
A team of researchers from Spanish institutions has found that polystyrene used in healthcare packaging shows strong resistance to UVC sterilization, with minimal chemical degradation detected using FT-IR and Raman spectroscopy.

Jerome Workman, Jr. is on the Editorial Advisory Board of Spectroscopy and is the Assoc. Editorial Director. He is the co-host of the Analytically Speaking podcast and has published multiple reference text volumes, including the three-volume Academic Press Handbook of Organic Compounds, the five-volume The Concise Handbook of Analytical Spectroscopy, the 2nd edition of Practical Guide and Spectral Atlas for Interpretive Near-Infrared Spectroscopy, the 2nd edition of Chemometrics in Spectroscopy, and the 4th edition of The Handbook of Near-Infrared Analysis. He is the recipient of the 2020 NYSAS Gold Medal Award (with Howard L. Mark). Direct correspondence to jworkman@mjhlifesciences.com

A team of researchers from Spanish institutions has found that polystyrene used in healthcare packaging shows strong resistance to UVC sterilization, with minimal chemical degradation detected using FT-IR and Raman spectroscopy.

A multinational research team explores Raman spectroscopy's expanding role in medicine and microbiology, revealing its powerful potential in diagnostics, drug analysis, and microbial classification.

Researchers at Georgia College and Purdue University have developed a fast, low-cost method using Raman and UV–visible spectroscopy combined with chemometric modeling to accurately screen and quantify active ingredients in over-the-counter oral syrups, helping to fight counterfeit medications.

The recipient of the 2025 NYSAS Gold Medal Award is Geraldine L. Richmond, Presidential Chair in Science and Professor of Chemistry at the University of Oregon.

A new study reveals how changes in refractive index can skew transient absorption data in thin-film materials, leading to misinterpretations unless properly corrected.

Researchers in Brazil have developed new optical techniques—SLIM, IC-scan, and RICO-scan—to probe the complex nonlinear properties of scattering and disordered materials, expanding potential applications in photonics, biomedicine, and thermometry.

A pioneer of FT-ICR Mass Spectrometry, Alan G. Marshall (1944–2025), is best known for co-inventing Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS), a transformative technique that enabled ultrahigh-resolution analysis of complex mixtures. Over a career spanning more than five decades at institutions like the University of British Columbia, The Ohio State University, and Florida State University, he published over 650 peer-reviewed papers and mentored more than 150 scientists. Marshall’s work profoundly impacted fields ranging from astrobiology to petroleomics and earned him numerous prestigious awards and fellowships. Revered for his intellect, mentorship, and dedication to science, he leaves behind a legacy that continues to shape modern mass spectrometry.
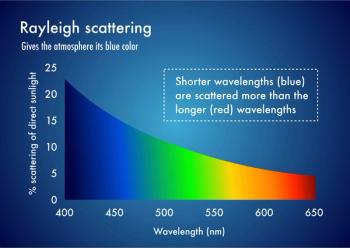
Researchers have introduced a simple yet powerful new rule based on Rayleigh scattering theory that accurately links the absorption behavior of composite media, like aerosols or colloids, to the properties of their nanoparticle constituents.

Chinese researchers have developed a powerful new method using near-infrared (NIR) hyperspectral imaging combined with a convolutional neural network (CNN) to identify hazardous explosive materials, like trinitrotoluene (TNT) and ammonium nitrate, from a distance, even when concealed by clothing or packaging.

Researchers have developed an analytical method combining remote near-infrared and Raman spectroscopy with machine learning to noninvasively map moisture and salt damage in historic buildings, offering critical insight into ongoing structural deterioration.

Researchers in Thailand have developed a cost-effective standoff Raman spectroscopy system using a night-vision intensified spectrometer and digital correction algorithms. The system reliably detects chemical compounds at distances up to 60 meters with high spectral resolution.

Explore the evolution of chemometrics in spectroscopy, celebrating 40 years of insights and mathematical exploration in this dynamic field.

Researchers at Wroclaw University of Science and Technology and Université catholique de Louvain have demonstrated how diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) in the 900 nm to 1100 nm range can non-destructively assess powder blend homogeneity in metal additive manufacturing. Their findings suggest that DRS offers a fast, reliable method for ensuring uniformity in aluminum alloy powders used in powder bed fusion 3D printing.

Researchers at Sun Yat-sen University have applied visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy to reveal how iron oxide minerals, particularly hematite, define the iconic red hues of China's Danxia landforms.

Researchers from Northwestern University, University of Cádiz, and University of Arizona have developed new formulae for analyzing optical thin films that outperform traditional models by accounting for complex geometries and absorbing substrates. These advances offer more precise ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared (UV-vis-NIR) spectroscopic analysis of film materials used in critical modern technologies.

In this Icons of Spectroscopy article, Executive Editor Jerome Workman Jr. delves into the life and impact of Bruce Kowalski, an analytical chemist whose major contributions to chemometrics helped establish the field of applying advanced quantitative and qualitative mathematics to extract meaningful chemical information from complex datasets. Kowalski’s visionary approach to chemical data analysis, education, and software development has transformed the landscape of modern analytical chemistry for academia and industry.


Spanish scientists have combined Raman imaging with powerful chemometric tools to identify and map organic molecules in a Martian meteorite, offering key insights for future Mars sample return missions and the search for past life on the Red Planet.

A team of scientists in Poland has unveiled the first detailed structural and magnetic analysis of the Ribbeck meteorite, a recently recovered space rock classified as an aubrite. Using Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and advanced magnetic testing, researchers revealed the meteorite's unique mineralogy and its connection to deep space conditions.

Researchers in Rome used advanced spectroscopic techniques to probe the mineralogy of the CM2 carbonaceous chondrite NWA 12184. This revealed the effects of space weathering and provided insights into C-type asteroid evolution.

Researchers have developed a powerful deep learning model that automates the identification of minerals using Raman spectroscopy, offering faster, more accurate results even in complex geological samples. By integrating attention mechanisms and explainable AI tools, the system boosts trust and performance in field-based mineral analysis.

A new review by researchers from IIT Delhi and the University of Queensland highlights how Terahertz (THz) and low-wavenumber Raman (THz-Raman) spectroscopy are advancing quality control and efficiency in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and mineral industries. These powerful non-invasive tools enable detailed multi-parameter sensing, offering deeper insight at the molecular level.

A team of international researchers has developed a faster, more accurate method to analyze soil carbon fractions using mid-infrared spectroscopy and deep learning. Their approach preserves the chemical balance of soil organic carbon components, paving the way for improved climate models and sustainable land management.

Scientists at the University of Barcelona have developed a fast and reliable way to identify natural, treated, and synthetic rubies and sapphires using Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Their study reveals unique spectral fingerprints for different gemstone types, offering a powerful tool in the fight against gem fraud.

A historical and technical overview from the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) explores how advanced scientific instruments—particularly spectroscopic methods—have transformed gem identification. From refractometers to modern spectrophotometers, this deep dive highlights the evolving challenges and solutions in gem testing.

New research from the Gemological Institute of America highlights the essential role of infrared spectroscopy in identifying gemstones, detecting treatments, and distinguishing natural from synthetic gems. The technique’s precision and non-destructive nature have made it an indispensable tool in modern gemology.

In this “Icons of Spectroscopy” column, Spectroscopy Executive Editor Jerome Workman, Jr. explores the life and contributions of Albert Abraham Michelson, a graduate of the United States Naval Academy, who showed early brilliance in physics and mathematics, eventually resulting in a teaching position at the Academy and the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1907.

Researchers have developed a wireless, wearable brain-monitoring device using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) to detect cognitive fatigue in real time. The miniaturized system enables mobile brain activity tracking, with potential applications in driving, military, and high-stress work environments.

A newly published review in the journal Advanced Materials explores how intelligent wearable sensors, powered by smart materials and machine learning, are changing healthcare into a decentralized, personalized, and predictive modeling system. An international team of researchers highlights emerging technologies that promise earlier diagnosis, improved therapy, and continuous health monitoring—anytime, anywhere.
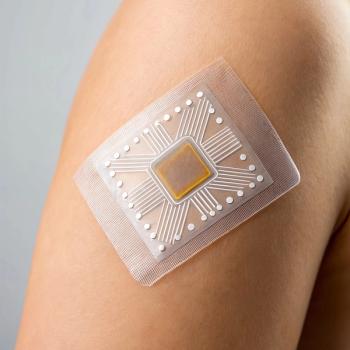
A new comprehensive review explores how wearable plasmonic sensors using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) are changing the landscape for non-invasive health monitoring. By combining nanotechnology, AI, and real-time spectroscopy analysis to detect critical biomarkers in human sweat, this integration of nanomaterials, flexible electronics, and AI is changing how we monitor health and disease in real-time.