
This report demonstrates that it is possible to meet and exceed EPA "statement of work" requirements using ICP-MS.


This report demonstrates that it is possible to meet and exceed EPA "statement of work" requirements using ICP-MS.
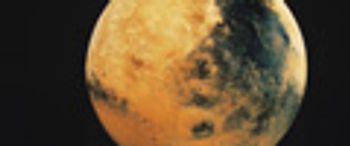
Since the discovery of gullies on Mars in 2000, NASA has endeavored to re-image areas known to have them. Now for the first time, using before and after images taken of the same region on Mars, a dune gully flow is shown to have happened very recently.

Some types of spectroscopy work better if the intensity of the light source increases and decreases in a regular pattern. Such a varying signal is called modulated, and here, the author explores the devices that perform this function.

The authors review the operating principles of a silicon Raman laser and show that by introducing a longitudinal variation of the waveguide width in the cavity, the lasing efficiency can be increased significantly.
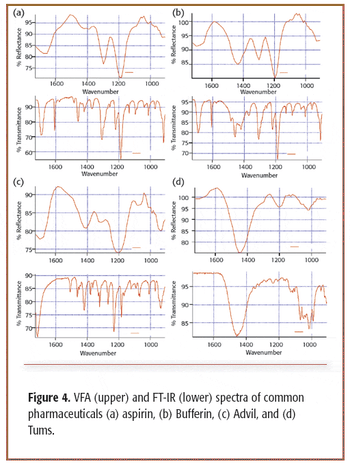
The basic characteristics of variable filter array (VFA) spectrometers, both near- and mid-infrared, make them well suited for routine infrared analysis applications outside and inside the laboratory. The performance of this spectrometer is discussed here.
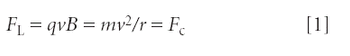
The second installment of this two-part series illustrates further technical principles and applications of the most common mass analyzers used in bioanalytical laboratories today, as well as novel techniques and mass analyzer designs. Examples are based upon the authors' research in small molecule applications.
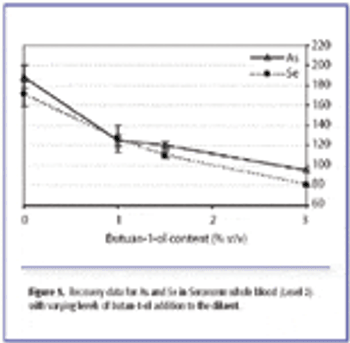
This study describes the development of a robust, high-throughput analytical method for the determination of 18 elements (15 trace elements and three electrolytes) in blood and serum samples using a collision/reaction cell quadrupole ICP-MS system.

Elemental analysis in biological samples generally is achieved using flame atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) and graphite furnace AAS (GFAAS). Flame AAS is fast, easy-to-use, and economical, but insufficiently sensitive for assays such as Se in serum and Pb/Cd in whole blood. These measurements require use of the more sensitive GFAAS. Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), despite its low detection limit capabilities and wide elemental range, has had relatively little impact to date on biomedical analysis because of the popularly held conception that it is complex to use and expensive. In recent years, the instrumentation has been simplified and purchase, running, and maintenance costs have fallen. As a result, clinicians are becoming more interested in ICP-MS, although the perception that it is still much more expensive than GFAAS remains. This article provides a comparison of the costs of ICP-MS and GFAAS for biomedical sample analysis and illustrates the performance of ICP-MS for..
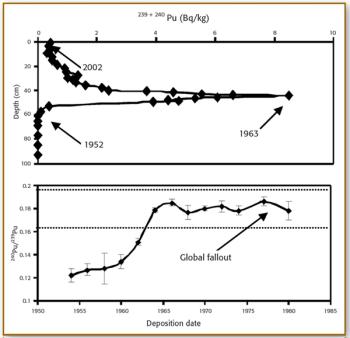
Plutonium is distributed globally in the Earth's surface environment as a result of atmospheric weapons tests, nuclear accidents, and nuclear fuel reprocessing. Mass spectrometry (MS), in particular, sector field ICP-MS, now is used widely to determine Pu activities and isotope ratios; 240Pu/239 is very useful in determining Pu origin. Determination of Pu by ICP-MS involves dissolution, column separation, and the MS determination; detection limits are 0.1–10 fg for each isotope. Applications of the determination of sector field ICP-MS to studies of environmental Pu include discerning sources of contamination near the Chernobyl reactor, and chronology of recent aquatic sediments.
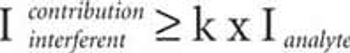
Acquisition and interpretation of a spectra database for ICP-AES analysis are described. The aim is the selection of nanometer-wide spectral windows containing several elements and several lines per element, so as to perform multiline analysis. An automatic line assignment procedure has been used. Information such as wavelength, sensitivity, line width, limit of detection, and level of detector saturation are stored. Filtering procedures are used for line selection, taking into account concentrations and possible spectral interferences.
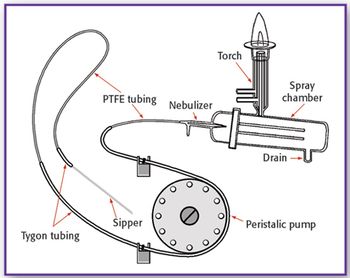
Sample introduction can be a significant source of random and systematic error in the measurement of samples by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) and ICP mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) systems.The considerations made in selecting a liquid introduction system include dissolved solids content, suspended solids presence, presence of hydrofluoric acid or caustic, detection limit requirements, precision requirements, sample load requirements, sample size limitations, and operating budget. The analyst is left with the task of choosing the best introduction components.This article discusses the key components of a typical liquid sample introduction system for inductively coupled plasma spectroscopy, and offers troubleshooting tips for problems commonly encountered by practitioners.
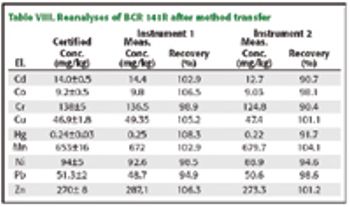
The analysis of soil and sewage sludge by ICP-OES using a novel CCD optic concept, which allows for the transfer of methods between different instruments, is described. Sample preparation was performed according to EN 13346:2000. The accuracy was investigated using the standard reference materials, BCR-141R and NIST 2781. It could be demonstrated that the requirements in terms of sensitivity, precision, and accuracy to perform the analysis of soil and sewage sludge can be met. The article includes line selection, detection limits, and studies on accuracy.
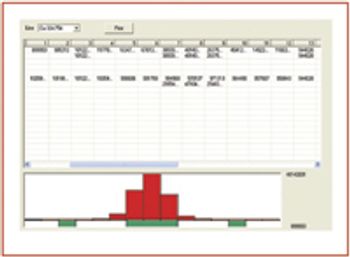
As the demand for accurate soil analysis increases, agriculturalists will need faster, less expensive analytical methods to determine the type and amount of fertilizer required for optimum crop growth. Today, inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) is the most commonly employed technique for the determination of nutrient elements in fertilizers, while combustion analysis is used for nitrogen. Until recently, ICP-OES could not achieve the accuracy and precision necessary to measure nitrogen due to the elevated background effects caused by atmospheric nitrogen, as well as the inherent stability limitations associated with older instrument designs. This paper describes a new ICP-OES configuration and sample introduction system designed to greatly reduce nitrogen backgrounds and thereby facilitate nitrogen determinations by ICP-OES. Furthermore, the nitrogen determinations are carried out concurrently with the other nutrient elements previously reported by ICP-OES without..

In various fields such as signal processing, imaging processing, analytical chemistry, and spectroscopic analysis, smoothing and differentiation is important and necessary. With a matrix approach, the Savitzky–Golay smoothing and differentiation filter was extended recently to even length. In this article, a more general approach is proposed for convenient computation.

Accurate and precise time and date stamps are critical to ensuring integrity of the data and results generated by each computerized system used in any spectroscopy laboratory.
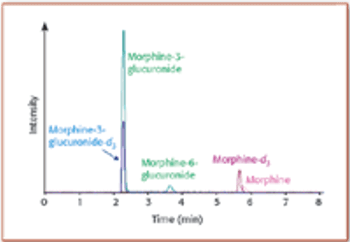
This tutorial illustrates the technical principles and typical applications of the most common mass analyzers used in bioanalytical laboratories today, as well as novel techniques and mass analyzer designs. Examples are based upon the authors' research in small molecule applications.
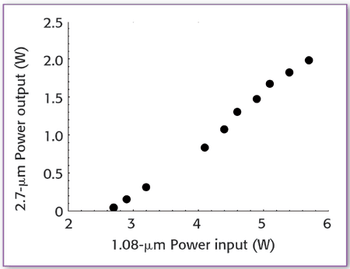
New mid-infrared spectroscopic sources, based upon advances in fiber lasers and in nonlinear frequency conversion, are now enabling high-resolution laser spectroscopy in the 2–4 μm wavelength region and beyond. With this in mind, the authors discuss continuous wave (CW) optical parametric oscillators (OPOs) in particular.
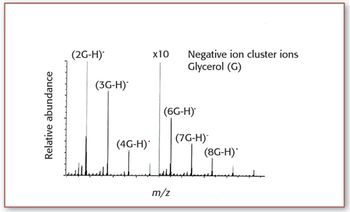
Part III of this four-part series continues the discussion of mass calibration.
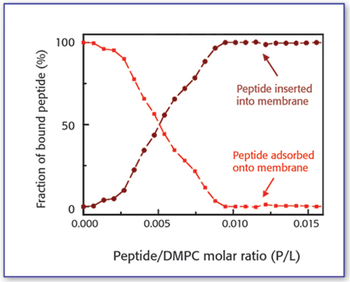
High-resolution ultrasonic spectroscopy titration analysis is a powerful new tool in research and analytical laboratory work for quantitative measurements of different processes and compounds. Here, the authors explore its potential.
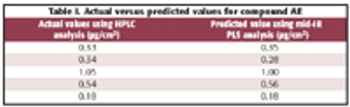
The authors describe an in-situ cleaning verification technique that promises to be faster and more efficient than traditional methods, which use swab sampling followed by HPLC analysis. The technique is based upon FT-IR spectroscopy in the middle-infrared (mid-IR) range using reflection at a grazing angle.
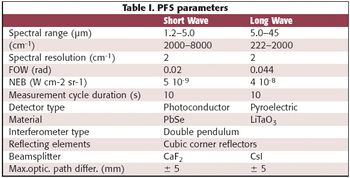
A report published earlier this year (1) discussed a UV–vis-NIR instrument designed for use on NASA Mars rover missions. This article follows up with coverage of the Planetary Fourier Spectrometer on the European Space Agency's Mars Express orbiter mission.

In this X-ray tutorial, the authors attempt to answer the frequently asked question, "How deep do the X-rays penetrate my sample?"
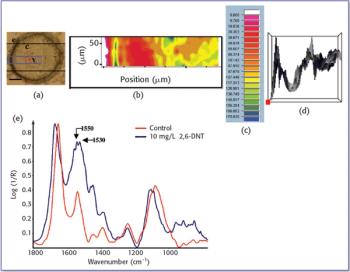
The fate and transport of organic contaminants and their impact upon plant development has been an important topic in environmental science. Here the authors report the use of synchrotron radiation Fourier-transform infrared microspectroscopy (SR-IMS) as a direct method for monitoring the fate and effects of 2,6-dinitrotoluene (2,6-DNT) in maize (Zea mays L.) root tissue.

Previous methods for linearity testing discussed in this series contain certain shortcomings. In this installment, the authors describe a method they believe is superior to others.

Innov-X Corporate Profile (PDF)