
With analytical advances, the clinical practice threshold for lead has dropped from 60 to 5 μL/dL.

With analytical advances, the clinical practice threshold for lead has dropped from 60 to 5 μL/dL.

This study explores the possibility of measuring the metal content of crude oils using EDXRF in samples as received in both the direct and indirect excitation mode.

A look at the implementation of the new United States Pharmacopeia (USP) chapters and the International Conference for Harmonization (ICH) guidelines for elemental impurities from an historical perspective, providing insight into the changes and considering the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead as the industry embraces the new methodology.

How to select the optimum atomic spectroscopic technique for orally delivered drugs, based on the J-values described in the validation protocols outlined in USP Chapter

How much lead is in our daily lives? We take a look at current research concerning lead in the United States food supply and investigations using ICP-MS into the measurement of high concentrations of lead in food.

An evaluation of the ability of XRF spectrometry to perform elemental impurity analysis of 12 elements in various pharmaceutical materials

Over the last few decades, elemental imaging using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) has emerged as an important tool in the study of solid samples from a variety of scientific disciplines, including medicine, biology, and geology. This article highlights recent analytical trends towards high-speed, high-spatial resolution, multi-elemental imaging that became possible with advances in both LA and ICP-MS technology, including the design of fast-washout ablation cells and commercialization of high-speed ICP-MS such as time-of-flight mass analyzers (TOFMS), This study will demonstrate the new imaging approach by coupling LA with an-ICP-TOFMS system (icpTOF from TOFWERK, Thun, Switzerland) on two application areas: quantitative mapping of trace elements in a sulfide mineral (sphalerite), and imaging of the distribution of a chemotherapy drug (Cisplatin) in a rat kidney. High-performance LA-ICP-TOFMS provides researchers with an effective new tool to study biological and geological processes, with much greater speed and in much greater detail than previously possible with conventional ICP-MS instrumental designs.

The National Nanotechnology Initiative defines engineered nanomaterials (ENM) as those with dimensions of 1–100 nm, where their unique characteristics enable novel applications to be carried out. ENMs often possess different properties than their bulk counterparts of the same composition, making them of great interest for a broad spectrum of industrial, commercial, and health care uses. However, the widespread application of ENMs will inevitably lead to their release into the environment, which raises concerns about their potential adverse effects on the ecosystems and their impact on human health.

October’s AP column highlights a team of geochemists at the University of Houston who have been developing methods to streamline multi-element analysis for a more complete fingerprinting of oils by using one sample preparation method utilizing a single reaction chamber microwave digestion system and then analyzing these solutions for major, and minor elements by ICP-OES and low abundance trace elements by triple quadrupole (QQQ) ICP-MS. Results to date using this approach have shown that complete elemental recovery and removal of organic matrices can be achieved safely and that up to 57 elements can be determined in oils with good accuracy and precision. Removal of organic matrices during digestion not only helps to limit the formation of polyatomic spectral interferences, but improves instrument stability and reduces carbon build in the sample introduction and interface regions, which have traditionally plagued “dilute and shoot” methods.

This month’s column will describe a novel ED-XRF system, which utilizes a combination of a Bragg polarizer, used simultaneously with a direct excitation source, together with a novel, highly annealed pyrolytic graphite (HAPG) crystal as a band-pass filter. By selection of the optimum configuration, it will allow for high precision of minor and major elements across a wide wavelength range and/or lower detection capability for smaller groups of elements from potassium to manganese. To show the practical benefits of this technology, this study will focus on these performance metrics for the determination of titanium in polymer samples, together with the multielement analysis of high purity graphite using the ashing sample preparation method. In particular, it will be shown that the improved performance for graphite will allow for lower sample weights to be used resulting in significantly shorter ashing times, which is a requirement for high sample workload laboratories and process control applications.

Selecting the correct wavelengths or isotopes and optimizing flame, furnace, or plasma conditions can seem a daunting task for a novice user, with a multitude of opportunities to introduce errors and generate poor quality data. While most elemental analysis instruments have intuitive operating software, they lack the intelligence to guide the operator through the early stages of method development and overcome associated problems along the way. This study describes an automated, intelligent approach to method development for trace element analysis using optical emission spectroscopy, and exemplifies this capability with a suite of real-world sample matrices.

This month’s column presents an overview of the new 11th edition of the ACS Book of Reagent Chemicals and discusses some of the updated methods, and new procedures being adopted. In particular, we focus on new plasma based spectrochemical methodologies for the determination of heavy metals in reagent chemicals, which have replaced the 100 year-old test using precipitation and colorimetric measurement of the metal sulfides.

This article offers some suggestions for routine maintenance and offers guidance to troubleshoot common problems encountered in the ICP-MS sample introduction area.

This installment describes the development of two novel X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques that enable the rapid analysis of samples using handheld instrumentation for remote applications. Both techniques can be applied to unprepared samples in the field, which is a highly favorable characteristic in many applications since the time required for laboratory-based sample preparation is avoided.

A novel adaptation to inductively coupled plasma–mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS), mass cytometry provides researchers with a tool to study the complexity of biology at the single-cell level.
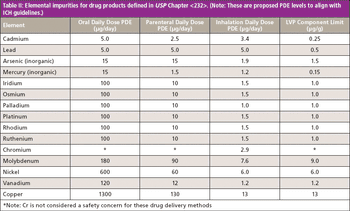
This installment evaluates the application requirements for the determination of 15 elemental impurities in pharmaceutical materials as described in the new United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Chapters and and offers suggestions about which atomic spectroscopic technique might be the most suitable to use.

An application of atomic spectroscopy for experiential learning through archaeological investigations is presented.


A new sodium peroxide fusion method is described, as well as the conditions for inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry, and a list of the accuracy and precision measurements for all prepared samples.

A critical review of the main developments in instrument technology, calibration, and sample preparation that have made it possible to determine low sulfur concentrations in fuels followed by a discussion of strategies to minimize spectral interferences related to sulfur determination by ICP-MS, such as collision–reaction cells, high-resolution mass analyzers, and the interference standard method.

Evaluation guidelines and important factors for laboratory scientists to consider when choosing an inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry instrument

The main areas of training necessary for a good foundation in the analytical methodology of XRF spectroscopy are discussed.

A case study demonstrating the use of an ICP-MS system to detect low levels of beryllium in urine, using a simple but highly sensitive method

A historical account of Talbot's contributions to spectroscopy

ICP-OES can provide assistance in setting up an EPA 200.7 soil analysis method.

How to reduce plasma-, matrix-, and solvent-induced polyatomic interference by bleeding a collision–reaction gas into the tip of the interface skimmer cone

This tutorial on the chemical principles involved in dissolution, stability, and matrix components will help you successfully analyze a broad spectrum of metal analytes with ICP-MS using liquid introduction or flow injection.

For any given spectrometric system with a defined resolution and excition results, the background equivalent concentration is a characteristic of spectral lines.

Wastewater from coal-fired power plants is linked to a wide range of environmental and human health concerns. Measuring low levels of toxic trace metals in these wastewaters is complicated, however, by high levels of interfering matrix elements. A new EPA method using ICP-MS addresses this analytical challenge.

The advantages and disadvantages of measuring mercury with cold vapor atomic absorption spectroscopy, cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy, and direct analysis by thermal decomposition are explained.