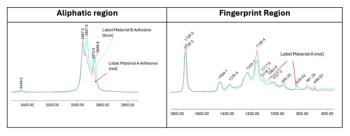
A new review by researchers from IIT Delhi and the University of Queensland highlights how Terahertz (THz) and low-wavenumber Raman (THz-Raman) spectroscopy are advancing quality control and efficiency in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and mineral industries. These powerful non-invasive tools enable detailed multi-parameter sensing, offering deeper insight at the molecular level.