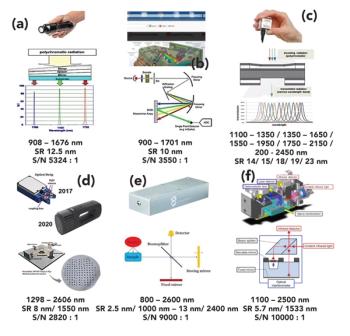
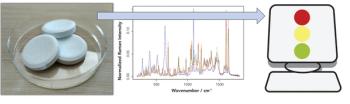
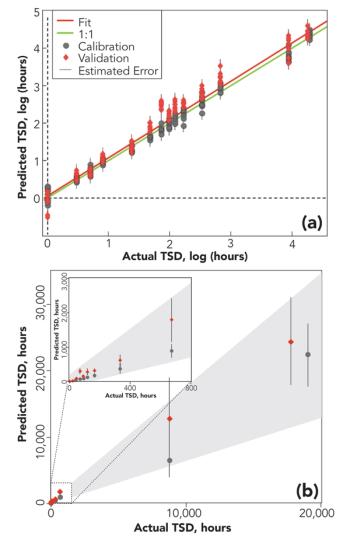
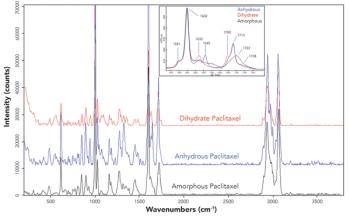
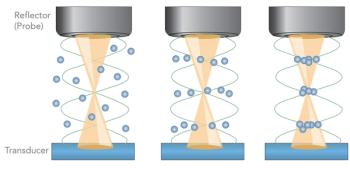
Forensic traces are physical remnants of past events that provide critical information for criminal and civil investigations and adjudications. The scientific examination of traces is an incredibly valuable tool for forensic investigations, because the skilled interpretation of traces yields factual answers to a range of pertinent questions.