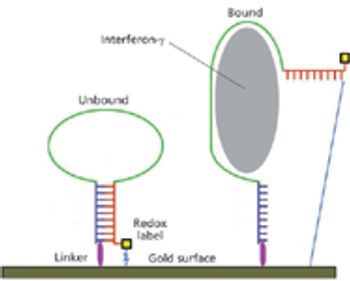
More-specific, sensitive, rapid, and portable spectroscopic methods detect biological threats.

More-specific, sensitive, rapid, and portable spectroscopic methods detect biological threats.

The revisions to GMP Annex 11 are examined in terms of the impact on computerized spectrometry systems operating in regulated GMP laboratories.
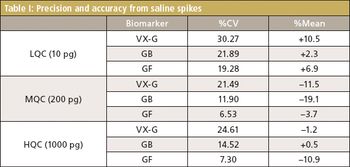
A fluoride-regeneration approach enables biomonitoring of chemical warfare nerve agents.
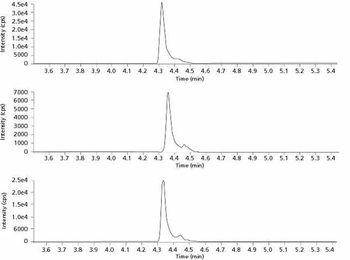
Increases in vitamin D testing frequency have required more rapid and cost-effective solutions for determining vitamin D levels in plasma. This LC–MS method was adapted for use with core-shell columns to achieve run times of less than 4 min.
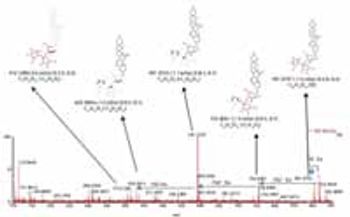
Most plants used in traditional Chinese medicine must be processed before their medicinal usage; hence the effective ingredients may differ from those in the freshly harvested plant extracts. In this work, we present a fast and generic approach using sub-2-?m liquid chromatography–time-of-flight–mass spectrometry (sub-2-?m-LC�–TOF-MS) coupled with multivariate statistical data analysis to systematically profile ingredient changes between fresh and processed samples of huang jing.
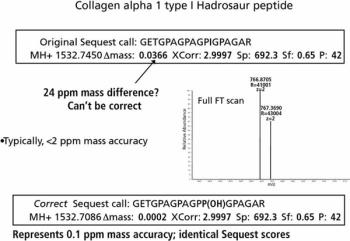
Fossilomics uses MS to extract amino acid sequence information from subpicomole quantities of protein and peptide fragments that remain in certain fossil samples. The sequences are compared to databases and validated with search statistics and high-confidence sequences. The validated sequences can then be used to place the fossils on the evolutionary tree.
The inclusion of time-resolved selected reaction monitoring (SRM) functionalities into mass spectrometer control software allows large numbers of peptides to be quantified using short LC–MS-MS methods.
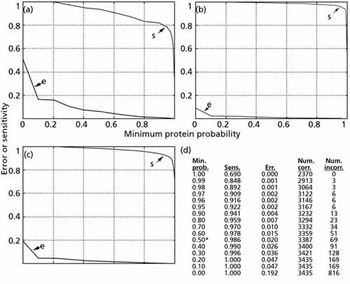
This new data-management method is specifically designed to handle the large amounts of data produced in proteomics studies. Experimental methods and data are presented from a recent study conducting proteomics profiling of Schizosaccharomyces pombe to demonstrate the effectiveness of the data management solution. The results demonstrate enhanced data search speeds as well as effective data analysis.
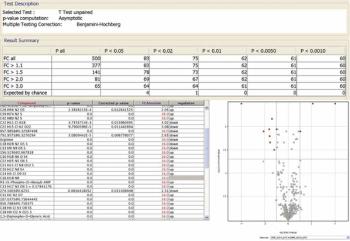
The metabolomics workflow described here combines untargeted (discovery) quadrupole time-of-flight (Q-TOF) liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS), targeted (confirmation) triple-quadrupole LC–MS-MS, and sophisticated data mining as an effective means to elucidate metabolite changes.

Analyses performed with hybrid mass spectrometers yield large volumes of complex data at high speeds and resolution.
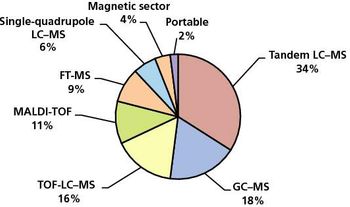
The spectroscopy market has benefited from the general return to global economic growth.
There are currently more than 1000 pesticides in use worldwide in the production of foodstuffs. There is a significant risk to human health and the environment due to increased pesticide use, poor agricultural practices and illegal use.
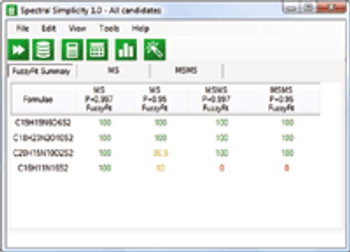
What tools can MS practitioners use to obtain unambiguous answers from unknown spectra?

This month's column describes the use of mass spectrometers in submarines and their more recent use for direct sampling of compounds dissolved in water at ever-increasing depths.
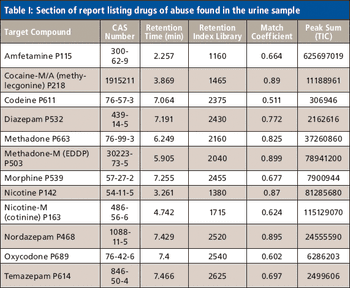
The analysis of urine for drugs of abuse via chromatographic methods is commonplace but can be complicated by high matrix effects and frequent coelution. Novel time-of-flight mass spectrometry in combination with sophisticated deconvolution software was tested and found to provide increased confidence in results due to the high sensitivity and quality of spectra achieved.
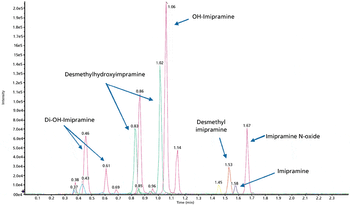
A new time-of-flight mass spectrometer was evaluated for performing simultaneous metabolic stability measurement and metabolite identification with ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography. Six representative compounds (clomipramine, diclofenac, imipramine, haloperidol, verapamil, and midazolam) were incubated in rat liver microsomes at a more physiologically relevant substrate concentration (1 ?M). High-resolution full-scan and product-ion spectra were acquired in a single injection using generic methodology. Quantitative clearance of the parent was measured using the full-scan data. Major metabolites were identified using the accurate mass product ion spectra. High scanning speed allowed for a sufficient number of data points to be collected across the chromatographic peak for quantitative analysis. Sensitivity was sufficient for obtaining meaningful kinetics with a 1 ?M initial substrate concentration.
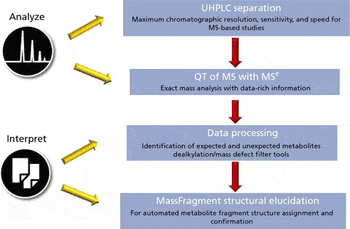
An effective metabolite identification study should ideally include both qualitative and quantitative information that for both identifying metabolites, and determining the rate of clearance and the metabolic routes of the parent drug. Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) is considered the standard analytical technique for metabolite identification studies. To date, however, qualitative and quantitative information has always been obtained from two separation platforms: quadrupole time-of-flight (QTof) MS for the exact mass full-scan qualitative study, and tandem quadrupole MS for the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) quantitative study. With advancements to QTof instrumentation, specifically, recent improvements in sensitivity and dynamic range, it is now possible to perform both qualitative and quantitative experiments on a single QTof mass spectrometer. This article describes a workflow that allows simultaneous qualitative and quantitative metabolite identification studies to be..

A high-throughput LC–MS method using core-shell UHPLC columns to screen for a panel of 11 drugs of abuse (expanded SAMHSA) was developed. The corresponding SPE method allowed the reproducible separation and quantitation of these 11 components in less than 2 min. This method demonstrates the power of new-generation HPLC media as well as some of the factors one must consider when developing such methods for LC–MS analysis.
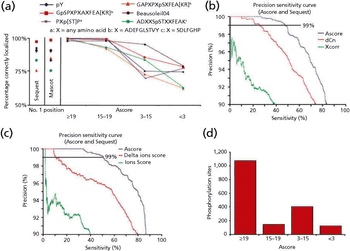
The development of a phosphorylation probability scoring tool in an automated data search engine resolves ambiguity in site localization when compared to manual methods.
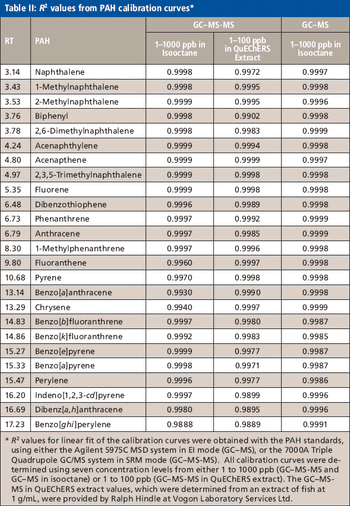
The authors look at the use of QuEChERS in the ongoing testing program in the gulf.
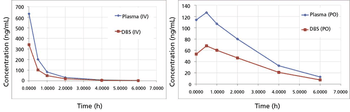
This article introduces the advantages of accurate mass high-resolution mass spectrometry LC–MS (HRMS) coupled to the dried blood spot (DBS) technique for fast PK applications in a discovery environment. Compared with the established norm of plasma bioanalysis using triple quadrupoles, HRMS coupled to DBS is a viable alternative. The benefit is access to critical new information (HRMS bioanalysis) and significantly less stress on the animal (DBS), both factors that potentially improve the quality of early PK data.
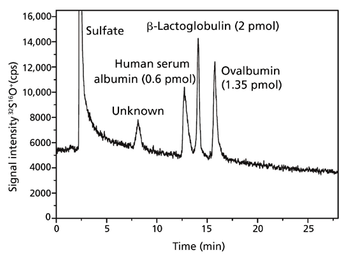
With recent research, the University of Oviedo's analytical spectrometry research group has taken a step closer to the absolute quantification of proteins. Quantification based upon isotope dilution mass spectrometry of sulfur is hampered by gas-based polyatomic interferences. By implementing a quadrupole inductively coupled mass spectrometer with collision/reaction cell technology, the group has been able to overcome the issues and has increased reliability while optimizing the efficiency of its analyses.

The amaZon series is the next step in Bruker Daltonics' family of ion trap mass spectrometers.
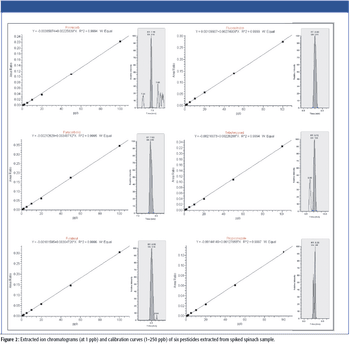
The increasing use of pesticide testing coupled with reductions in maximum permissible residue levels of pesticides in food have driven demand for fast, sensitive, and cost-effective analytical methods for high-throughput screening of multiclass pesticides in food. Detection of 510 pesticides at low parts-per-billion levels can be achieved within minutes using orbital trap technology. The high resolving power of these systems enables accurate mass confirmation of all compounds, including isobaric pesticides. This article will provide an overview of current legislation and illustrate how mass spectrometry instrumentation can enable fast and accurate pesticide screening.
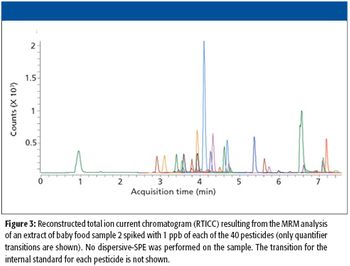
The safety of the food that our children eat is a global concern. Regulations are in place that limit the maximum level of pesticides that can be present in food meant for children, and methods to detect levels well below those limits are needed to ensure the safety of the food supply. Combining the speed and separation efficiency of ultrahigh-pressure liquid hromatography (UHPLC) with the sensitivity and selectivity of triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry (MS)-MS results in a method that can deliver ultralow quantification of pesticides in baby food, with limits of detection more than an order of magnitude below the allowed maximum levels.