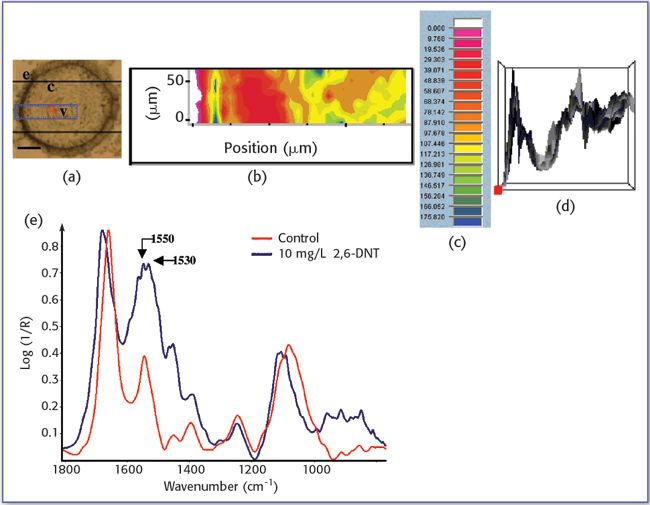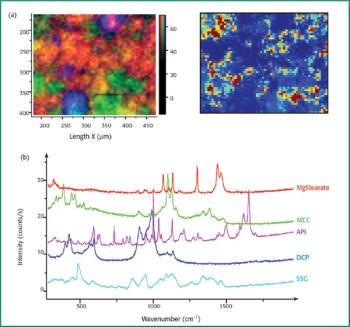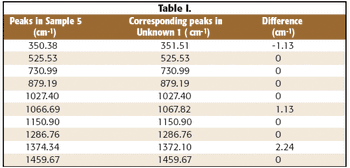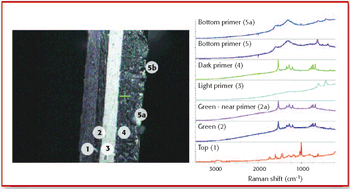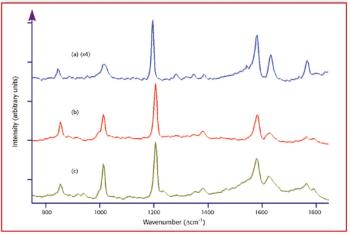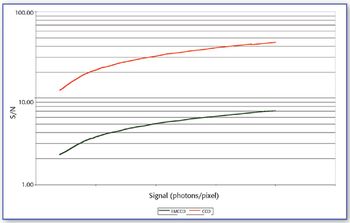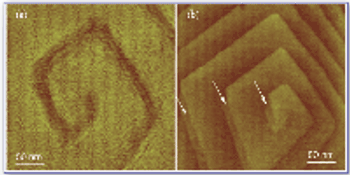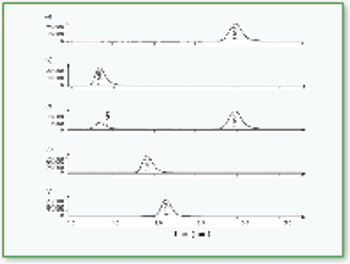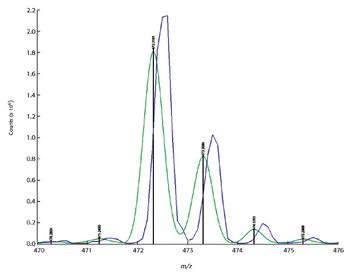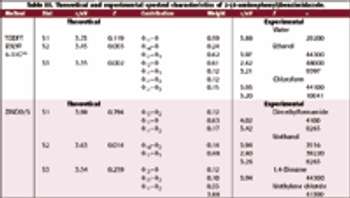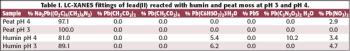
In this study X-ray absorption was used to determine the effect of pH on the coordination of lead to humin and sphagnum peat moss. The authors determined the oxidation state and the coordination of lead to both humin and sphagnum peat moss using X-ray near edge structure and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. In addition, inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy was used to determine the amount of lead bound to the humin and sphagnum peat moss in the pH range 2–6.