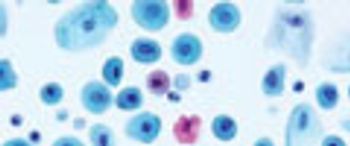
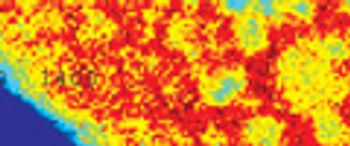
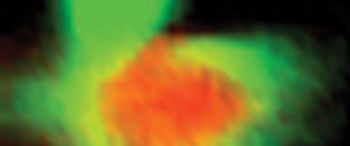
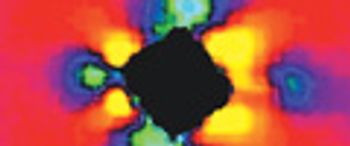
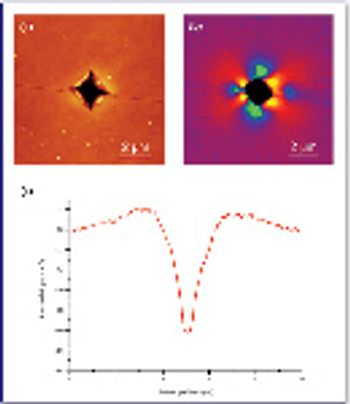
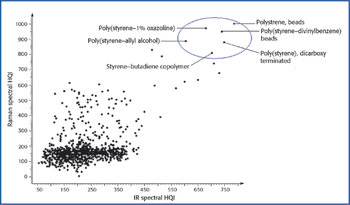
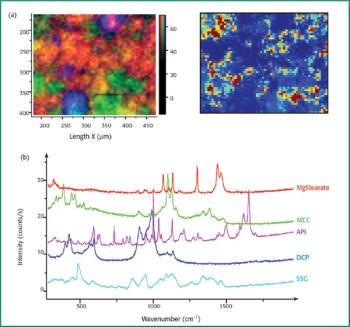
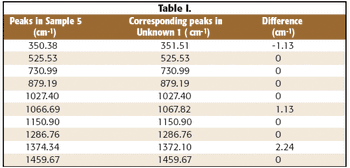
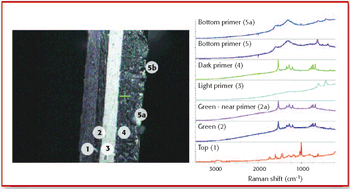
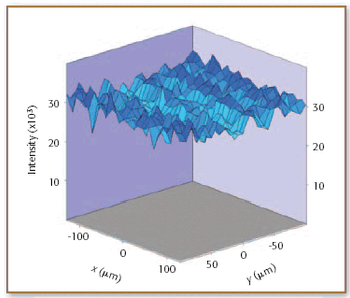
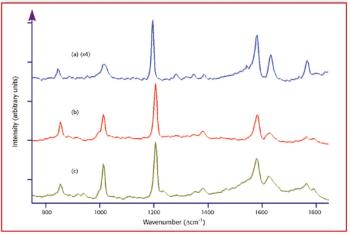
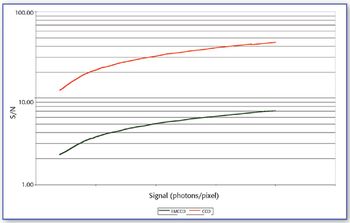
Raman microspectroscopy is a powerful tool for noninvasive chemical analysis of tissues, cells, and cellular structures. To achieve the highest signal-to-noise ratio and fidelity of Raman spectra, the background must be minimized. The difference in temporal dependence of Raman and fluorescence signals can be used for very effective discrimination. A careful system design, based upon the employment of very efficient Kerr-gating materials, makes confocal Raman microscopy possible with significantly shorter acquisition times. The new instrument is tested for a variety of biomedical systems. The possible applications are outlined together with the routes for further improvement.