Raman Spectroscopy
Latest News

Latest Videos

More News

As part of our coverage of the SciX Conference, Spectroscopy sat down with Witte, a graduate student at The Ohio State University, to talk about how machine learning (ML) algorithms can differentiate between spectral features associated with radiation dose and those reflecting temporal changes post-exposure, as well as the benefits of using Raman spectroscopy to detect and quantify radiation-induced molecular changes.

A recent review by Jhonatan Contreras and Thomas Bocklitz from Friedrich Schiller University Jena and the Leibniz Institute of Photonic Technology delves into the emerging field of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in spectroscopy.

This tutorial examines the development of universal spectral libraries, reviewing standardization efforts, mathematical frameworks, and practical examples across multiple spectroscopies, while emphasizing metadata harmonization, FAIR principles, and the emerging role of AI in building interoperable, machine-readable repositories. This remains an unsolved problem in spectroscopy.

The StellarScope AM/PA Raman Particle Analyzer, launched by StellarNet Inc., is an advanced analytical platform that merges automated mapping with particle analysis.

Researchers utilize Raman spectroscopy to uncover the lost colors of prehistoric mollusk shells, revealing their cultural significance and aesthetic choices.

Recently, a team of researchers from Chongqing University (China) developed a new Raman spectroscopy technique that could significantly improve natural gas monitoring and leak detection systems.

This tutorial explores the challenges posed by nonlinearities in spectroscopic calibration models, including physical origins, detection strategies, and correction approaches. Linear regression methods such as partial least squares (PLS) dominate chemometrics, but real-world data often violate linear assumptions due to Beer–Lambert law deviations, scattering, and instrumental artifacts. We examine extensions beyond linearity, including polynomial regression, kernel partial least squares (K-PLS), Gaussian process regression (GPR), and artificial neural networks (ANNs). Equations are provided in full matrix notation for clarity. Practical applications across near-infrared (NIR), mid-infrared (MIR), Raman, and atomic spectroscopies are discussed, and future research directions are outlined with emphasis on hybrid models that integrate physical and statistical knowledge.
Recently, a team of researchers from Portugal examined a new method that could improve accessibility to kidney disease diagnostics.
Despite decades of major monetary investment for applied research in multiple spectroscopic sensing technologies, achieving an accurate, portable, and painless noninvasive glucose monitor remains a major unmet goal in diabetes care. This goal is extremely difficult due to persistent challenges with sensitivity, analyte specificity, accuracy, calibration stability, and biological interference.
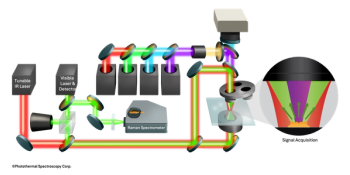

This tutorial explores the motivation, mathematical underpinnings, and practical approaches to fusing spectral data, with emphasis on early, intermediate, and late fusion strategies.

This Icons of Spectroscopy Series article features William George “Bill” Fateley, who shaped modern vibrational spectroscopy through landmark reference books and research papers, pioneering instrumentation, decades of editorial leadership, and deep commitments to students and colleagues. This article reviews his career arc, scientific contributions, and enduring legacy.

This tutorial provides an in-depth discussion of methods to make machine learning (ML) models interpretable in the context of spectroscopic data analysis. As atomic and molecular spectroscopy increasingly incorporates advanced ML techniques, the black-box nature of these models can limit their utility in scientific research and practical applications. We present explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) approaches such as SHAP, LIME, and saliency maps, demonstrating how they can help identify chemically meaningful spectral features. This tutorial also explores the trade-off between model complexity and interpretability.

A recent study conducted by researchers from Northwestern Polytechnical University explored how to improve laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for analyzing complex mineral samples

This tutorial contrasts classical analytical error propagation with modern Bayesian and resampling approaches, including bootstrapping and jackknifing. Uncertainty estimation in multivariate calibration remains an unsolved problem in spectroscopy, as traditional, Bayesian, and resampling approaches yield differing error bars for chemometric models like PLS and PCR, highlighting the need for deeper theoretical and practical solutions.

Researchers from Brazil have developed an improved method combining infrared and Raman spectroscopic techniques to better identify and characterize microplastics. This integrated approach enhances accuracy in distinguishing various polymer types and provides refined spectral analysis crucial for environmental studies.

Raman spectroscopy, combined with computational modeling and machine learning, shows strong potential for distinguishing PFAS compounds, offering a promising new framework for environmental monitoring and contamination analysis.

A new study investigates how colorants embedded in microplastics (MPs) interfere with Raman spectroscopy, one of the key tools used to identify microplastic particles. The research details how fluorescence from these additives complicates spectral analysis, underscoring challenges in environmental microplastic detection.

Researchers have developed a novel approach to quantify microplastics in water environments by combining Raman spectroscopy with convolutional neural networks (CNN). This integrated method enhances the accuracy and speed of microplastic identification, offering a promising tool for environmental monitoring.
A recent study found that coffee, red wine, and Coca-Cola significantly reduce the hardness and alter the chemical structure of dental resin composites.

This tutorial investigates the persistent issue of sample heterogeneity—chemical and physical—during spectroscopic analysis. Focus will be placed on understanding how spatial variation, surface texture, and particle interactions influence spectral features. Imaging spectroscopy, localized sampling strategies, and adaptive averaging algorithms will be reviewed as tools to manage this problem, as one of the remaining unsolved problems in spectroscopy.

This tutorial guides spectroscopy practitioners through the integration of Raman spectroscopy and machine learning (ML) techniques for detecting microplastics (MPs) in aquatic and environmental samples.

This Icons of Spectroscopy Series article features E. Bright Wilson, a pioneer of chemical physics. Wilson’s contributions to infrared, Raman, and microwave spectroscopy provided the theoretical and practical foundation for analyzing molecular structure and dynamics. As a revered professor at Harvard and coauthor of landmark texts, he mentored nearly 150 students and researchers, leaving a lasting legacy of scientific excellence and integrity.

In this column, we will describe what is known about the structures of these materials and how Raman spectroscopy can characterize them.

Chinese Academy of Sciences researchers combine spectroscopic methods with deep learning to classify microplastics at near-perfect accuracy.









