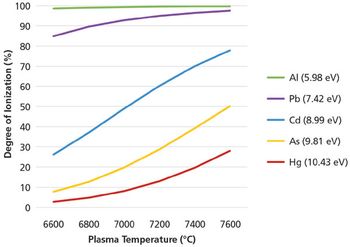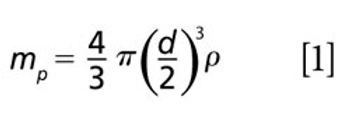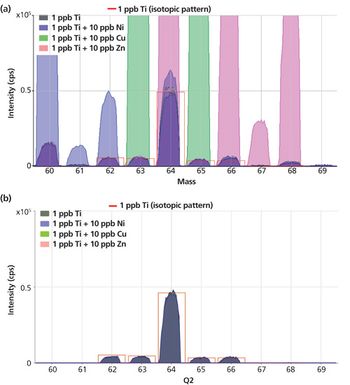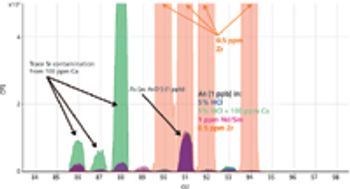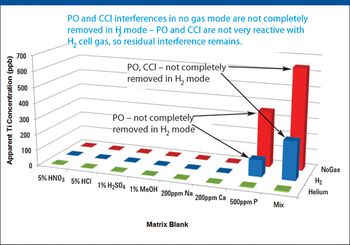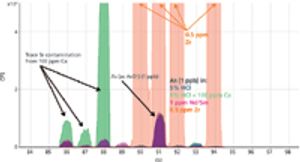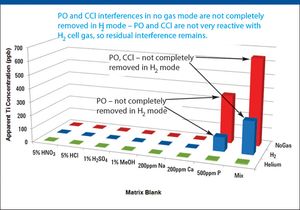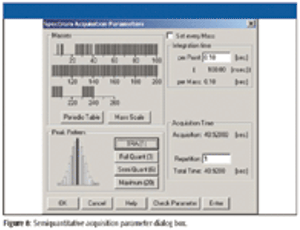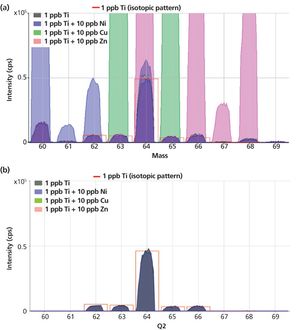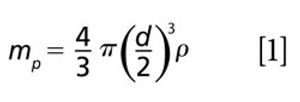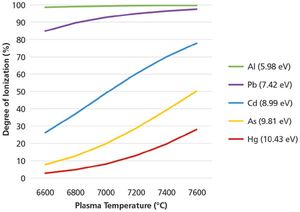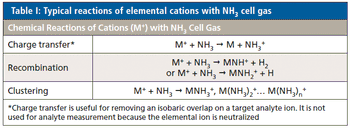
Method setup and optimization steps are explored to illustrate how an ICP-MS/MS method can be defined and tested to ensure consistent performance. Users can benefit from improved interference removal performance without the complex method development inherent in the use of ion-molecule reaction chemistry