
A recent study out of Russia examined the application of Raman spectroscopy in biomedical and biological research.

Using Raman and UV-vis Spectroscopy with Multivariate Regression Analysis to Improve Quality Control of Over-the-Counter Medications

A recent study out of Russia examined the application of Raman spectroscopy in biomedical and biological research.

As a preview to the SciX 2024 conference, Spectroscopy sat down with Ioan Notingher to talk about his research.

A recent study from Japan explored how to improve rice processing and other agricultural products using Raman scattering spectroscopy.

In the final part of our interview with Nick Stone, he discusses standardizing Raman technology across multiple clinical centers, and what it means to him to be attending the SciX Conference as the recipient of the Charles Mann award.

In part 2 of our conversation with Nick Stone, we discuss topics such as machine learning (ML) and spectrometer transferability in clinical settings.

In a preview to the upcoming SciX Conference October 20 to 25 in Raleigh, North Carolina, Spectroscopy sat down with Nick Stone of the University of Exeter to discuss his recent work in oncology and clinical analysis.

In this preview interview for SciX 2024, Jason Dwyer of the University of Rhode Island discusses his experience with SERS and his feelings on winning the American Electrophoresis Society's Mid-Career Award.

A pioneering study integrates laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) with Raman spectroscopy (RS) and applies machine learning (ML) to achieve exceptional accuracy in mineral identification. The combined approach not only leverages the strengths of both techniques but also enhances classification precision, achieving up to 98.4% accuracy.

Researchers at King Saud University have successfully improved the efficiency of methylammonium lead triiodide (MAPbI3) perovskite solar cells by doping them with Germanium Sulfide (GeS). By enhancing the crystalline quality and surface morphology of the perovskite layer, the team achieved a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 17.46%, making this doping technique a promising method for improving solar cell performance.

Pakorn Patimetha, Detective Sergeant with the New Jersey State Police's Hazardous Materials Response Unit spoke to Spectroscopy about how officers use portable spectroscopy technology to detect potentially harmful materials at crime scenes.

For "The Future of Forensic Analysis” series, we interviewed Barry Lavine, regents professor from The Department of Chemistry at Oklahoma State University in Stillwater, Oklahoma, to describe his most recent work in applying Raman and infrared (IR) spectroscopy in forensic paint analysis.

Spectroscopy sat down with Brandon Gayle, who specializes in training first responders to use FT-IR, Raman, and other analytical techniques in emergency situations.

Spectroscopic analytical techniques are crucial for the analysis of agricultural products. This review emphasizes the latest advancements in several key spectroscopic methods, including atomic, vibrational, molecular, electronic, and X-ray techniques. The applications of these analytical methods in detecting important quality parameters, adulteration, insects and rodent infestation, ripening, and other essential applications are discussed.

A recent study reveals on the challenges and limitations of AI-driven spectroscopy methods for rapid food analysis. Despite the promise of these technologies, issues like small sample sizes, misuse of advanced modeling techniques, and validation problems hinder their effectiveness. The authors suggest guidelines for improving accuracy and reliability in both research and industrial settings.

Researchers using a portable Raman spectroscopy system have begun in-field analysis of Stonehenge's Altar Stone, aiming to determine its origin and composition, potentially uncovering new insights into the ancient monument's history.
Researchers at Budapest University of Technology and Economics have developed a novel method for real-time monitoring of the protein purification process using Raman and near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. Their study compares the effectiveness of these two spectroscopic techniques in tracking the removal of imidazole, a process-related impurity, during the purification of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein's receptor-binding domain (RBD).

A trip to the Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center served as a reminder of the importance of space exploration and the key role spectroscopy plays in this industry.

Researchers from Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and the German Aerospace Center (DLR) have developed a cutting-edge fiber-dispersive Raman spectrometer (FDRS) capable of detecting low-density biological matter in space. By combining a single-photon detector with a dispersive optical fiber element, the team achieved a breakthrough in in-situ Raman spectroscopy, promising unprecedented sensitivity and reliability in the search for extraterrestrial rudimentary life.

Metrohm Spectro Inc., a New Jersey-based company that develops and manufactures analytical science instruments, announced the expansion of its Raman Chemical Warfare Agents library to include 111 deadly substances.
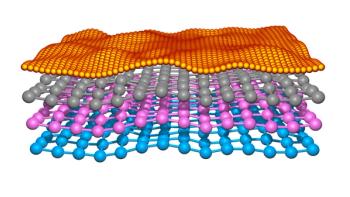
A recent study explores the strengths and limitations of spatially offset Raman spectroscopy (SORS) and micro-SORS, offering new insights into their applications for non-invasive subsurface material analysis. The findings provide valuable guidelines for choosing between these techniques based on sample characteristics and analytical needs.

An innovative study has demonstrated that two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy (2D-COS) can effectively differentiate between toxic and biocompatible carbon nanofibers (CNFs), offering a novel method for evaluating the safety of nanomaterials intended for medical use.
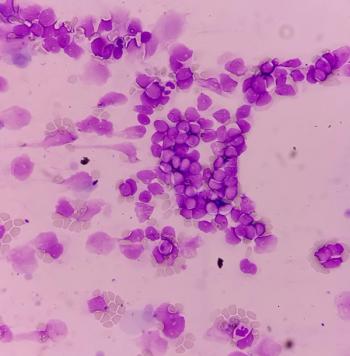
A recent study examined using Raman spectroscopy to screen leukemia in patients.

A recent study from Sichuan, China, leveraged a few spectroscopic techniques with chemometrics to analyze key components of the beer brewing process.

A recent study looks at using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy to distinguish between platinum-resistant and platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer tissues.

A recent study combined Raman spectroscopy with chaos theory to improve the reliability of diagnosing several types of cancers.