliant to ASTM F2617-08. The TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards were used to set up the calibration on Epsilon 5. The accuracy of the calibration is demonstrated by determination of European Reference Material (ERM) EC681k.

The development of advanced polymeric materials requires detailed information about the phase separation process on the nanometer scale. Confocal Raman microscopy contributes to the analysis of such materials by visualizing the distribution of individual components based on the unique Raman spectra for different polymeric materials. Using a confocal setup, polymer domains can be imaged three-dimensionally with a resolution down to 200 nm. As a Raman image typically consists of tens of thousands of spectra, a powerful data analysis software is essential in order to extract the relevant information. Hidden structures in the images should ideally be visualized automatically, ensuring an objective and consistent interpretation of the imaging data.

A drug-eluting stent (DES) is an expandable metal alloy framework placed into narrowed coronary arteries that slowly releases a drug coating to treat atherosclerosis. Production of DES is a labor-intensive batch process that requires very tight control. Fourier Transform Near-InfraRed spectroscopy (FT-NIR) is an efficient technique to perform accurate quantification of the different components in DES coating solutions.

A prerequisite for a successful biotherapeutic formulation is one where the protein is stable and correctly folded. The new technique of dynamic multi-mode spectroscopy (DMS) was used to study the stability of a monoclonal antibody biotherapeutic formulated in acetate and lactate buffers. The samples were measured several times over a period of weeks and it became apparent that the antibody behaved differently as it aged in the two formulations, with the lactate formulation imparting greater robustness than the acetate.

Spectral measurements to 153 nm can be achieved easily and economically with the high-sensitivity Maya2000 Pro with Extra-Deep-UV Option. Nitrogen purging of the spectrometer helps to mitigate water and oxygen absorption in the vacuum ultraviolet.

Raman Chemical Imaging technology is able to identify and differentiate multiple components in complex formulated nasal spray suspensions based on chemical makeup. Particle size distribution statistics for the ingredient of interest are produced in a rapid, objective and semi-automated manner. Both solitary and aggregated drug particle sizing information may be obtained.

The analysis of toy samples for toxic trace elements has been undertaken for many years. However, a number of recent cases of toys contaminated with heavy metals has attracted global media attention. This has resulted in an increase in the number of toy manufacturers performing their own 'in-house' testing. This 'in-house' testing is not only to ensure regulatory compliance; it is also proving significantly more cost effective than outsourcing the analysis.