
The polymer processing can impact FTIR-ATR spectra, and if these processing factors are not considered may lead to incomplete or inconsistent results.

The polymer processing can impact FTIR-ATR spectra, and if these processing factors are not considered may lead to incomplete or inconsistent results.

Using an automated FT-IR reflection sampling accessory, the surface of a polymer-coated aluminum film was analyzed. Spectral results were used to investigate chemical uniformity across the sample area.


Data show that for applications where increased absorbance leads to added sensitivity, a variable angle ATR offers a powerful tool for making FTIR measurements.
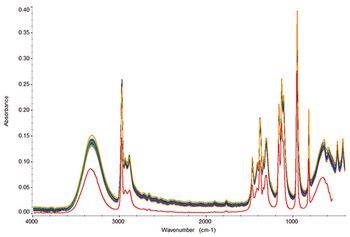

Ocean microbiological activity of chemical species present in the sea surface microlayer was investigated using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. We observe chemical differences before and during the peak of an induced phytoplankton bloom.

Protein secondary structure during thermal unfolding and aggregation is readily acquired using IR spectroscopy and a temperature-controlled Mid-IR transmission accessory.
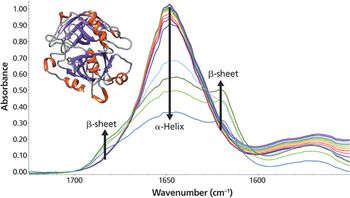
As the temperature increases, significant changes in the myoglobin secondary structure are observed. Between 25 °C and 70 °C, the 1649 cm-1 peak height decreases and linewidth increases. These changes in the amide I band reflect increased protein structural disorder. A temperature increase from 70 °C to 75 °C causes a drop in the 1649 cm-1 band intensity. Simultaneously, two peaks grow in at 1683 and 1637 cm-1. These changes indicate conversion of random coil/α-helix to intermolecular β-sheet. Further conversion to β-sheet is observed as the temperature rises to 90 °C. The final β-sheet structure is an insoluble aggregate. This aggregation process is not reversed when the temperature is driven back to 25 °C.

An infrared transmission spectrum of lens tissue was collected and compared with a sample spectrum collected in the FT-IR sample compartment. Benefits of using an integrating sphere are discussed.

Measuring the transmission of diffuse samples such as paper or filled polymer films requires an integrating sphere to obtain accurate transmission values and useful chemical information, because the IR light is scattered as it passes through the sample. An integrating sphere serves as a collection device for the scattered light.
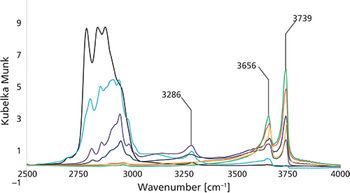
The thermal treatment of a grafted Sn-SiO2 catalyst was monitored in situ using diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS).
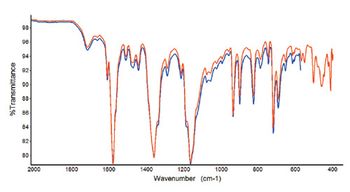
Experimental data show the crystal dimensions of an ATR-FT-IR sampling accessory influence the usable spectral range. An expanded range germanium crystal is introduced for the measurement of high refractive index samples.
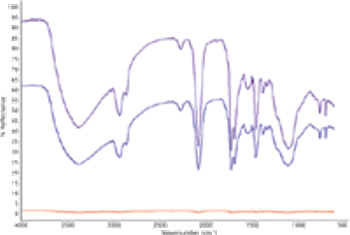
The approach to infrared measurements of diffusely scattering materials often is dictated by the objective of the analysis. Spectral data from three different mid-infrared reflectance sampling accessories are contrasted.

In ATR/FT-IR, magnified visual monitoring of a sample benefits many applications. For micro-sampling and defect analysis, viewing capabilities decrease overall measurement time by allowing the user to locate the desired sampling area quickly and enhance confidence in the collected data by assuring the sampling point. Visual changes in the sample also may be easily monitored during testing. As an example application, the ease of micro-sampling is shown through fiber analysis and the results are discussed.

Published: February 1st 2022 | Updated:

Published: September 1st 2021 | Updated:
Published: September 1st 2012 | Updated:
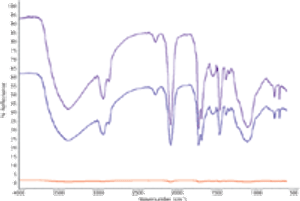
Published: September 1st 2011 | Updated:

Published: September 1st 2009 | Updated:
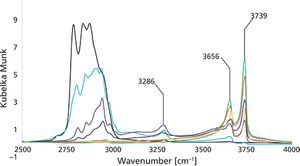
Published: September 1st 2014 | Updated: