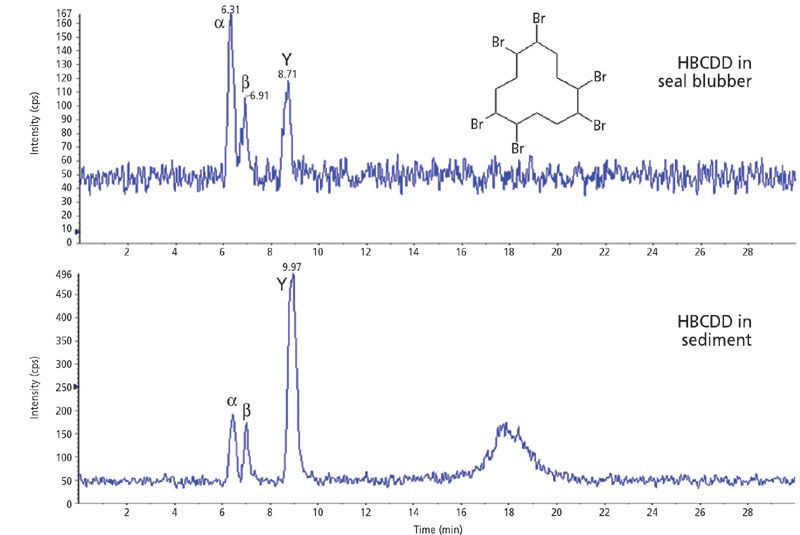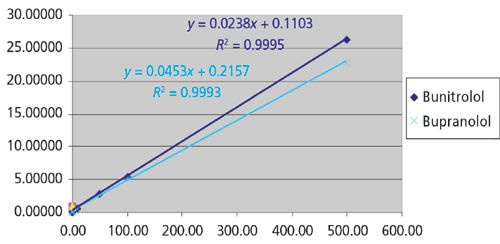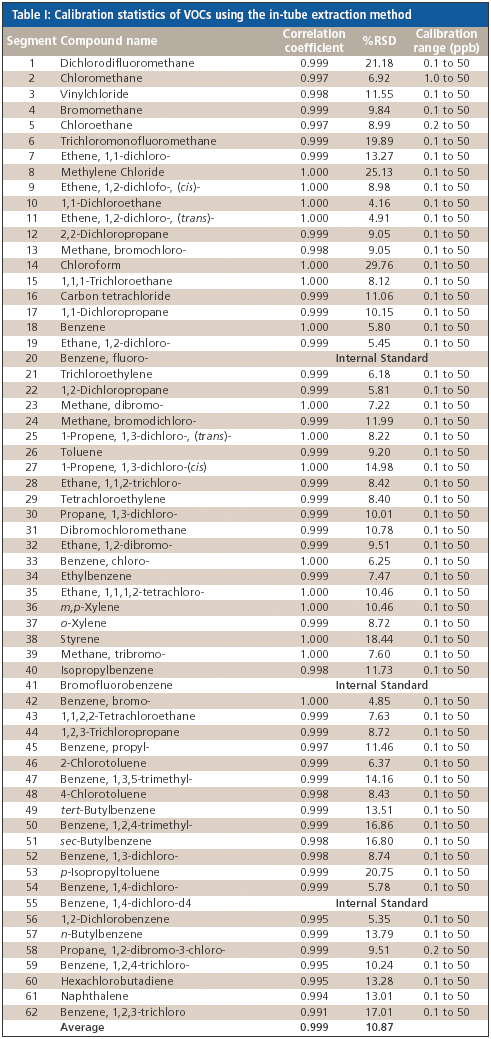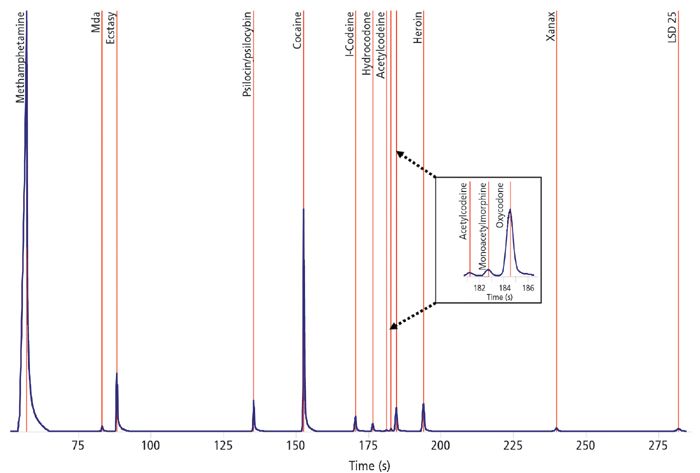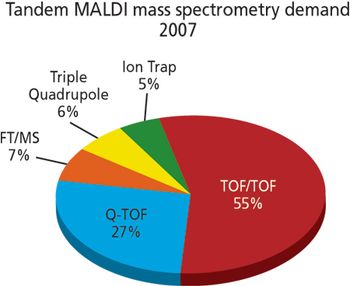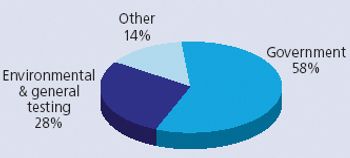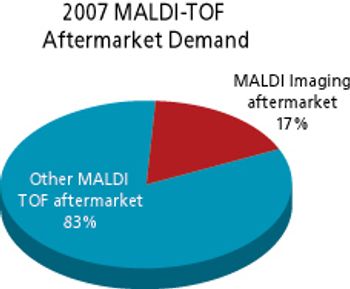
The adoption of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for imaging applications is a major recent development in the market. Applications lie squarely in the life sciences area, being primarily in histopathology. The market for MALDI imaging products already accounts for a significant and rapidly growing portion of the aftermarket for MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.