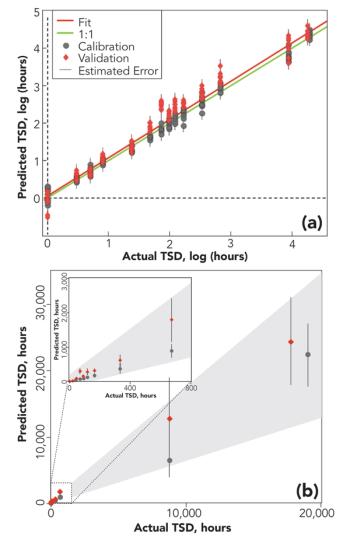
In celebration of Spectroscopy’s 35th Anniversary, leading experts discuss important issues and challenges in analytical spectroscopy.

In celebration of Spectroscopy’s 35th Anniversary, leading experts discuss important issues and challenges in analytical spectroscopy.

In celebration of Spectroscopy’s 35th Anniversary, leading experts discuss important issues and challenges in analytical spectroscopy.
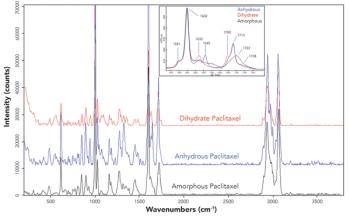
Raman spectroscopy and imaging techniques are well suited for the characterization of surfaces, interfaces, and coatings to support research, development, and manufacturing of medical devices. Here, we describe applications in surface modifications and coatings, differentiation of drug polymorphs, degradation of biomaterials, and forensic identification of unknown materials.
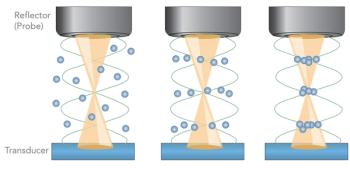
Of the 78 million tons of plastic packaging manufactured every year, approximately one-third ends up in the ocean, the air, and most foods and beverages. To monitor the proliferation of these plastics, an ultrasonic capture method is demonstrated that produces a 1500-fold enhancement of Raman signals of microplastics in water.
![[1].jpg](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/0vv8moc6/spectroscopy/a2dab742ea2699afc0b9759d147265b91dbef0bf-415x60.jpg?w=350&fit=crop&auto=format)
Raman spectroscopy is proving to be a powerful technique for characterizing the structural and morphological properties of nanopowders. Specifically, Raman spectroscopy can provide details of the grain size and thickness of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanopowder films. These measured film properties affect the efficiency of photovoltaic devices, such as solar cells, and also the effectiveness of nanopowders in catalysis applications.
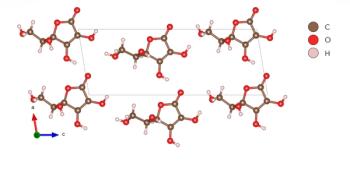
A Raman study of vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is conducted at high pressure to determine phase changes and crystal symmetry through spectral interpretation.
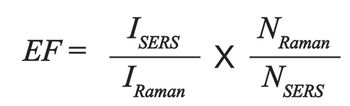
The SERS signal arises from the combination of the number of molecules, the polarizability or cross-section of the molecule, and the electric field experienced by the molecules. Understanding how these variables interact to generate the SERS response is the key to applying SERS accurately.

Recent technical advances in biomedical Raman imaging pave a way to its application in the biomedical fields, where morphological information of samples provides rich information. A recent technical conference in Osaka, Japan, explored these developments.

Raman imaging provides detailed crystal orientation information for two-dimensional MoS2 prepared by chemical vapor deposition on silicon substrates. These two-dimensional crystals consist of individual atomic layers of sulfur, molybdenum, and sulfur atoms.
The Raman Terminology Guide you now have before you is a comprehensive set of definitions for topics of interest to molecular spectroscopists and those specifically using Raman spectroscopy in their daily work. This guide includes the types of Raman spectroscopy techniques and many terms related to the applications of Raman spectroscopy instruments. This terminology guide includes definitions for more than 250+ molecular spectroscopy terms in sufficient detail to provide readers with a reasonable understanding of the concepts covered.

Ping-Heng Tan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences is advancing the use of Raman spectroscopy to characterize graphene-based materials.

Raman 2D-COS spectral data provide information on conformational changes of polymers. Here, Raman spectra of ethylene vinyl acetate and vinyl acetate copolymer are measured and interpreted, enabling a description of morphological changes related to the vinyl acetate group.

Christy L. Haynes, of the University of Minnesota (Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota), has been working with her research team to explore the use of a rapid and facile technique to empirically screen affinity agents of diverse compositions for all manner of targets. Here, she describes the advantages of using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) for screening of polymer affinity agents for use with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS).

Alignment of the instrument y-axis is a critical step for quantitative and qualitative measurements using spectroscopy. Here, we explain in detail how to use photometric standards for ultraviolet, visible, near infrared, infrared, and Raman spectroscopy.

Spectroscopy can be difficult to carry out outside a controlled laboratory environment. Imagine, then, the hurdles that would accompany performing spectroscopy in the extreme conditions of deep space or the ocean floor. Mike Angel, a professor of chemistry at the University of South Carolina, has taken on those challenges, working on new types of instruments for remote and in- situ laser spectroscopy, with a focus on deep-ocean, planetary, and homeland security applications of deep ultraviolet Raman, and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy to develop the tools necessary to work within these extreme environments.

When stress is applied to an object, it can produce strain. Strain can be detected through changes in peak position and bandwidth in Raman spectra. Here, we show examples of how strain in technologically important materials appears in the Raman spectra.
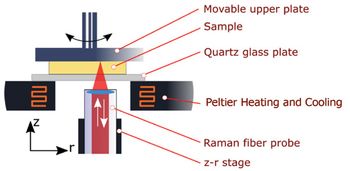
By combining Raman spectra interpretation with rheometric measurements, molecular conversion from crystalline to amorphous structures for polymers is revealed.

Ishan Barman, PhD, an assistant professor at Johns Hopkins University, has won the 2019 Emerging Leader in Molecular Spectroscopy Award, which is presented by Spectroscopy magazine. This annual award recognizes the achievements and aspirations of a talented young molecular spectroscopist, selected by an independent scientific committee. The award will be presented to Barman at the SciX 2019 conference in October, where he will give a plenary lecture and be honored in an award symposium.
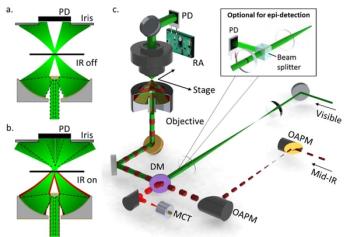
Significant progress is being made to harness the power of spectroscopy technique for medical research. An ongoing challenge, and area of development, in this effort, is to “see” more and more detail about biological activity, even within individual cells. Ji-Xin Cheng, a professor of biomedical engineering at Boston University, is advancing such work, by developing techniques like midinfrared photothermal (MIP) imaging and Raman spectromicroscopy. Cheng is the 2019 winner of the Ellis R. Lippincott Award, which is awarded annually by the Optical Society, the Coblentz Society, and the Society for Applied Spectroscopy, to an individual who has made significant contributions to the field of vibrational spectroscopy. Here, Cheng speaks to us about those techniques.
Five key qualitative factors–speed, sensitivity, resolution, modularity and upgradeability, and combinability–contribute to the quality of confocal Raman imaging microscopes. Using application examples, this article introduces modern Raman imaging and correlative imaging techniques, and presents state-of-the-art practice examples from polymer research, pharmaceutics, low-dimensional materials research, and life sciences.
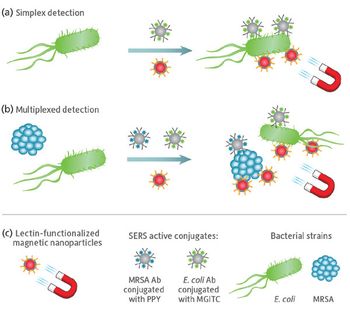
A new application of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) is described for quantifying low concentrations of pathogens with high reproducibility. In this novel assay, bacteria are captured and isolated using functionalized metal nanoparticles for rapid optical identification via SERS. Initial tests with a portable SERS system validated the ability to identify the presence of Escherichia coli and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.

In this study, macro- and microscopic Raman spectroscopy were used to identify different commercial microplastic fibers using measured spectra with database searches. Raman microscopy is demonstrated as a powerful technique for microplastic fiber characterization, especially for samples that contain mixtures of components, including multiple polymers, or additives.
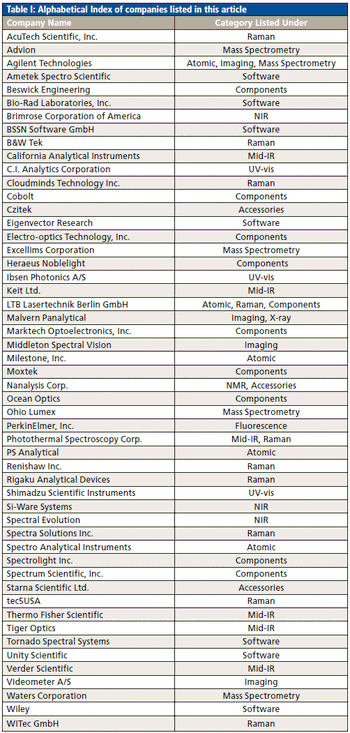
Our annual review of products introduced at Pittcon or during the previous year
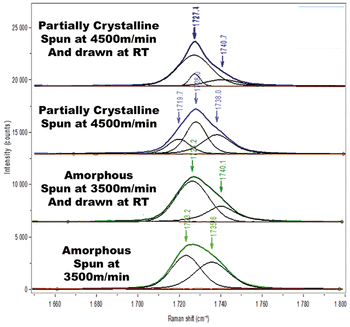
Spectral changes revealed by two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy can be used to interpret structural changes in polymers determined by processing conditions, so that materials can be rationally engineered for particular applications with known mechanical requirements.