
A new study demonstrates the feasibility of using attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR FT-IR) mapping for the identification of the prescribed and abnormal ingredients of herbal powder preparations (HPPs) for medicines.

A new study demonstrates the feasibility of using attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR FT-IR) mapping for the identification of the prescribed and abnormal ingredients of herbal powder preparations (HPPs) for medicines.

Slip agents are commonly used amide small molecules that lubricate the molds in injection molding processes. By studying the spectra of a primary amide, we can see how they can contaminate the spectra of polymeric materials.

Researchers have developed a sum frequency generation spectroscopy setup to characterize the output profile of an infrared free electron laser, providing valuable insight into the development of more efficient and accurate lasers.
In a recent study, attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FT-IR) was proven to be a cost-effective method for analyzing herapins in pharmaceutical applications.

Webinar Date/Time: Europe: Thursday, May 4, 2023, at 9 am BST | 10 am CEST North America: Thursday, May 4, 2023, at 11 am PDT | 2 pm EDT Asia: Friday, May 5, 2023, at 10:30am IST | 1 pm SST | 2 pm JST | 3 pm AEDT

Dmitry Kurouski has won the 2023 Emerging Leader in Molecular Spectroscopy Award for his molecular spectroscopy studies revolving around plants.

A smartphone-based, portable visible-near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) method can perform pre-symptomatic detection of late blight disease in potato leaves.

Webinar Date/Time: Tue, Apr 11, 2023 1:00 PM EDT

Webinar Date/Time: Europe: Tuesday, May 9, 2023, at 3pm BST | 4pm CEST North America: Tuesday, May 9, 2023, at 11am PDT | 2pm EDT Asia: Wednesday, May 10, 2023, at 8:30am IST | 11am HKT | 12pm JST | 1pm AEDT

Craig Prater was named the 2023 recipient of the Williams-Wright Award, which is given out annually by the Coblentz Society. He was recognized at Pittcon 2023, which took place in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.

The United States Pharmacopeia–National Formulary (USP–NF) has contributed to ensuring the quality of dietary supplements, foods, and medicines for more than 200 years. This overview explains the use of vibrational spectroscopy techniques in meeting USP–NF requirements and how the information is organized.
We study the spectra of organic nitrogen polymers with a particular focus on polyamides.

In combination with attenuated total reflectance (ATR), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy can be used to classify different moss species.

Webinar Date/Time: On-Demand
We study the spectrum of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)—otherwise known as plexiglass—and the spectra of PMMA mixtures and copolymers.

We continue our survey of the spectra of carbonyl-containing polymers by looking at cellulose acetate and the economically important polycarbonate Lexan.

North America: Wednesday, November 16, 2022 at 11am PST | 1pm CST | 2pm EST Europe: Thursday, November 17, 2022, at 11am BST | 12pm CET Asia: Thursday, November 17, 2022, at 10:30 IST | 1pm SGT | 2pm JST | 4pm AEST Fast, easy, and accurate analysis of microplastics is a key need of anyone with an interest in this area. With the capacity to conduct this analysis directly on the filter in the Agilent 8700 LDIR for microplastics, this analysis has now reached a new level.

The implementation of 120 open-path spectroscopy analyzers at oil refineries has taught us lessons about compound identification, target species detectability, interferences, and data management, which can help spectroscopists generate more accurate data when monitoring air quality.
An exploration of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), one of the most important polymers, is presented.

We continue our survey of the infrared (IR) spectra of polymers with a look at the spectra of polymers that contain carbonyl or C=O bonds. Our long-term goal is to examine the spectra of polymers that contain ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, and carbonate linkages. Studying these spectra is vital, because these molecules are important economically and are ubiquitous in society.

This issue presents a selection of peer-reviewed articles on the subject of infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
In this study, the measured spectra of acetic anhydride, acetic acid, salicylic acid, and aspirin are used for in situ monitoring of the progression of aspirin synthesis in a reaction system. Traditional methods such as HPLC and titration ultraviolet (UV) absorption are not optimal for such real-time monitoring because of long analytical times and complicated procedures. ATR-FT-IR offers an alternative solution that overcomes the shortcomings of traditional techniques.

FT-IR offers an alternative method for the quantification and classification of lignocellulose in biofuel pellets, based on determination of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin content. The IR spectroscopic evaluation presented here provides an understanding of the pretreatment and storage of biofuel pellets.
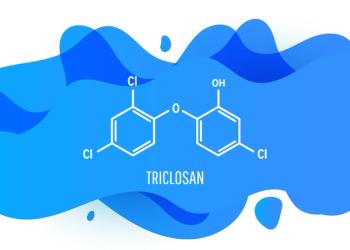
Selecting the correct basis set is essential for enhancing accuracy of DFT simulations. Here, the effects of five basis sets on the theoretical frequencies and calculated infrared intensities are compared to predict the molecular structural and vibrational properties of the triclosan. The demonstrated methods can help provide a benchmark for studying the pollution mechanisms and ecological effects of antibacterial products like triclosan.

By extracting the RGB, HSI, and grayscale information from a spectral range of 400–1100 nm and comparing the spectral features of sound and bruised peaches, the authors provided a classification system and theoretical basis for online fruit bruise detection.