
The USP proposes the use of analytical techniques capable of measuring impurities at the specified limits with optimal selectivity, sensitivity, simplicity, and robustness.

The USP proposes the use of analytical techniques capable of measuring impurities at the specified limits with optimal selectivity, sensitivity, simplicity, and robustness.
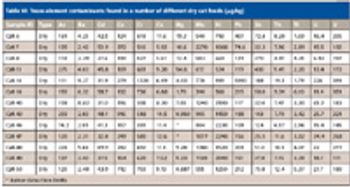
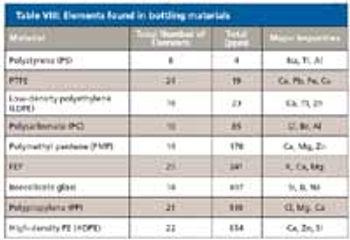
Part I of this two-part article focuses on the raw materials used in pet food manufacturing and all the potential sources of contamination.
Inductively coupled plasma (ICP) spectroscopy and ICP–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) provide an interesting set of similarities and contrasts.
Technology in the manufacture of instruments has evolved by leaps and bounds in the past few decades. The capability of these instruments to measure and quantify concentration at picogram levels has made the analyst more aware of trace contaminants unintentionally introduced during analysis. By raising awareness of contamination issues and sources, it is hoped that analysts can take an active role in reducing error in their ICP and ICP-MS analyses.
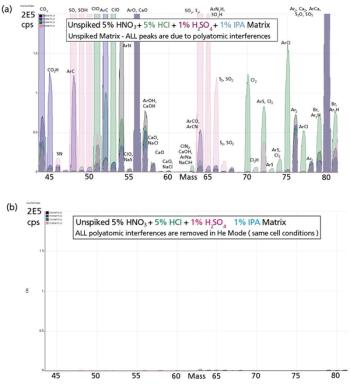
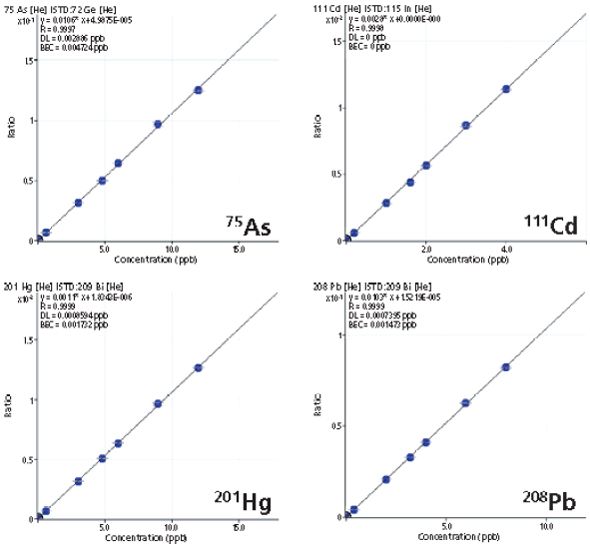
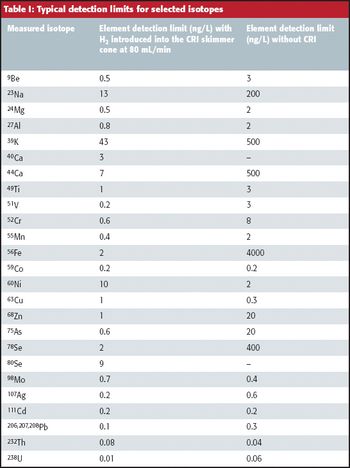
Almost all current quadrupole ICP-MS systems use collision/reaction cell technology to reduce polyatomic interferences, but the effectiveness of these devices for the removal of unexpected interferences remains a contentious issue. Here, we demonstrate that helium cell mode operation on the instrument described provides an opportunity for analysts to report reliable multielement data from complex, variable, and unknown matrices, using a single He mode method for all required analytes.
Recently, the attention of the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) has turned to the elemental impurities found in drug products. Before its most recent activities, USP methods for determining elemental impurities have relied upon outdated methodology that is qualitative, relatively insensitive, and can be used only for the determination of a subset of the toxic elements that should be quantified (USP Chapter <231> - Heavy Metals). Proposed changes have been made that utilize modern analytical techniques for measuring a larger number of heavy metals at toxicologically relevant concentrations. As of this publication, the expected date for implementing changes to USP Chapter <231> is September 2013.
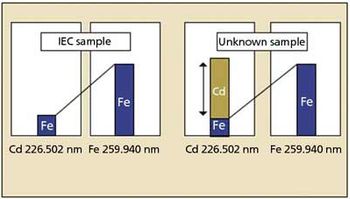
With ICP emission spectrometry, many spectral lines are emitted for each element. The fact that spectral lines for samples containing several elements can overlap is well known as spectral interference. For this reason, it is necessary to use a spectrometer with a resolution over a certain level. Even then, spectral interference might be possible. This article describes a way to measure water samples using inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy using a simultaneous instrument with a CCD detector and a software package that incorporates the knowledge of experienced analysts as a database, simplifying the selection and confirmation of wavelengths, to allow high precision and interference-free analytical results.

The determination of elements in oils and petroleum products is important to refineries, industrial processes, machinery, and transports. This article explores the analysis of fuel oils using ICP-MS for the routine determination of elements at low concentration levels in both clean and dirty fuel oil samples.
The determination of trace metals in volatile organic solvents is of utmost importance to prevent catalyst poisoning and final product contamination. This article discusses the need for the analysis of trace metals in volatile organic solvents and reviews the challenges and problems that have been traditionally associated with this type of analysis when performed using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). A new method is highlighted, combining ICP-MS with an advanced dual syringe pump sample introduction system. The unique capabilities of the technique to deliver direct, efficient, accurate, and contamination-free analysis of trace metals in volatile organic solvents are demonstrated in an application example.

Guest columnist Steven Wilbur discusses the elemental nature of ICP-MS and its strength as a universal quantifier, an aspect of the technique he believes has not received enough attention.

The authors discuss the use of ICP-MS as an effective chromatographic detection method that is relatively easy to interface to gas chromatography for gas analysis.

Columnist Ken Busch discusses the ability to "dial in" resolving power as needed in newer trap mass analyzers, which shows promise for speciation analysis in ICP-MS with chromatographic separation of sample components.
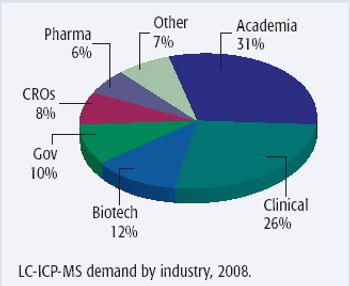
The coupling of HPLC with ICP-MS is a relatively new technique that combines two very well established analytical methods. The combination of these analytical methods provides what could prove to be a very useful technique in clinical analysis. The total LC-ICP-MS market amounts to only a few percent of the overall ICP-MS market, but it is rapidly developing into a significant niche market.

The authors discuss the use of ICP-MS as an effective chromatographic detection method that is relatively easy to interface to gas chromatography for gas analysis.
The author looks at methods used to detect the presence of contaminants in biodiesel.

The authors present an overview of the chemical analysis process.
The authors discuss the ICP-MS method, its usability in environmental and geological analysis and relevant regulations, and how to address its limitations.
Elemental analysis of food substances presents a challenge because of the wide variety of food types and range of concentrations that need to be analyzed. This article discusses the analysis of a variety of food matrices with a single digestion procedure and instrumental method.
The authors discuss a new approach to the control of spectral overlap interferences in inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry.

In this article, the author describes the components available for the "front end" of an inductively coupled plasma spectrometer and discusses the pros and cons of each.
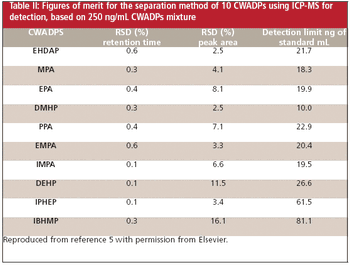
Research regarding detection of chemical warfare agents has become vital for finding solutions that will help reduce the threat of these substances. This article looks at the use of collision cell ICP-MS for the analysis and detection of organophosphorus agents.

While inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is capable of part-per-quadrillion (ppq) detection limits under ideal conditions, most applications do not require this level of sensitivity and do not justify the cost associated with achieving it. Practical sensitivity in ICP-MS is determined not by instrument signal-to-noise ratio, but rather by controlling interferences and matrix effects in real samples. Understanding the sources of these effects and their management is critical in determining the most practical way to achieve specific data quality objectives.
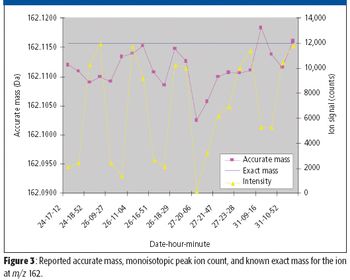
With electron ionization (EI) used in most gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) applications, the molecular ion typically is broken apart into multiple fragment ions during the EI process.

In drug discovery, determining information about the extent of metabolism and the elucidation of metabolite structures is a vital step for lead optimization and drug scaffold refinement. The identification and characterization of metabolites plays an important role in both the drug discovery and development phases, as unsuitable pharmacokinetics (bioavailability and drug distribution), toxicity, and adverse drug reactions might be linked to metabolic instability. Historically, metabolite identification was carried out after a compound had been chosen for drug development. However, to reduce candidate failures attributed to toxicity effects, many pharmaceutical companies now conduct these experiments in the earliest phases of candidate drug selection.
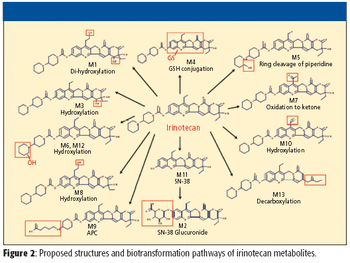
In this article, the authors evaluate the use of multiple mass defect filters on metabolite identification data from a hybrid mass spectrometer. The study also investigates the use of higher energy collisional dissociation for structural elucidation in metabolite identification experiments.