
A recent study highlighted a novel method for recycling aging wind turbine blades, transforming waste into valuable materials while minimizing environmental impact.

Will Wetzel is a Senior Editor for Spectroscopy magazine. He specializes in creating engaging, high-value content for diverse audiences. His role involves driving digital growth through KPI assessments, social media strategies, and innovative content development.
Wetzel is also a sports writer and commentator, serving as a freelance writer for several sports websites, including FanSided. He currently serves as the host, producer, and creator of “The Inside Fastball,” a LinkedIn newsletter that discusses topical issues in Major League Baseball (MLB). Outside of work, Wetzel volunteers with the Nashville Humane Association and Habitat for Humanity. His stated goal is to help build one house with Habitat for Humanity in every U.S. state.

A recent study highlighted a novel method for recycling aging wind turbine blades, transforming waste into valuable materials while minimizing environmental impact.

Explore how spectroscopy enhances sustainability in energy, from solar panel durability to real-time gas monitoring and lithium-ion battery safety.

In this interview segment with Rohith Reddy, he discusses how mid-infrared spectroscopic imaging (MIRSI) can be used to help detect numerous disease types.

A recent study presented a novel deep learning model that could improve the prediction of fuel properties in the petroleum industry.

Spectroscopy is playing a sizable role in expanding the capabilities of remotely operated and manned submersibles. A recently published nonfiction book highlights the advancements made in deep-sea exploration technology, and we discuss spectroscopy's role in all of this.

This article provides a clear refresher on key spectroscopy techniques—IR/NIR, Raman, UV–Vis, XPS/XAS, NMR, ICP-MS, and LIBS—and their applications in the energy industry, from batteries and solar panels to fuel production and emissions monitoring.

Researchers uncover the hidden dangers of ship paint-derived microplastics, revealing their complex composition and ecological risks in marine environments.

Recently, a team of researchers investigated a new approach for manipulating electron motion at the femtosecond timescale.

In this edition of “Inside the Laboratory,” we profile the Schultz Laboratory at The Ohio State University in Columbus, Ohio, speaking with Zac Schultz, Spencer Witte, Nishadi Nadeeshani, and Renee Romano about their work.

Top articles published this week include an interview with our Emerging Leader in Molecular Spectroscopy award winner Lingyan Shi, a mini-tutorial highlighting practical workflows and innovative applications, and an inside look at single-particle ICP-TOF-MS.

Researchers at Tianjin University of Technology develop a rapid, in situ technique for identifying adulteration in starch sausages using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy.

Discover the latest advancements in medical devices and artificial intelligence, focusing on the transformative impact of IoMT devices in healthcare.

A recent study highlights novel analytical techniques for phosphorus detection, enhancing pollution control and sustainability in environmental monitoring.


In this final interview segment with Lingyan Shi, she discusses the challenges of developing multimodal metabolic nanoscopy systems, and where these systems could be applied in the future.

A review article from researchers at Liaocheng University explores the challenges of applying vibrational spectroscopy techniques to food authentication.

In the second part of a three-part interview, Lingyan Shi recaps the award technical session that she chaired at the SciX Conference, highlighting the speakers she invited and what they discussed.

A new study reveals that resveratrol binds to peanut protein arachin through hydrophobic and hydrogen-bond interactions, enhancing protein stability and offering valuable insights for developing functional peanut-based food products.

In this interview segment, Shi recaps her talk that she delivered at the SciX Conference and the four major technologies that she and her team developed over the past few years at the University of California, San Diego.
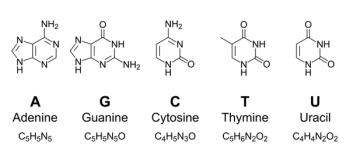
In a recent study, a team of researchers from Peking University and the National Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro and Nano Manufacture Technology have proposed a new method for identifying DNA nucleobases using a fusion of terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) and advanced deep learning techniques.

Top articles published this week include several video interviews from our coverage of the SciX Conference and an inside look at classical correction methods.

In this video segment, Fay Nicolson discusses her career trajectory, from her time in graduate school to her time as a postdoctoral candidate to her time as an independent researcher.

In this interview segment, Karl Booksh dives deeper into a new technique called conformal prediction, and how his group has been applying it in their research.

In the second and final part of our interview with Rob Lascola, he addresses the main challenges in achieving accurate acidity measurements using Raman spectroscopy in complex, highly absorptive systems, as well as explains what he has learned about dissolution mechanisms, and how these insights can influence future nuclear processing strategies.

In this interview segment, Reddy discusses how O-PTIR combined with mid-infrared frequency comb technologies enhances both resolution and throughput in tissue analysis and how this integration address the limitations of conventional MIRSI approaches in clinical settings.

In this interview segment, Rafael Davalos discusses contactless dielectrophoresis, highlighting the utility of this technique not just in cancer research, but other application areas as well.

In this interview segment, Rob Lascola discusses how Raman spectroscopy complements other techniques in fuel dissolution and solvent extraction and what Raman can detect in off-gas streams.

In this video segment, Karl Booksh of the University of Delaware explains how his study highlighted a major improvement in classification accuracy using stacked models for differentiating exotic hardwood species.

In this segment, Bell addresses the key barriers that are preventing SERS from being more widely adopted in complex environments.

In this interview, Yingchan Guo of the University of Florida discusses high-throughput IMS and identifying fatty acyl chains of lipids using mass spectrometry, particularly in matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) imaging.