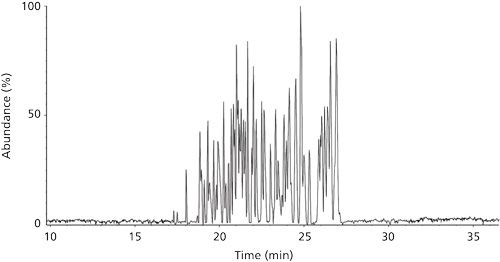
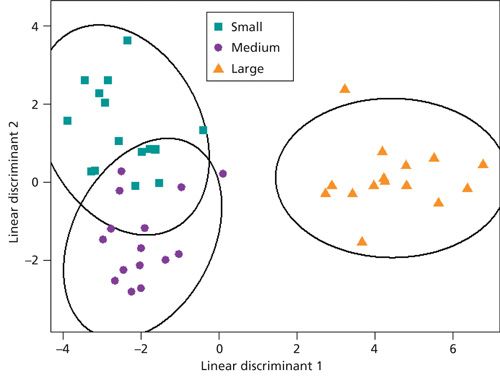
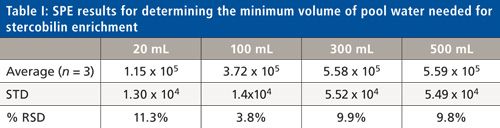
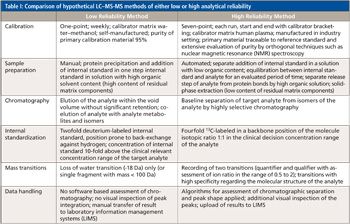
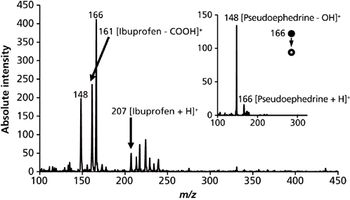
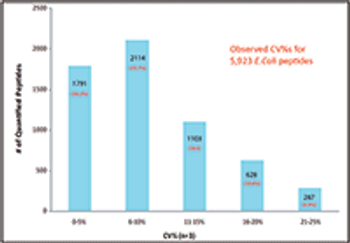
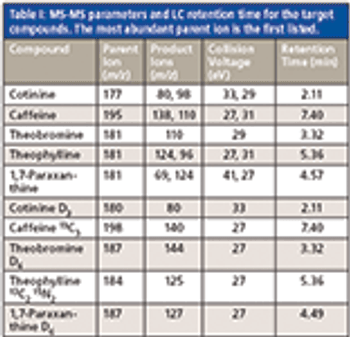
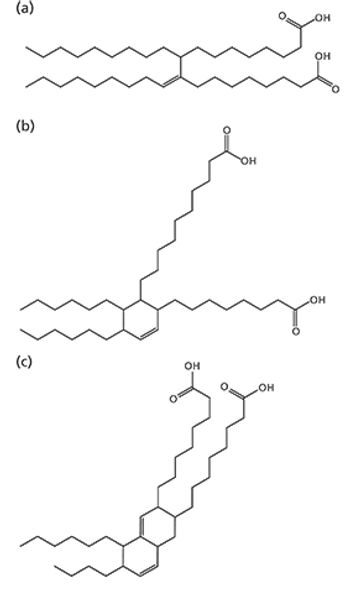
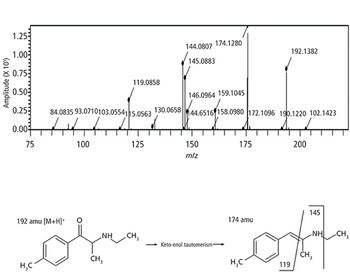
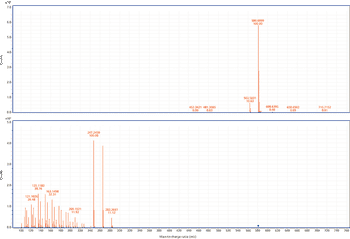
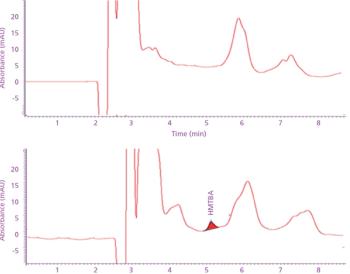
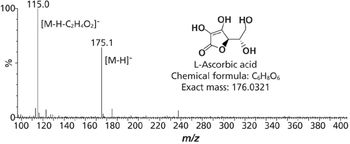
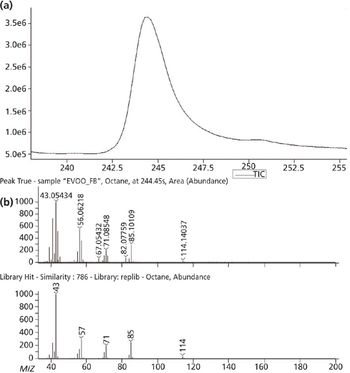
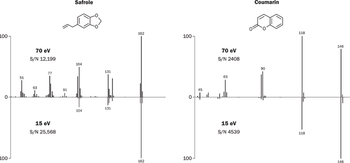
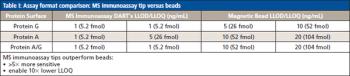
We recently spoke to Gary Duncan and Wendy Russell of the Rowett Institute of Nutrition & Health in Aberdeen, Scotland, about the significance of phytochemical bioavailability to human health and the important role of liquid chromatography linked to tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS-MS) in their research.