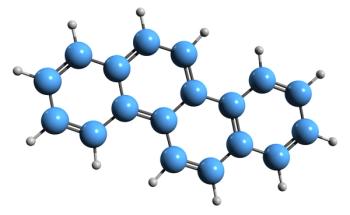
A recent study from Spain used surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to study cancer cells with methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) deletions, shedding new insights into the metabolic interactions inside the tumor microenvironment that could influence cancer aggression.