
In this edition of “Inside the Laboratory,” we profile the Schultz Laboratory at The Ohio State University in Columbus, Ohio, speaking with Zac Schultz, Spencer Witte, Nishadi Nadeeshani, and Renee Romano about their work.

In this edition of “Inside the Laboratory,” we profile the Schultz Laboratory at The Ohio State University in Columbus, Ohio, speaking with Zac Schultz, Spencer Witte, Nishadi Nadeeshani, and Renee Romano about their work.

Top articles published this week include an interview with our Emerging Leader in Molecular Spectroscopy award winner Lingyan Shi, a mini-tutorial highlighting practical workflows and innovative applications, and an inside look at single-particle ICP-TOF-MS.

Researchers at Tianjin University of Technology develop a rapid, in situ technique for identifying adulteration in starch sausages using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy.

Discover the latest advancements in medical devices and artificial intelligence, focusing on the transformative impact of IoMT devices in healthcare.

A recent study highlights novel analytical techniques for phosphorus detection, enhancing pollution control and sustainability in environmental monitoring.


A sweeping review, “Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: A Half-Century Historical Perspective” traces the evolution of SERS from its foundational experiments in the 1970s through the nanoscience era and modern high-spatial-resolution techniques.

In this final interview segment with Lingyan Shi, she discusses the challenges of developing multimodal metabolic nanoscopy systems, and where these systems could be applied in the future.

A review article from researchers at Liaocheng University explores the challenges of applying vibrational spectroscopy techniques to food authentication.

An analytical method was established for determining the contents of 17 impurity elements in aluminum nitride by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. The experiment investigated a dissolution method for samples, working conditions of the instrument, analytical spectral lines, matrix interference and correction methods, and detection limits.

Here are ten main unsolved problems in vibrational and atomic spectroscopy, each accompanied by a tutorial-style synopsis suitable for advanced practitioners or graduate-level students. Each of these tutorials, spanning advanced spectroscopy modeling, chemometrics, machine learning (ML) interpretability, and standardization, consists of a descriptive article. Each piece is well-referenced (with detailed matrix equations, radiative transfer models, chemometric derivations, and so forth), and includes the following. • Special focus on each topic—including mathematical derivations in matrix notation. • Conservative, verifiable content anchored to established reference sources. • Appropriate tutorial article structure: Title, Summary, Abstract, Introduction, Theory with equations, Examples, Discussion & Future Research, and References.

In the second part of a three-part interview, Lingyan Shi recaps the award technical session that she chaired at the SciX Conference, highlighting the speakers she invited and what they discussed.

A new study reveals that resveratrol binds to peanut protein arachin through hydrophobic and hydrogen-bond interactions, enhancing protein stability and offering valuable insights for developing functional peanut-based food products.

Spectroscopy spoke to Benjamin Manard, Senior R&D Staff Scientist and the Group Leader of the Chemical & Isotopic Mass Spectrometry Group at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) as well as to Sarah Szakas and Jordan Stanberry, postdoctoral researchers at ORNL, regarding their work using examined single-particle inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SP-ICP-TOF-MS) as a novel technique for uranium particle isotope ratio measurements.

This curated collection of recent Spectroscopy magazine mini-tutorials highlights the latest analytical and data-driven innovations in vibrational spectroscopy. Covering NIR, Raman, O-PTIR, and related optical methods, the series emphasizes practical workflows, emerging machine learning integrations, and advanced chemometric techniques for real-world laboratory applications—from food and environmental monitoring to biomedical analysis and nanoscale imaging.

In this interview segment, Shi recaps her talk that she delivered at the SciX Conference and the four major technologies that she and her team developed over the past few years at the University of California, San Diego.
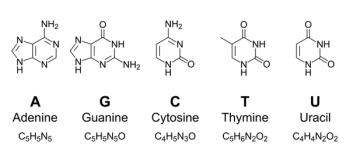
In a recent study, a team of researchers from Peking University and the National Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro and Nano Manufacture Technology have proposed a new method for identifying DNA nucleobases using a fusion of terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) and advanced deep learning techniques.
Discover how an improved wavelet denoising technique enhances methane detection accuracy in TDLAS systems, optimizing signal quality and reducing noise.

Top articles published this week include several video interviews from our coverage of the SciX Conference and an inside look at classical correction methods.

In this episode, podcast co-hosts Dr. Dwight Stoll and Dr. James Grinias talk with Professor Luis Colon about the influence his father had on his pursuit of science and his interest in materials development for chromatography.

In this video segment, Fay Nicolson discusses her career trajectory, from her time in graduate school to her time as a postdoctoral candidate to her time as an independent researcher.

In this interview segment, Karl Booksh dives deeper into a new technique called conformal prediction, and how his group has been applying it in their research.

In the second and final part of our interview with Rob Lascola, he addresses the main challenges in achieving accurate acidity measurements using Raman spectroscopy in complex, highly absorptive systems, as well as explains what he has learned about dissolution mechanisms, and how these insights can influence future nuclear processing strategies.

A new perspective from researchers at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology explores the evolving relationship between human expertise and artificial intelligence in polymer chemistry.

In this interview segment, Reddy discusses how O-PTIR combined with mid-infrared frequency comb technologies enhances both resolution and throughput in tissue analysis and how this integration address the limitations of conventional MIRSI approaches in clinical settings.

James Dudley Winefordner was a preeminent figure in analytical chemistry whose contributions to spectrochemical method development, instrumentation, and mentoring shaped generations of scientists.

Scientists have developed IR-Bot, an autonomous robotic platform that combines infrared spectroscopy, machine learning, and quantum chemistry to perform real-time analysis of chemical mixtures. The system promises to transform autonomous experimentation by delivering rapid, accurate feedback to guide chemical reactions without human oversight.

In this interview segment, Rafael Davalos discusses contactless dielectrophoresis, highlighting the utility of this technique not just in cancer research, but other application areas as well.

In this interview segment, Rob Lascola discusses how Raman spectroscopy complements other techniques in fuel dissolution and solvent extraction and what Raman can detect in off-gas streams.

In this video segment, Karl Booksh of the University of Delaware explains how his study highlighted a major improvement in classification accuracy using stacked models for differentiating exotic hardwood species.