
Fran Adar is the winner of the 2021 Gold Medal Award from the New York and New Jersey Society of Applied Spectroscopy (SAS).

Fran Adar is the winner of the 2021 Gold Medal Award from the New York and New Jersey Society of Applied Spectroscopy (SAS).

Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), using gold nanoparticles, is useful for detection of low-levels of many analytes, including the water pollutant malachite green (MG).
SERS can be used for the detection and monitoring of drugs as pure compounds and mixtures. A demonstration of a sample preparation method used to detect components with weak substrate adsorption in the spectrum of a mixed solution is shown.

The application of data mining combined with data fusion of Raman and mid- infrared spectra was studied to improve discrimination ability for modeling the geographical origins of rice.
Raman and photoluminescence spectroscopy were combined with imaging to examine the spatial variation of solid-state structure and electronic character of two-dimensional (2-D) tungsten disulfide (WS2) crystals, which represent a family of new inorganic 2-D materials.

For analysis of non-particulate solids, the diffuse reflection sampling technique may offer an easy, non-destructive method for mid-infrared measurements. Spectral results of a polypropylene face mask collected via diffuse reflection and attenuated total reflection (ATR) were compared.

Tri-Range Applications of the Spectrum 3 Infrared Spectrometer

Confocal Raman microscopy is a powerful tool for analyzing the chemical composition of samples on the submicrometer scale. In the food industry, various ingredients, additives, and bio-polymers (such as emulsifiers, stabilizers, carbohydrates, or thickeners) are commonly used to optimize the texture or the flavor of food. The distribution and microstructure of the ingredients strongly influence the properties of the final product. Therefore, research and development, as well as quality control, require powerful analytical tools for studying the distribution of compounds in food. Raman imaging has proven to be an effective and versatile technique for food analysis (1,2).

Raman measurements of chromite minerals demonstrated that chromium content could be accurately determined, supporting a possible application of portable Raman devices on Earth or in space for mineral analysis of asteroids and planets.
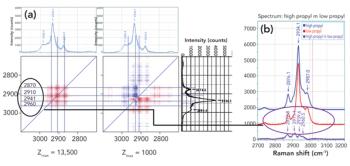
Raman spectra were measured in combination with 2D-COS analysis to understand how the addition of propyl side groups to a biopolymer backbone influences the structure of the polymer at the atomic level.

Zeolites are the most-used catalyst in industry. Synthesizing tailor-made zeolites is hampered by a poor understanding of how zeolite crystals actually form in solution. Scott M. Auerbach of the University of Massachusetts at Amherst is addressing this challenge with Raman spectroscopy.

Raman spectroscopy is extremely useful for characterizing crystalline materials.

Chemistry can help us understand the past.

This article provides a convenient summary of portable and handheld spectroscopy techniques, outlining the most prominent types of compact instruments for both atomic and molecular spectroscopy.
Graphene exhibits special properties, such as high strength and high electrical and thermal conductivity and as such is highly desirable for key electronic components. A new Raman spectroscopy sampling technique has been applied to the characterization of batches of graphene that provides a simple, at-line method for obtaining key product data.

Raman spectroscopy is a valuable process analytical technology (PAT) for many applications across multiple industries, as a result of its many advantages, such as molecular specificity, ability to be directly coupled to a reaction vessel, and compatibility with solids, liquids, gases, and turbid media.

New Raman spectroscopy applications are emerging in non-traditional fields because of advances in easy-to-use commercial Raman spectroscopy instrumentation. With improvements in lasers, optics, and detectors, Raman spectroscopy has developed into a powerful measurement solution for manufacturing and quality control applications.

Low frequency Raman scattering measurements can be used to predict physical properties of polymers and the crystalline polymorphic form of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). These measurements are made by recording the Stokes and anti-Stokes side of the laser line with the laser centered on the detector. Spectra of polyethylene and linear alkanes were recorded down to 4 cm-1.

Spectroscopy Magazine spoke with Claudia Conti about her work in micro-SORS.

Spectroscopy Magazine sat down with Kay Sowoidnich to talk about how his group has demonstrated the potential of shifted-excitation Raman difference spectroscopy (SERDS) as an efficient tool for soil nutrient analysis.


In general, many Raman measurements suffer from fluorescence, which forces the use of longer excitation wavelength (lower photon energy) lasers to prevent the fluorescence signal from overwhelming the Raman signal. However, this results in reduced sensitivity of low-cost silicon CCD detectors at higher wavenumbers, making it difficult (or impossible) to observe the “stretch” portion of the Raman spectra.
The Oxigraf state-of-the-art Oxygen Deficiency Monitor, the Model O2iM, is a responsive, accurate, and reliable safety monitor for oxygen displacement monitoring in quantum computer laboratory, MRI, NMR, and liquid nitrogen and helium storage facilities. Our reliable solid-state sensor does not require routine maintenance or factory calibration, and the O2iM is equipped with an automatic, programmable auto-calibration system. The system easily interfaces with alarm system and building management systems.

Markita Landry, the winner of the 2020 Emerging Leader in Molecular Spectroscopy Award, works at the intersection of single-molecule biophysics and nanomaterial-polymer science to develop new tools for understanding biological systems.

This application note demonstrates determining the correct orientation of the polarizer for these measurements and illustrates the importance of polarized measurements in specific examples.