
A recent study reveals insights for precise elemental mapping using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS).

A recent study reveals insights for precise elemental mapping using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS).

Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology unveil a sophisticated collisional-radiative model offering insights into laser-produced copper plasma through precise electron impact excitation cross-section calculations.

Award recipient John McLean of Vanderbilt University said hybrid techniques do not exist purely as combinations of letters, slashes, and hyphens—they have been built on the shoulders of decades’ worth of analysis intended to refine and simplify workflow.

Getting your finances in order ensures you can be prepared for the unexpected, said Tarshae Drummond, a lab manager and research technician at Fayetteville State University.

Luis G. Vieira from Universidade do Minho presents a new method in Applied Spectroscopy to address poor contact issues between the sample and the internal reflection element in attenuated total reflection (ATR) spectroscopy, ensuring accurate optical function determination and opening new avenues for precise material analysis

The latest issue of Applied Spectroscopy explores the transformative progress in gas detection technology through photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS), providing a comprehensive review and guidance for researchers navigating the nuanced landscape of advanced photoacoustic cells.

Researchers at Nanjing University of Science and Technology, led by corresponding have introduced an advancement in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) with two-dimensional amorphous titanium dioxide/silver (a-TiO2/Ag) nanosheets, demonstrating exceptional sensitivity and repeatability in chemical detection applications.

X-ray emission induced by charged particles, also known as particle-induced X-ray emission (PIXE), is a powerful analytical technique for the elemental and chemical characterization of materials.

NELIBS has gained prominence in various analytical fields, including microscopy, biomedicines, electrochemical and biosensors.

A recent study shows how near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy was integrated to create a new coal calorific value analyzer.

In a recent study, researchers used laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) to examine the complexities of plasma conditions, focusing on the addition of matrix elements.

In a recent study, researchers used ICP-MS to learn new insights into ancient coinage and gold purification techniques are revealed through the analysis of platinum-group elements and gold in silver coins from various ancient civilizations.
In a recent study, researchers introduced several analytical techniques, such as ESI-MS, RP-HPLC, and ICP-MS, to separate and detect various technetium species.

A spectral analysis technique was used to classify soil samples based on their soil organic matter (SOM).

In a recent study, collaborative spectroscopic methods, such as LIBS-Raman, were used for detecting and combatting heavy metal lead contamination in wheat seedlings, revealing critical insights for food security and human health.

In a recent study, a team of researchers used Raman spectroscopy to study wood ash glass tessera from Malbork Madonna, revealing two phases detected in tessera for the first time, leucite and pseudowollastonite.

At SciX, Dmitri Kurouski of Texas A&M University will be recognized as the 2023 Spectroscopy Emerging Leader in Molecular Spectroscopy Award recipient. Here's a summary of the award session.

At SciX, Johannes Pedarnig of Johannes Kepler University will be recognized as the 2023 SAS and Applied Spectroscopy William F. Meggers Award recipient. Here's a summary of the award session.

At the SciX Conference in Sparks, Nevada, Spectroscopy magazine sat down with Mathew Horrocks of the University of Edinburgh to discuss his research developing and using single-molecule and super-resolution microscopy techniques to study amyloid oligomers and their commonality regarding a variety of neurodegenerative disorders.

At the SciX Conference in Sparks, Nevada, Spectroscopy magazine sat down with Karen Esmonde-White of Endress+Hauser to talk about her career transition and how Raman spectroscopy has evolved over the years.

On Wednesday October 11th from 8:30–10:10 am, an oral symposium on international mail security will take place. We preview this session here.

Veronica Bradley's talk at SciX 2023 unveiled the transformative potential of single-particle mass spectrometry, enabling precise elemental and isotopic analysis at the particle level.

In the Chemometrics in Food and Agriculture oral symposia today at SciX 2023, Barry Lavine of Oklahoma State University delivered a talk titled, “Authentication of Edible Oils Using an Infrared Spectral Library and Digital Sample Sets for Calibrated and Uncalibrated Adulterants.” Here is a brief reflection of his talk.

Horrocks and his research group focus on single-molecule and super-resolution microscopy.

Popp and his team are focused on translating Raman spectroscopy for clinical applications.

On Tuesday October 10th from 1:30–3:10 pm, an oral session focusing on chemometrics in food and agriculture will take place. We preview this session here.

On Tuesday October 10th from 3:50–5:30 pm, an oral session focusing on 50 years in mass spectrometry will take place. We preview this session here.

On Tuesday October 10th from 8:30–10:10 am, an Ellis R. Lippincott Award Symposium Honoring Peter Griffiths will take place. We preview this session here.

On Monday October 9th from 3:50–5:30 pm, an oral session on machine and deep learning for biomedical diagnostics will take place. We preview this session here.
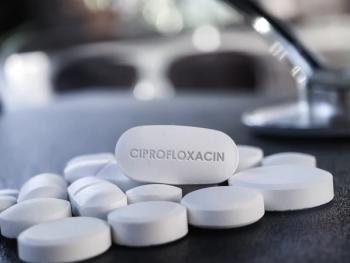
In a recent study, the contents of ciprofloxacin and metronidazole tablets were quantified using a handheld near-infrared (NIR) spectrophotometers.