
Researchers have developed a non-destructive method for identifying monoclonal antibody drug substances using Raman spectroscopy.

Researchers have developed a non-destructive method for identifying monoclonal antibody drug substances using Raman spectroscopy.

Researchers explore the antioxidant potential of Corema album (L.) D. Don by conducting a spectrochemical analysis on its leaf extracts. The study uncovers seasonal and sexual variations in antioxidant activity and phenolic compound composition, providing valuable insights for harnessing the bioactive properties of this plant species.

Researchers delve into the interaction between calf thymus DNA and an anticancer platinum (Pt) complex, uncovering its binding mechanism through spectroscopy and molecular dynamic simulations, offering valuable knowledge for future therapeutic advancements.

Researchers identify osmundacetone as a strong inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, revealing its interaction mechanism and paving the way for the development of novel uric acid-related disorder treatments.

Researchers have developed a selective fluorescent probe, derived from flavone derivatives, called FlaN-DN for hydrogen sulfide (H2S) detection and intracellular imaging.

This study provides insights into the alternative use of barochromic studies for determining the polarizability of organic molecules in excited states.

Scientists have investigated the sorption mechanism of organic compounds on a mineral composite sorbent using infrared spectroscopy providing insights for the development of effective wastewater purification methods.

A research team has designed and synthesized two fluorescent sensors, CAA and CAB, for fluorescence detection of copper ion (Cu2+) and formaldehyde.

Researchers have developed a novel fluorophore, diaryl maleimide (DAM), with multichromic properties potentially useful for volatile vapor detection in LED lighting systems, showcasing its versatility and applications in sensing technologies.

A new study has been conducted on the phase transitions in 1-adamantylamine and 1-adamantanol. Through various experimental techniques, they revealed the nature of these transitions, including changes in dielectric properties and sensitivity to pressure, providing valuable insights into the behavior of these compounds.

A new study introduces a filter fluorometer calibration method that eliminates the need for the fluorometer itself.
A scientific team has developed a two-photon phosphorescent probe, Ir-CN, for the sensitive detection of sulfur dioxide derivatives in living cell mitochondria.

Researchers have successfully applied laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) technology to quantitatively detect raw ore turquoise, a key ingredient in Tibetan medicines.

Researchers have developed a new methodology using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and the support vector machine model (SVM) to classify defects in metal-additive manufacturing (AM) parts.
A new study reveals the potential of Raman spectroscopy in recognizing nucleophosmin (NPM1) mutant gene expression in leukemia cells.

A new study presents significant improvements in the online-laser ablation of solids in liquids (online-LASIL) technique for quantitative analysis of trace elements in technological materials.
Scientists have developed an innovative method combining response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial intelligence network (AIN) to accurately estimate malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, a crucial biomarker for lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress measurement.

A look at how the spectral properties single-phase green emission phosphor make it suitable for near-UV light-emitting diode (NUV-LED) applications.

A research team has developed a novel method for rapidly detecting the grade of molybdenum ore using a combination of visible-infrared spectroscopy and machine learning.

A research group has made significant progress in enhancing the sensitivity of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for analyzing polymer additives.

A recent study utilized Raman spectroscopy to confirm the presence of microplastics in karst spring waters.

Researchers have compared two types of bismuth atomic lamps for atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) and found that the electrodeless discharge lamp (EDL) exhibited significantly higher sensitivity and lower detection limits compared to the boosted discharge hollow cathode lamp (Superlamp).

Scientists have developed a novel method for detecting toxic mixed red tide algae in the Qinhuangdao sea area using three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy and chemometrics.

A researcher group has utilized laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) to develop a method for food authentication and quality analysis.

A research team has developed a nondestructive method to assess the healing ability of plant tissues by analyzing the fluorescence properties of wounds on soybean seedlings.

Researchers have developed advanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) methods for rapid element quantification in alloy particles, aiding in the efficient analysis and identification of their source materials.

In a recent study, researchers analyzed the correlation between laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and acoustic signals captured by the microphone (MIC) on NASA's Perseverance rover during its mission on Mars.
Researchers have developed microbiological and spectrophotometric methods for the quantitative determination of tioconazole, an antifungal drug, providing valuable tools for the analysis and quality control of tioconazole in pharmaceutical preparations.
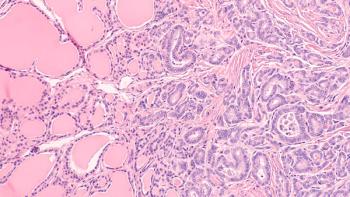
A recent study utilized infrared microspectroscopy to investigate the chemical composition of psammoma bodies (PBs) in ovarian and thyroid cancer tissues.

A recent study utilized laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) to examine the uptake and distribution of heavy metals in industrial hemp and white mustard plants.