
At SciX, Dmitri Kurouski of Texas A&M University will be recognized as the 2023 Spectroscopy Emerging Leader in Molecular Spectroscopy Award recipient. Here's a summary of the award session.
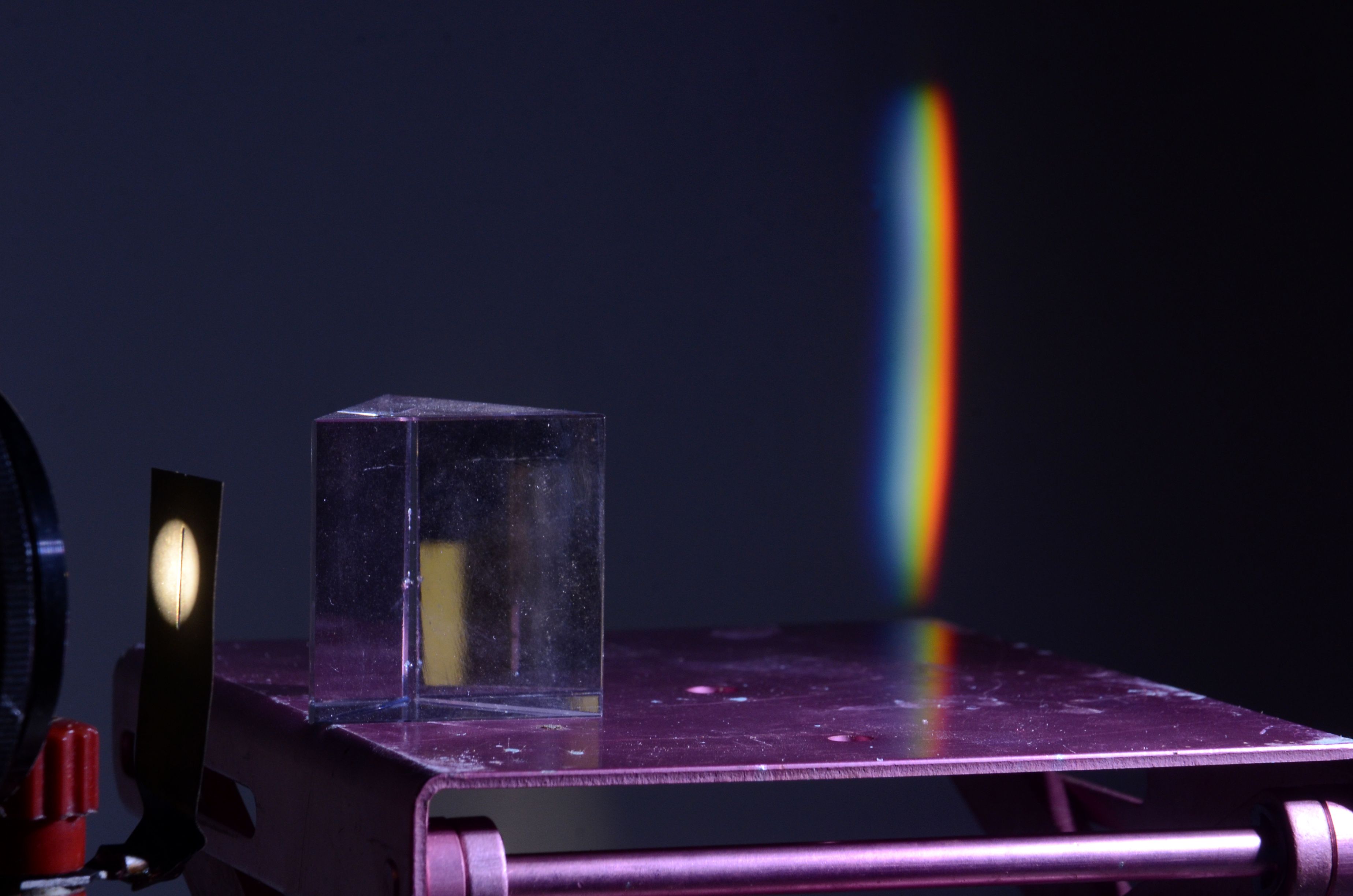

This study explores the enhanced performance of modified alternating least squares (MALS) over alternating least squares (ALS) in analyzing infrared and Raman image spectral data, highlighting the stability and computational efficiency of MALS.

At SciX, Dmitri Kurouski of Texas A&M University will be recognized as the 2023 Spectroscopy Emerging Leader in Molecular Spectroscopy Award recipient. Here's a summary of the award session.

At the SciX Conference in Sparks, Nevada, Spectroscopy magazine sat down with Karen Esmonde-White of Endress+Hauser to talk about her career transition and how Raman spectroscopy has evolved over the years.

Anastasia Rousaki and her team at Ghent University in Belgium are utilizing advanced Raman spectroscopy techniques, including mobile non-invasive methods, to analyze the composition of art from various historical periods, from prehistoric rock art paintings in Patagonia to 19th to 20th century Greek paintings and 21st-century murals in Reggio Emilia, providing insights for art preservation and historical understanding.

Ishan Barman, the 2023 recipient of the Coblentz Society Clara Craver Award, held a plenary session during SciX that focuses on transformative biophotonics in disease detection and monitoring.

As a preview to SciX 2023, Spectroscopy magazine sat down with Juergen Popp of the Leibniz Institute of Photonic Technology to ask him about his research exploring the use of Raman spectroscopy in applications such as infectious diseases and cancer diagnostics.

The Coblentz Society created the Clara Craver Award to recognize young individuals who have made significant contributions in applied analytical vibrational spectroscopy. The work may include any aspect of infrared (IR), terahertz (THz), or Raman spectroscopy in applied analytical vibrational spectroscopy. This year’s recipient, Ishan Barman, is an Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the Johns Hopkins University with joint appointments in Oncology and Radiology and Radiological Science.

A more successful blueprint for analyzing Raman spectral data is outlined by following the 11 important steps, which are outlined here.
In a recent study, a research team from China used Raman spectroscopy to uncover serum biomarkers for aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndromes.

To effectively classify tobacco stems and impurities, a group of scientists from Jiangsu, China used hyperspectral superpixels to separate classify compounds and avoid the influence of interference fringes.

Bruno Pagano, full Professor of Physical Chemistry at the University of Naples Federico II (Italy), and his team have turned to UV resonance Raman (UVRR) spectroscopy to better understand these interactions. Spectroscopy spoke to Prof. Pagano about his work and the potential of UVRR spectroscopy as a valuable tool for studying G-quadruplex structures in biologically relevant conditions.

In a recent study published in Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, two researchers from India studied the molecular composition of topiramate, revealing new insights.

With more than four decades of experience, Larsen made significant contributions to the field of analytical chemistry.
In a recent study, scientists used a combination of SERS, butanol, and gold nanoparticles to analyze the virus.

A study published in Scientific Reports has given intricate details into the production and composition of Roman Egyptian blue pigment. Using advanced Raman microspectroscopy, researchers explored pigment balls and murals from ancient Swiss cities, uncovering evidence of raw material provenance, crystal lattice disorder, and the formation of a copper-bearing green glass phase, revealing the sophisticated techniques employed by Roman artisans.

Arzak Mohamed from Macquarie University in Australia broke down how she uses spectroscopy to analyze ancient manuscripts.

Scientists used spectroscopic techniques to learn more about paintings in the blue room of Ariadne’s house.

Accurately calibrating instruments is of the utmost importance for harmonization of Raman data.

Liquid crystals are used in a variety of fields including optics, electro-optics, biomedical and fast switching devices.

Webinar Date/Time: Thu, Sep 14, 2023 10:00 AM EDT
A recent study tests new systems meant to better analyze components in the semiconductor industry and pave the way for better electronic devices.
Scientists at West Virginia University have created a new LIBS system meant to better identify the components of gunshot residue at crime scenes and in evidence.
A study employing Raman spectroscopy has uncovered distinct metabolic alterations in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) isolated from overweight and obese endometrial cancer patients, providing valuable insights into the mechanistic link between obesity and endometrial cancer progression.

Shifted-excitation Raman difference spectroscopy (SERDS) is a technique that is capable of reducing the interference caused by fluorescence and improve the potential of Raman for distinguishing drug compounds in seized samples with fluorescent additives. Here, 43 drugs were analyzed to show the practical application of SERDS.
Researchers from Humboldt-Universität in Berlin have utilized ultraviolet resonance Raman (UVRR) spectroscopy to differentiate between bovine serum albumin (BSA) and human serum albumin (HSA) based on their similar structures and amino acid composition. By comparing the UVRR spectra of the proteins with those of specific amino acids, they have identified distinctive features that allow for accurate discrimination and provide insights into the secondary structure and binding sites of serum albumins.

Author Jean-Pierre P. de Vera talks to Spectroscopy magazine about his study in which seven biomolecules were exposed to a simulated Martian environment outside the International Space Station (ISS) for a period of approximately 15 months.