
All News


This Icons of Spectroscopy Series article features William George “Bill” Fateley, who shaped modern vibrational spectroscopy through landmark reference books and research papers, pioneering instrumentation, decades of editorial leadership, and deep commitments to students and colleagues. This article reviews his career arc, scientific contributions, and enduring legacy.

A recent study conducted by researchers from the Taiyuan University of Technology (China) explored a new way to detect pesticide residues at very low levels.
A research team in Japan has proposed a new principle, called the emission integral effect, to explain how mid-infrared passive spectroscopic imaging can detect blood glucose levels without invasive methods. Their findings suggest that dilute components like glucose may be more identifiable than concentrated ones when using this technique.

Researchers have developed a miniature non-invasive blood glucose monitoring system using near-infrared (NIR) technology. The compact, low-cost device uses infrared light to measure sugar levels through the fingertip, offering a painless alternative to traditional finger-prick tests.
Researchers from Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, present an approach using near-infrared absorbance and molar absorptivity to estimate blood glucose with a drawn blood sample—showing comparable performance to methods that apply principal components regression (PCR).

Spectroscopy is being used in speleology more frequently now. In this brief article, we highlight how it is being used and what spectroscopic techniques are being applied.

A recent study investigated the deterioration mechanisms of rammed earth materials from the UNESCO World Heritage Pingyao Ancient City walls.

Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy combined with aquaphotomics shows potential for a rapid, non-invasive approach to detect subtle biochemical changes in biofluids and agricultural products. By monitoring water molecular structures through water matrix coordinates (WAMACs) and visualizing water absorption spectrum patterns (WASPs) via aquagrams, researchers can identify disease biomarkers, food contaminants, and other analytes with high accuracy. This tutorial introduces the principles, practical workflow, and applications of NIR aquaphotomics for everyday laboratory use.

This explainer video highlights how nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is being used to improve the evaluation of vegetable oil quality.

This tutorial provides an in-depth discussion of methods to make machine learning (ML) models interpretable in the context of spectroscopic data analysis. As atomic and molecular spectroscopy increasingly incorporates advanced ML techniques, the black-box nature of these models can limit their utility in scientific research and practical applications. We present explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) approaches such as SHAP, LIME, and saliency maps, demonstrating how they can help identify chemically meaningful spectral features. This tutorial also explores the trade-off between model complexity and interpretability.

In this episode of Analytically Speaking, explore the intersection of forensic science and cannabis research with Brent Wilson as he shares insights on analytical chemistry and standards.
![Figure 3: Plots of lg[(F0-F)/F] vs. lg[Q] of ZNF191(243-368) by DNA.](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/0vv8moc6/spectroscopy/a1aa032a5c8b165ac1a84e997ece7c4311d5322d-620x432.png?w=350&fit=crop&auto=format)
To investigate its DNA-binding properties, a GST-ZNF191(243–368) fusion protein was used in fluorescence quenching studies with two DNA sequences (GGAGGGTGGTTA and GAAATAATGTTA).

Researchers have demonstrated a non-invasive method using milk and near-infrared spectroscopy combined with Aquaphotomics to accurately detect Paratuberculosis in dairy cattle. The technique offers faster, more sensitive diagnosis than traditional methods.

Researchers at the University of the Basque Country, along with Català Restauradors S.L. analyzed the emergence of soluble salts on mural paintings in the vault of the Valencia Cathedral, using Raman and micro-energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy combined with ion chromatography.
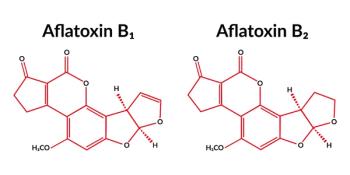
Researchers have demonstrated that visible and near-infrared spectroscopy, combined with chemometric and aquaphotomic analysis, can accurately classify and quantify aflatoxin contamination in white and yellow maize, offering a faster, non-destructive alternative to traditional methods.
A recent study tested a new mitochondria-targeting fluorescent probe, known as Mito-CDM, to see if it can improve the monitoring of mitochondrial viscosity.
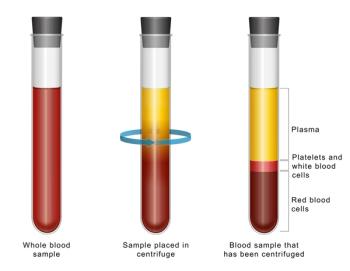
Researchers have developed a rapid, non-invasive screening method for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) using near-infrared spectroscopy and aquaphotomics. The approach analyzes plasma water patterns, achieving over 95% accuracy in distinguishing patients from healthy controls

A recent study demonstrated that combining hyperspectral imaging with multivariate curve resolution can non-invasively detect and monitor intestinal necrosis in acute mesenteric ischemia, offering a promising tool for earlier diagnosis and improved patient outcomes.

Metabolite identification is critical in drug development, with mass spectrometry (MS) as the primary tool, but limited in full structural elucidation. Infrared ion spectroscopy (IRIS) overcomes some of these limitations by combining MS sensitivity with IR-based structural fingerprints, enabling characterization without reference standards. Spectroscopy spoke to Giel Berden regarding applications in metabolite identification by determining the site of glucuronidation and phase I oxidation in selected drug molecules.

This Icons of Spectroscopy article profiles Lester W. Strock, whose innovative research in crystal chemistry and spectroscopy bridged fundamental science and applied geochemistry.

In Part 2 of this “Inside the Laboratory,” feature on George Shields, a professor of chemistry at Furman University and the founder and director of the Molecular Education and Research Consortium in Undergraduate Computational ChemistRY (MERCURY), Consortium, we discuss his research into computational approaches to improve our understanding of molecular behavior in both biochemistry and atmospheric chemistry and his work applying replica exchange molecular dynamics (REMD) for breast cancer drug design.

Top articles published this week include a video highlighting some of the icons of spectroscopy and a news article about using machine learning to quantify uncertainty in spectroscopic analyses.

New Model Improves Exoplanet Surface Characterization by Accounting for Overlooked Brightness Effect
This explainer video describes the role that reflection and emission spectroscopy play in characterizing rocky exoplanets.

In this edition of “Inside the Laboratory,” George Shields, a professor of chemistry at Furman University and the founder and director of the Molecular Education and Research Consortium in Undergraduate Computational ChemistRY (MERCURY), discusses the goal of MERCURY and some of its most recent projects

Analytica USA, debuting September 10–12 in Columbus, Ohio, combines a trade exhibition with a scientific conference for analytical science.

A new study demonstrates how a machine learning technique, quantile regression forest, can provide both accurate predictions and sample-specific uncertainty estimates from infrared spectroscopic data. The work was applied to soil and agricultural samples, highlighting its value for chemometric modeling.

In a recent press release, Horiba, an analytical and measurement technology company, announced the release of its Aqualog-Next A-TEEM Spectrometer.

This explainer video highlights how energy-dispersive inelastic X-ray scattering (EDIXS) can be used to discriminate between different stamps.


