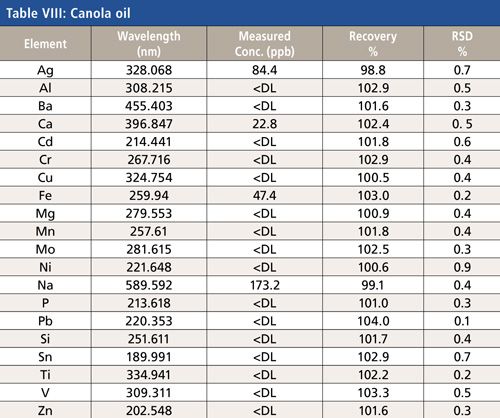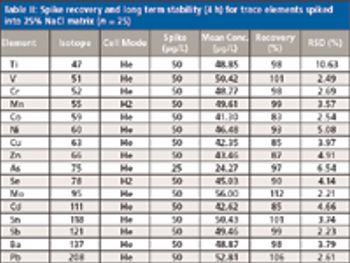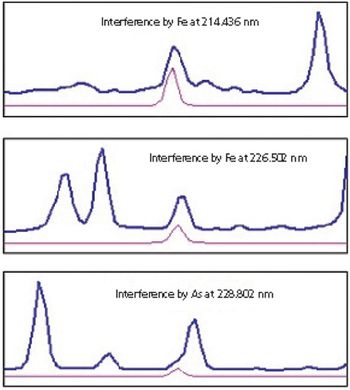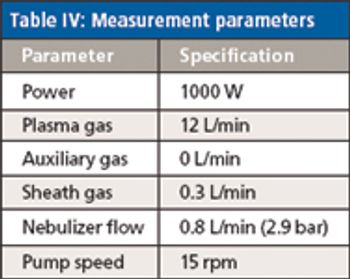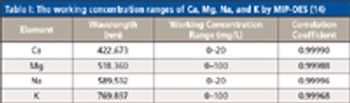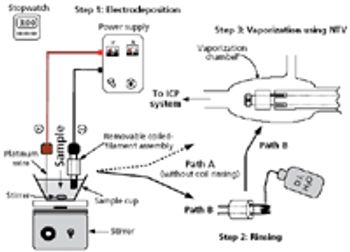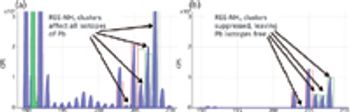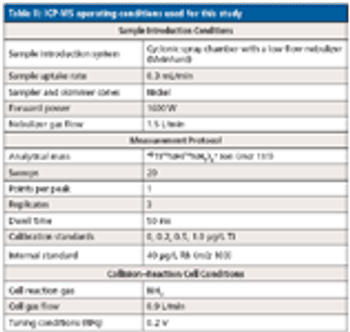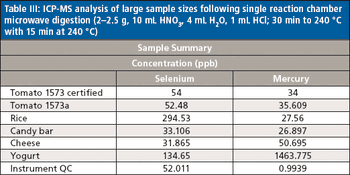
Low-level analysis of food matrices has placed a demand on manufacturers, testing laboratories, and instrumentation vendors worldwide. Stricter regulations, better analytical instrumentation, and greatly improved sample preparation (preanalytical) techniques have focused efforts to simplify and standardize these analyses. Often overlooked, the preanalytical step determines the quality of the resulting data and requires careful attention to a number of details, including sample size, digestion parameters, and the level of detection needed.