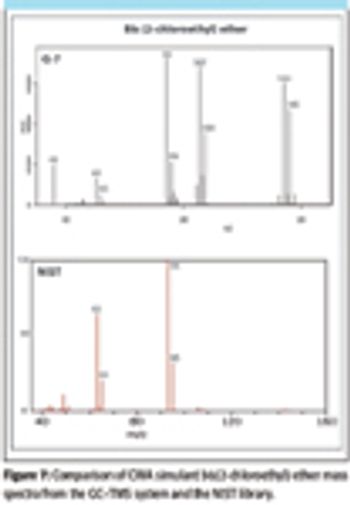
In this article, methods developed for rapid, automated detection of CWAs and TICs using a low thermal mass capillary gas chromatograph coupled to a toroidal ion trap mass spectrometer (TMS) are presented.

In this article, methods developed for rapid, automated detection of CWAs and TICs using a low thermal mass capillary gas chromatograph coupled to a toroidal ion trap mass spectrometer (TMS) are presented.

This article discusses the analysis of a wide range of CWAs at current exposure limits and describes a number of recent beneficial developments in TD and associated analytical technologies for the identification and quantification of CWAs at these levels.

The authors demonstrate the capacity to separate petroleum-derived molecules having the same nominal mass in the mobility dimension using IM-MS spectrometry.
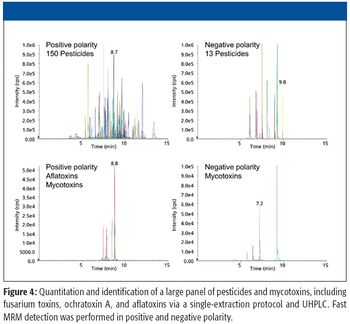
This article describes trends of using LC-MS-MS for multicompound analysis of food and environmental contaminants.
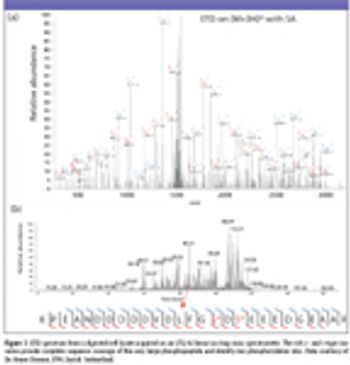
The authors discuss the use of electron transfer dissociation as a reliable tool in proteomic research, especially in conjunction with a linear ion trap, for sequence analysis of post-translationally modified and highly basic peptides.

This article describes the use of a microfluidic chip system, paired with a simple, automated interface to a wide range of mass spectrometers for both protein and small molecule applications.

The authors present a novel method for analyzing and characterizing complex proteomic samples using multidimensional liquid chromatography with an emphasis on the reproducibility of results generated in different laboratories.

The authors discuss the use of reversed-phase LC-MS for oligonucleotide characterization.
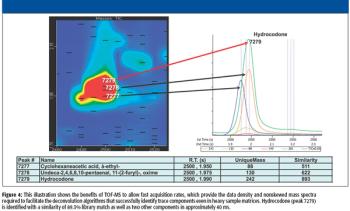
This article discusses the potential use and application of comprehensive multidimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry in forensic toxicology analysis for illicit drugs in urine without sample derivatization.
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a broadly used analytical technique that is often combined with some form of chromatography to provide a second dimension of separation. However, vendors recently have begun incorporating ion mobility separation (IMS) into high-end LC–MS instruments, thus providing an additional level of ion separation.

In the second installment of this tutorial, the authors explain the instrumentation for measuring naturally occurring stable isotopes, specifically the magnetic sector mass spectrometer.

Columnist Ken Busch discusses the lack of a formal ethics training program for physical scientists and the need for some type of self-regulation within the field.

The authors discuss the use of electron-capture dissociation coupled with a linear ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometer to investigate the structure of human transferrin.

At a symposium attended almost exclusively by practitioners of chromatography, the one thing they all wanted more of was mass spectrometry information.

The authors discuss the challenges presented by the many new applications of mass spectrometry.
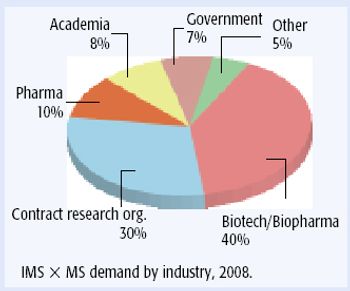
The authors discuss the emergence of liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry as a complementary method to traditional methodology used for clinical applications.

The author discusses the impact of fast chromatography methods on the performance of high-resolution mass spectrometry.
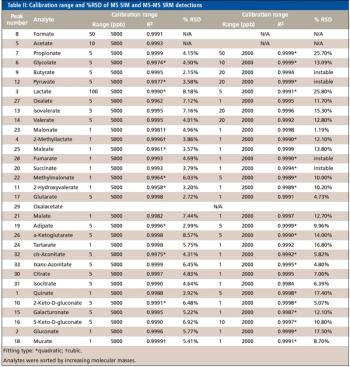
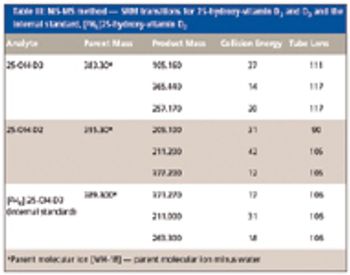
This article describes an ion chromatography–mass spectrometry (IC-MS) method for profiling low molecular mass organic acids in consumer beverages and biomass used in biofuel production.
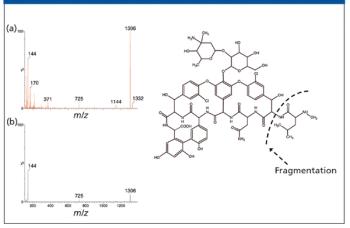
The authors discuss the changes that have taken place in the last two decades regarding the users and capabilities of LC–MS.
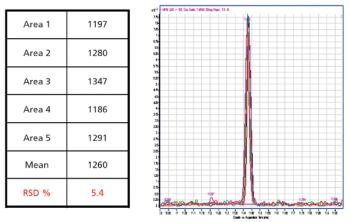
This article provides an overview of the instrument platforms, tools, and workflow for analyzing pesticides.

In the fourth part of this five-part series, columnist Ken Busch discussed weighted regression analysis as used in QMS. In this final column, he adds an additional explanation.

Data are presented for a pH-adjustable liquid UV-matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix for mass spectrometry analysis. The liquid matrix system possesses high analytical sensitivity within the same order of magnitude as that achievable by the commonly used solid UV-MALDI matrices but with improved spot homogeneity and reproducibility. The pH of the matrix has been adjusted, achieving an on-target pH range of 3.5?8.6, which has allowed for the performance of a tryptic digest within the diluted pH-optimized liquid matrix.

The authors introduce a compact ECD device coupled to a linear ion trap time-of-flight instrument, and use it to analyze protein phosphorylation in both offline and online modes.
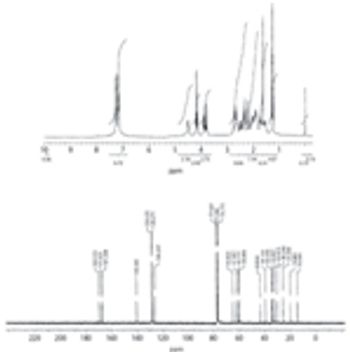
In this article, the authors take a look at the identification, synthesis, and characterization of impurities in Ramipril tablets.

This article describes the ability to increase the sensitivity for a target compound in the presence of high-level background impurities by removing the dosing vehicle using a high-field asymmetric waveform ion mobility spectrometry gas-phase separation before mass spectrometry analysis.