
All News


ATR FT-IR shows polyethylene and polypropylene particles were common in facial scrubs and creams.

Top articles published this week include a tutorial about calibration transfer techniques and inter-instrument variability, a couple news articles about quantifying microplastics, and a feature on the “pressure to publish.”

Researchers from the U.S. Horticultural Research Laboratory’s Agricultural Research Service present a preliminary characterization of the citrus peel materials responsible for elevated high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet (HPLC-UV) chromatogram baselines from citrus peel extracts through the use of Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) and proton-nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) spectroscopy.

Chinese Academy of Sciences researchers combine spectroscopic methods with deep learning to classify microplastics at near-perfect accuracy.

Tracking Microplastics Across Air, Water, and Soil: What Spectroscopy Reveals About Global Pollution
A new study uses spectroscopic tools to analyze the spread and transformation of microplastics across water, soil, and air systems. Researchers also examined the limitations of global policies in addressing this multidimensional pollutant.

Researchers from Zhejiang University highlight how combining machine learning with spectroscopic imaging can transform biomedical research by enabling more precise, interpretable, and efficient analysis of complex molecular data.

Jiangnan University researchers map the evolution, challenges, and future of spectroscopy in preserving humanity’s shared legacy.


The findings suggest that bottling processes and PET containers are major contributors to beverage contamination, raising concerns about food safety and environmental pollution.

A new study by researchers from Spain and Brazil demonstrates that combining near- and mid-infrared spectroscopy with advanced statistical analysis can identify how growing site, harvest season, and clonal variation influence yerba mate’s chemical composition.

Researchers at the National Institute of Technology Rourkela have developed a highly accurate machine learning-assisted FT-IR spectroscopy method to detect and quantify sawdust adulteration in coriander powder, offering a fast and scalable solution to enhance food safety and authenticity.

A new study using infrared spectroscopy reveals that commercial beet sugar contains microplastic particles, raising concerns over food processing and packaging practices. Scientists identified various plastic types in sugar samples, including polyethylene and PET.

A recent study reveals that microplastics, primarily blue polyolefin fibers, are widespread throughout the western Arctic Ocean’s water column.
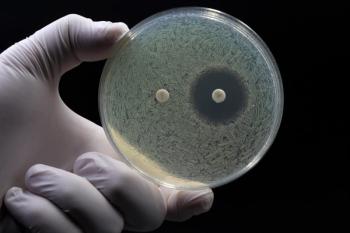
A research team from Putian University has developed a dual surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) approach to reveal detailed molecular changes in E. coli exposed to different antibiotics.
Researchers at Santiago de Compostela University (Santiago, Spain) find ultraviolet–visible (UV–vis) spectroscopy can detect and quantify post-COVID condition with high accuracy, paving the way for real-time clinical use.

A new study reveals that anthocyanin-rich fruit extracts degrade rapidly under sunlight but remain most stable in cold, dark storage.

Inter-instrument variability is a major obstacle in multivariate spectroscopic analysis, affecting the reliability and portability of calibration models. This tutorial addresses the theoretical and practical challenges of model transfer across instruments. It covers spectral variability sources—such as wavelength shifts, resolution differences, and line shape variations—and presents key standardization techniques including direct standardization (DS), piecewise direct standardization (PDS), and external parameter orthogonalization (EPO). We discuss the underlying mathematics of these approaches using matrix notation and highlight limitations that must be considered for reliable universal calibration.

Top articles published this week include an article about pioneering analytical chemist Charles Kenneth Mann, a tutorial about using Raman spectroscopy and machine learning for chemical monitoring, and an article about magma storage in Hawaii volcanoes.

Algerian researchers used X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Rietveld refinement and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy to show how long-term exposure to desert conditions causes microstructural and compositional degradation in solar panels, offering critical insights for improving monocrystalline photovoltaic (PV) durability in extreme climates.

Researchers in Brazil have demonstrated that near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, combined with chemometric modeling, can accurately and non-invasively analyze methane, carbon dioxide, and water content in high-pressure natural gas systems.


A team of researchers from universities in China have developed a rapid, smartphone-integrated sensor system that uses uranium-based fluorescent probes to detect pesticides and antibiotics in food samples with exceptional speed and selectivity.

Researchers have developed a fast, chemical-free method using near-infrared spectroscopy to accurately analyze the quality of dark chocolate, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional testing techniques.

A recent study explored a new robust, multi-technique approach to detect ferric oxide red in spices.

Showcase spectroscopy products that are advancing the future of analytical chemistry.

A new study reveals that as Hawaiian volcanoes evolve, their magma storage shifts from shallow crustal reservoirs to deeper mantle zones, offering critical insights into volcanic behavior and future hazard potential.


Researchers at the Central University of Venezuela (Caracas, Venezuela) have developed a robust, definite, and economical methodology for rapid and accurate quantification of theobromine and caffeine in cocoa beans extracts from Venezuelan cocoa using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)

